The GTPase Arf1p and the ER to Golgi cargo receptor Erv14p cooperate to recruit the golgin Rud3p to the cis-Golgi
- PMID: 15504911
- PMCID: PMC2172552
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200407088
The GTPase Arf1p and the ER to Golgi cargo receptor Erv14p cooperate to recruit the golgin Rud3p to the cis-Golgi
Abstract
Rud3p is a coiled-coil protein of the yeast cis-Golgi. We find that Rud3p is localized to the Golgi via a COOH-terminal domain that is distantly related to the GRIP domain that recruits several coiled-coil proteins to the trans-Golgi by binding the small Arf-like GTPase Arl1p. In contrast, Rud3p binds to the GTPase Arf1p via this COOH-terminal "GRIP-related Arf-binding" (GRAB) domain. Deletion of RUD3 is lethal in the absence of the Golgi GTPase Ypt6p, and a screen of other mutants showing a similar genetic interaction revealed that Golgi targeting of Rud3p also requires Erv14p, a cargo receptor that cycles between the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi. The one human protein with a GRAB domain, GMAP-210 (CEV14/Trip11/Trip230), is known to be on the cis-Golgi, but the COOH-terminal region that contains the GRAB domain has been reported to bind to centrosomes and gamma-tubulin (Rios, R.M, A. Sanchis, A.M. Tassin, C. Fedriani, and M. Bornens. 2004. Cell. 118:323-335). In contrast, we find that this region binds to the Golgi in a GRAB domain-dependent manner, suggesting that GMAP-210 may not link the Golgi to gamma-tubulin and centrosomes.
Figures


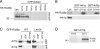

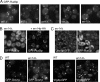

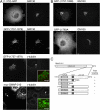
Similar articles
-
An acidic sequence of a putative yeast Golgi membrane protein binds COPII and facilitates ER export.EMBO J. 2001 Dec 3;20(23):6742-50. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.23.6742. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11726510 Free PMC article.
-
Multilayer interactions determine the Golgi localization of GRIP golgins.Traffic. 2006 Oct;7(10):1399-407. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2006.00473.x. Epub 2006 Aug 10. Traffic. 2006. PMID: 16899086
-
Ric1p and Rgp1p form a complex that catalyses nucleotide exchange on Ypt6p.EMBO J. 2000 Sep 15;19(18):4885-94. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.18.4885. EMBO J. 2000. PMID: 10990452 Free PMC article.
-
Golgi positioning: are we looking at the right MAP?J Cell Biol. 2005 Mar 28;168(7):993-8. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200501088. Epub 2005 Mar 21. J Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15781478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Organization of transport from endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi in higher plants.Biochem Soc Trans. 2000;28(4):505-12. Biochem Soc Trans. 2000. PMID: 10961949 Review.
Cited by
-
Multiple roles of ADP-ribosylation factor 1 in plant cells include spatially regulated recruitment of coatomer and elements of the Golgi matrix.Plant Physiol. 2007 Apr;143(4):1615-27. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.094953. Epub 2007 Feb 16. Plant Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17307898 Free PMC article.
-
The Golgi protein p115 associates with gamma-tubulin and plays a role in Golgi structure and mitosis progression.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jun 17;286(24):21915-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.209460. Epub 2011 May 2. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21536679 Free PMC article.
-
The golgin coiled-coil proteins capture different types of transport carriers via distinct N-terminal motifs.BMC Biol. 2017 Jan 26;15(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12915-016-0345-3. BMC Biol. 2017. PMID: 28122620 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo characterization of Drosophila golgins reveals redundancy and plasticity of vesicle capture at the Golgi apparatus.Curr Biol. 2022 Nov 7;32(21):4549-4564.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2022.08.054. Epub 2022 Sep 13. Curr Biol. 2022. PMID: 36103876 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insight into an Arl1-ArfGEF complex involved in Golgi recruitment of a GRIP-domain golgin.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 2;15(1):1942. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46304-w. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38431634 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe, A., N. Emi, M. Tanimoto, H. Terasaki, T. Marunouchi, and H. Saito. 1997. Fusion of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor β to a novel gene CEV14 in acute myelogenous leukemia after clonal evolution. Blood. 90:4271–4277. - PubMed
-
- Barr, F.A., and B. Short. 2003. Golgins in the structure and dynamics of the Golgi apparatus. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 15:405–413. - PubMed
-
- Barr, F.A., M. Puype, J. Vandekerckhove, and G. Warren. 1997. GRASP65, a protein involved in the stacking of Golgi cisternae. Cell. 91:253–262. - PubMed
-
- Behnia, R., B. Panic, J.R. Whyte, and S. Munro. 2004. Targeting of the Arf-like GTPase Arl3p to the Golgi requires N-terminal acetylation and the membrane protein Sys1p. Nat. Cell Biol. 6:405–413. - PubMed
-
- Caldwell, S.R., K.J. Hill, and A.A. Cooper. 2001. Degradation of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) quality control substrates requires transport between the ER and Golgi. J. Biol. Chem. 276:23296–23303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

