Unexpected deposition patterns of recombinant proteins in post-endoplasmic reticulum compartments of wheat endosperm
- PMID: 15489278
- PMCID: PMC527145
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.104.050153
Unexpected deposition patterns of recombinant proteins in post-endoplasmic reticulum compartments of wheat endosperm
Abstract
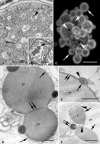
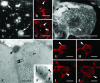
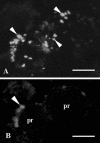
Protein transport within cereal endosperm cells is complicated by the abundance of endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-derived and vacuolar protein bodies. For wheat storage proteins, two major transport routes run from the ER to the vacuole, one bypassing and one passing through the Golgi. Proteins traveling along each route converge at the vacuole and form aggregates. To determine the impact of this trafficking system on the fate of recombinant proteins expressed in wheat endosperm, we used confocal and electron microscopy to investigate the fate of three recombinant proteins containing different targeting information. KDEL-tagged recombinant human serum albumin, which is retrieved to the ER lumen in leaf cells, was deposited in prolamin aggregates within the vacuole of endosperm cells, most likely following the bulk of endogenous glutenins. Recombinant fungal phytase, a glycoprotein designed for secretion, was delivered to the same compartment, with no trace of the molecule in the apoplast. Glycan analysis revealed that this protein had passed through the Golgi. The localization of human serum albumin and phytase was compared to that of recombinant legumin, which contains structural targeting information directing it to the vacuole. Uniquely, legumin accumulated in the globulin inclusion bodies at the periphery of the prolamin bodies, suggesting a different mode of transport and/or aggregation. Our results demonstrate that recombinant proteins are deposited in an unexpected pattern within wheat endosperm cells, probably because of the unique storage properties of this tissue. Our data also confirm that recombinant proteins are invaluable tools for the analysis of protein trafficking in cereals.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Native and artificial reticuloplasmins co-accumulate in distinct domains of the endoplasmic reticulum and in post-endoplasmic reticulum compartments.Plant Physiol. 2001 Nov;127(3):1212-23. Plant Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11706200 Free PMC article.
-
RNA targeting to a specific ER sub-domain is required for efficient transport and packaging of α-globulins to the protein storage vacuole in developing rice endosperm.Plant J. 2012 May;70(3):471-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04880.x. Epub 2012 Jan 18. Plant J. 2012. PMID: 22168839
-
Expression patterns of genes encoding endomembrane proteins support a reduced function of the Golgi in wheat endosperm during the onset of storage protein deposition.J Exp Bot. 2001 Dec;52(365):2387-8. doi: 10.1093/jexbot/52.365.2387. J Exp Bot. 2001. PMID: 11709589
-
Deposition of storage proteins.Plant Mol Biol. 1998 Sep;38(1-2):77-99. Plant Mol Biol. 1998. PMID: 9738961 Review.
-
Vacuolar protein sorting mechanisms in plants.FEBS J. 2013 Feb;280(4):979-93. doi: 10.1111/febs.12092. Epub 2013 Jan 11. FEBS J. 2013. PMID: 23241209 Review.
Cited by
-
Visualisation of plastids in endosperm, pollen and roots of transgenic wheat expressing modified GFP fused to transit peptides from wheat SSU RubisCO, rice FtsZ and maize ferredoxin III proteins.Transgenic Res. 2008 Aug;17(4):529-43. doi: 10.1007/s11248-007-9126-7. Epub 2007 Aug 21. Transgenic Res. 2008. PMID: 17710559
-
Recognition motifs rather than phylogenetic origin influence the ability of targeting peptides to import nuclear-encoded recombinant proteins into rice mitochondria.Transgenic Res. 2020 Feb;29(1):37-52. doi: 10.1007/s11248-019-00176-9. Epub 2019 Oct 10. Transgenic Res. 2020. PMID: 31598902 Free PMC article.
-
ER stress response induced by the production of human IL-7 in rice endosperm cells.Plant Mol Biol. 2013 Mar;81(4-5):461-75. doi: 10.1007/s11103-013-0016-5. Epub 2013 Feb 1. Plant Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23371559
-
Comparative proteome analysis of embryo and endosperm reveals central differential expression proteins involved in wheat seed germination.BMC Plant Biol. 2015 Apr 8;15:97. doi: 10.1186/s12870-015-0471-z. BMC Plant Biol. 2015. PMID: 25888100 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin fusion expression and tissue-dependent targeting of hG-CSF in transgenic tobacco.BMC Biotechnol. 2011 Oct 11;11:91. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-11-91. BMC Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21985646 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bechtel DB, Wilson JD, Shewry PR (1991) Immunocytochemical localization of wheat storage protein triticin in developing endosperm tissue. Cereal Chem 68: 573–577
-
- Christensen AH, Quail PH (1996) Ubiquitin promoter-based vectors for high level expression of selectable and/or screenable marker genes in monocotyledonous plants. Transgenic Res 5: 213–218 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

