Normal biogenesis and cycling of empty synaptic vesicles in dopamine neurons of vesicular monoamine transporter 2 knockout mice
- PMID: 15496457
- PMCID: PMC539174
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-07-0559
Normal biogenesis and cycling of empty synaptic vesicles in dopamine neurons of vesicular monoamine transporter 2 knockout mice
Abstract
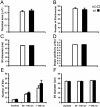
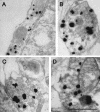
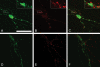
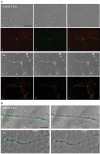
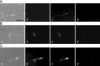
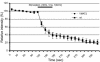
The neuronal isoform of vesicular monoamine transporter, VMAT2, is responsible for packaging dopamine and other monoamines into synaptic vesicles and thereby plays an essential role in dopamine neurotransmission. Dopamine neurons in mice lacking VMAT2 are unable to store or release dopamine from their synaptic vesicles. To determine how VMAT2-mediated filling influences synaptic vesicle morphology and function, we examined dopamine terminals from VMAT2 knockout mice. In contrast to the abnormalities reported in glutamatergic terminals of mice lacking VGLUT1, the corresponding vesicular transporter for glutamate, we found that the ultrastructure of dopamine terminals and synaptic vesicles in VMAT2 knockout mice were indistinguishable from wild type. Using the activity-dependent dyes FM1-43 and FM2-10, we also found that synaptic vesicles in dopamine neurons lacking VMAT2 undergo endocytosis and exocytosis with kinetics identical to those seen in wild-type neurons. Together, these results demonstrate that dopamine synaptic vesicle biogenesis and cycling are independent of vesicle filling with transmitter. By demonstrating that such empty synaptic vesicles can cycle at the nerve terminal, our study suggests that physiological changes in VMAT2 levels or trafficking at the synapse may regulate dopamine release by altering the ratio of fillable-to-empty synaptic vesicles, as both continue to cycle in response to neural activity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vesicular monoamine and glutamate transporters select distinct synaptic vesicle recycling pathways.J Neurosci. 2010 Jun 9;30(23):7917-27. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5298-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20534840 Free PMC article.
-
Presynaptic control of striatal dopamine neurotransmission in adult vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) mutant mice.J Neurochem. 2003 May;85(4):898-910. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01732.x. J Neurochem. 2003. PMID: 12716422
-
Regulation of dopamine quantal size in midbrain and hippocampal neurons.Behav Brain Res. 2002 Mar 10;130(1-2):203-7. doi: 10.1016/s0166-4328(01)00419-3. Behav Brain Res. 2002. PMID: 11864736
-
Electron microscopic immunolabeling of transporters and receptors identifies transmitter-specific functional sites envisioned in Cajal's neuron.Prog Brain Res. 2002;136:145-55. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(02)36014-x. Prog Brain Res. 2002. PMID: 12143378 Review.
-
Dopamine transporters and neuronal injury.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1999 Oct;20(10):424-9. doi: 10.1016/s0165-6147(99)01379-6. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1999. PMID: 10498956 Review.
Cited by
-
Sensorineural deafness and seizures in mice lacking vesicular glutamate transporter 3.Neuron. 2008 Jan 24;57(2):263-75. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.11.032. Neuron. 2008. PMID: 18215623 Free PMC article.
-
Morphological Differentiation Towards Neuronal Phenotype of SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cells by Estradiol, Retinoic Acid and Cholesterol.Neurochem Res. 2016 Apr;41(4):731-47. doi: 10.1007/s11064-015-1743-6. Epub 2015 Oct 30. Neurochem Res. 2016. PMID: 26518675 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise protects against MPTP-induced neurotoxicity in mice.Brain Res. 2010 Jun 23;1341:72-83. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.01.053. Epub 2010 Jan 29. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20116369 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic vesicle protein trafficking at the glutamate synapse.Neuroscience. 2009 Jan 12;158(1):189-203. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.03.029. Epub 2008 Mar 22. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 18472224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monitoring synaptic function at the neuromuscular junction of a mouse expressing synaptopHluorin.J Neurosci. 2007 May 16;27(20):5422-30. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0670-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17507564 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bergevin, A., Girardot, D., Bourque, M. J., and Trudeau, L. E. (2002). Presynaptic mu-opioid receptors regulate a late step of the secretory process in rat ventral tegmental area GABAergic neurons. Neuropharmacology 42, 1065-1078. - PubMed
-
- Bourque, M. J., and Trudeau, L. E. (2000). GDNF enhances the synaptic efficacy of dopaminergic neurons in culture. Eur. J. Neurosci. 12, 3172-3180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

