Endothelial barrier disruption by VEGF-mediated Src activity potentiates tumor cell extravasation and metastasis
- PMID: 15504909
- PMCID: PMC2172541
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200408130
Endothelial barrier disruption by VEGF-mediated Src activity potentiates tumor cell extravasation and metastasis
Abstract
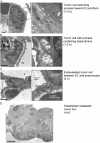
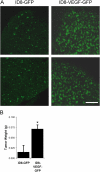
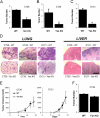
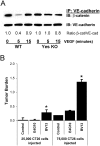
VEGF is unique among angiogenic growth factors because it disrupts endothelial barrier function. Therefore, we considered whether this property of VEGF might contribute to tumor cell extravasation and metastasis. To test this, mice lacking the Src family kinases Src or Yes, which maintain endothelial barrier function in the presence of VEGF, were injected intravenously with VEGF-expressing tumor cells. We found a dramatic reduction in tumor cell extravasation in lungs or livers of mice lacking Src or Yes. At the molecular level, VEGF compromises the endothelial barrier by disrupting a VE-cadherin-beta-catenin complex in lung endothelium from wild-type, but not Yes-deficient, mice. Disrupting the endothelial barrier directly with anti-VE-cadherin both amplifies metastasis in normal mice and overcomes the genetic resistance in Yes-deficient mice. Pharmacological blockade of VEGF, VEGFR-2, or Src stabilizes endothelial barrier function and suppresses tumor cell extravasation in vivo. Therefore, disrupting Src signaling preserves host endothelial barrier function providing a novel host-targeted approach to control metastatic disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Contact inhibition of VEGF-induced proliferation requires vascular endothelial cadherin, beta-catenin, and the phosphatase DEP-1/CD148.J Cell Biol. 2003 May 26;161(4):793-804. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200209019. J Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12771128 Free PMC article.
-
A novel role of vascular endothelial cadherin in modulating c-Src activation and downstream signaling of vascular endothelial growth factor.J Biol Chem. 2008 Mar 14;283(11):7261-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M702881200. Epub 2008 Jan 7. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18180305 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis by resveratrol through interruption of Src-dependent vascular endothelial cadherin tyrosine phosphorylation.Mol Pharmacol. 2003 Nov;64(5):1029-36. doi: 10.1124/mol.64.5.1029. Mol Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 14573751
-
Delineating Pro-Angiogenic Myeloid Cells in Cancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Aug 29;19(9):2565. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092565. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30158456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunological Regulation of Vascular Inflammation During Cancer Metastasis.Front Immunol. 2019 Aug 21;10:1984. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01984. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31497019 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Vascular permeability--the essentials.Ups J Med Sci. 2015;120(3):135-43. doi: 10.3109/03009734.2015.1064501. Epub 2015 Jul 29. Ups J Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26220421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The endothelin-integrin axis is involved in macrophage-induced breast cancer cell chemotactic interactions with endothelial cells.J Biol Chem. 2014 Apr 4;289(14):10029-44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.528406. Epub 2014 Feb 18. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24550382 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in dynamics of tumor/endothelial cell adhesive interactions depending on endothelial cell growth state and elastic properties.PLoS One. 2022 Jun 6;17(6):e0269552. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0269552. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35666755 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Roles for SSeCKS/Gravin/AKAP12 in the Control of Cell Proliferation, Cancer Malignancy, and Barriergenesis.Genes Cancer. 2010 Nov;1(11):1147-56. doi: 10.1177/1947601910392984. Genes Cancer. 2010. PMID: 21779438 Free PMC article.
-
Dissemination from a Solid Tumor: Examining the Multiple Parallel Pathways.Trends Cancer. 2018 Jan;4(1):20-37. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2017.12.002. Epub 2018 Jan 10. Trends Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29413419 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boguslawski, G., P.W. McGlynn, K.A. Harvey, and A.T. Kovala. 2004. SU1498, an inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2, causes accumulation of phosphorylated ERK kinases and inhibits their activity in vivo and in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 279:5716–5724. - PubMed
-
- Boschelli, D.H., F. Ye, Y.D. Wang, M. Dutia, S.L. Johnson, B. Wu, K. Miller, D.W. Powell, D. Yaczko, M. Young, et al. 2001. Optimization of 4-phenylamino-3-quinolinecarbonitriles as potent inhibitors of Src kinase activity. J. Med. Chem. 44:3965–3977. - PubMed
-
- Bruns, C.J., M. Shrader, M.T. Harbison, C. Portera, C.C. Solorzano, K.W. Jauch, D.J. Hicklin, R. Radinsky, and L.M. Ellis. 2002. Effect of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 antibody DC101 plus gemcitabine on growth, metastasis and angiogenesis of human pancreatic cancer growing orthotopically in nude mice. Int. J. Cancer. 102:101–108. - PubMed
-
- Eliceiri, B.P., R. Paul, P.L. Schwartzberg, J.D. Hood, J. Leng, and D.A. Cheresh. 1999. Selective requirement for Src kinases during VEGF-induced angiogenesis and vascular permeability. Mol. Cell. 4:915–924. - PubMed
-
- Esser, S., M.G. Lampugnani, M. Corada, E. Dejana, and W. Risau. 1998. Vascular endothelial growth factor induces VE-cadherin tyrosine phosphorylation in endothelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 111:1853–1865. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA095262/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA050286/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA95262/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- EY14174/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA050286/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA50286/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA078045/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL57900/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1F32HL69701/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA045726/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R24 EY014174/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HL069701/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL057900/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA78045/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA45726/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

