Plant alkaloid tetrandrine downregulates IkappaBalpha kinases-IkappaBalpha-NF-kappaB signaling pathway in human peripheral blood T cell
- PMID: 15504755
- PMCID: PMC1575940
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706000
Plant alkaloid tetrandrine downregulates IkappaBalpha kinases-IkappaBalpha-NF-kappaB signaling pathway in human peripheral blood T cell
Abstract
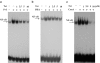
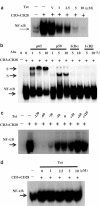
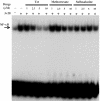
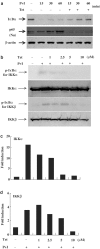
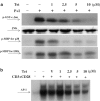
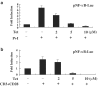
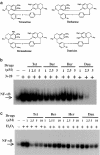
Plant alkaloid tetrandrine (Tet), purified from Chinese herb Han-Fang Chi, is a potent immunomodulator used to treat rheumatic disorders, silicosis and hypertension in mainland China. We previously demonstrated that Tet effectively suppresses cytokine production and proliferation of CD28-costimulated T cells. In the present study, we investigated the possible involvement of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) transcription factors, critical in CD28 costimulation, in Tet-mediated immunosuppression in human peripheral blood T cells. We showed that Tet inhibited NF-kappaB DNA-binding activities induced by various stimuli, including CD28 costimulation. At equal molar concentrations, Tet was as strong as methotrexate in suppressing CD28-costimulated NF-kappaB activities. Since Tet itself did not affect NF-kappaB binding to its corresponding DNA sequence, the results suggested that Tet might regulate NF-kappaB upstream signaling molecules. Further studies demonstrated that Tet could prevent the degradation of IkappaBalpha and inhibit nuclear translocation of p65 by blocking IkappaBalpha kinases alpha and beta activities. In addition, the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases such as c-jun N-terminal kinase, p38 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase and activator protein-1 DNA-binding activity were all downregulated by Tet. Transfection assays performed in purified human peripheral blood T cells also confirmed the inhibition of NF-kappaB transcriptional activity by Tet. When four Tet analogues were readily compared, dauricine appeared to preserve the most potent inhibition on CD28-costimulated but not on H(2)O(2)-induced NF-kappaB DNA-binding activities. Our results provide the molecular basis of immunomodulation of Tet for being a potential disease-modifying antirheumatic drug in the therapy of autoimmune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Plant alkaloid tetrandrine and its analog block CD28-costimulated activities of human peripheral blood T cells: potential immunosuppressants in transplantation immunology.Transplantation. 1999 Nov 15;68(9):1383-92. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199911150-00027. Transplantation. 1999. PMID: 10573080
-
Dauricine induces apoptosis, inhibits proliferation and invasion through inhibiting NF-kappaB signaling pathway in colon cancer cells.J Cell Physiol. 2010 Oct;225(1):266-75. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22261. J Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20509140
-
Transient and selective NF-kappa B p65 serine 536 phosphorylation induced by T cell costimulation is mediated by I kappa B kinase beta and controls the kinetics of p65 nuclear import.J Immunol. 2004 May 15;172(10):6336-44. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.10.6336. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15128824
-
Immunomodulatory effects and mechanisms of plant alkaloid tetrandrine in autoimmune diseases.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2002 Dec;23(12):1093-101. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2002. PMID: 12466046 Review.
-
Therapeutic effects of tetrandrine in inflammatory diseases: a comprehensive review.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Jun;32(3):1743-1757. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01452-9. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 38568399 Review.
Cited by
-
Tetrandrine ameliorates dextran-sulfate-sodium-induced colitis in mice through inhibition of nuclear factor -kappaB activation.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2009 Jan;24(1):5-12. doi: 10.1007/s00384-008-0544-7. Epub 2008 Aug 7. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2009. PMID: 18685855
-
Tetrandrine attenuated cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury and induced differential proteomic changes in a MCAO mice model using 2-D DIGE.Neurochem Res. 2013 Sep;38(9):1871-9. doi: 10.1007/s11064-013-1093-1. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Neurochem Res. 2013. PMID: 23780673
-
Tetrandrine Prevents Bone Loss in Ovariectomized Mice by Inhibiting RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jan 10;10:1530. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01530. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31998129 Free PMC article.
-
Tetrandrine suppresses LPS-induced astrocyte activation via modulating IKKs-IkappaBalpha-NF-kappaB signaling pathway.Mol Cell Biochem. 2008 Aug;315(1-2):41-9. doi: 10.1007/s11010-008-9787-4. Epub 2008 May 23. Mol Cell Biochem. 2008. PMID: 18498042
-
Voacanga globosa Spirobisindole Alkaloids Exert Antiviral Activity in HIV Latently Infected Cell Lines by Targeting the NF-kB Cascade: In Vitro and In Silico Investigations.Molecules. 2022 Feb 5;27(3):1078. doi: 10.3390/molecules27031078. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35164343 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AUPPERLE K., BENNETT B., HAN Z., BOYLE D., MANNING A., FIRESTEIN G. NF-kappa B regulation by I kappa B kinase-2 in rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes. J. Immunol. 2001;166:2705–2711. - PubMed
-
- CRANNEY A., TUGWELL P. The use of Neoral in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North Am. 1998;24:479–488. - PubMed
-
- FENG Y.X., CHEN H. Pharmacognostic and chemical identification of Fang Ji (Stephania tetrandra) Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 1985;5:28–31.
-
- FOX D.A. The role of T cells in the immunopathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: new perspectives. Arthritis Rheum. 1997;40:598–609. - PubMed
-
- HANDEL M.L., MCMORROW L.B., GRAVALLESE E.M. Nuclear factor-kappa B in rheumatoid synovium. Localization of p50 and p65. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38:1762–1770. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

