Promiscuous protein biotinylation by Escherichia coli biotin protein ligase
- PMID: 15459338
- PMCID: PMC2286582
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.04911804
Promiscuous protein biotinylation by Escherichia coli biotin protein ligase
Abstract
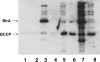
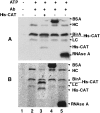
Biotin protein ligases (BPLs) are enzymes of extraordinary specificity. BirA, the BPL of Escherichia coli biotinylates only a single cellular protein. We report a mutant BirA that attaches biotin to a large number of cellular proteins in vivo and to bovine serum albumin, chloramphenicol acetyltransferase, immunoglobin heavy and light chains, and RNAse A in vitro. The mutant BirA also self biotinylates in vivo and in vitro. The wild type BirA protein is much less active in these reactions. The biotinylation reaction is proximity-dependent in that a greater extent of biotinylation was seen when the mutant ligase was coupled to the acceptor proteins than when the acceptors were free in solution. This approach may permit facile detection and recovery of interacting proteins by existing avidin/streptavidin technology.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Targeted and proximity-dependent promiscuous protein biotinylation by a mutant Escherichia coli biotin protein ligase.J Nutr Biochem. 2005 Jul;16(7):416-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2005.03.017. J Nutr Biochem. 2005. PMID: 15992681
-
Expression and purification of E. coli BirA biotin ligase for in vitro biotinylation.Protein Expr Purif. 2012 Mar;82(1):162-7. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2011.12.008. Epub 2012 Jan 2. Protein Expr Purif. 2012. PMID: 22227598 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo biotinylation of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II/peptide complex by coexpression of BirA enzyme for the generation of MHC class II/tetramers.Hum Immunol. 2004 Jul;65(7):692-9. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2004.04.001. Hum Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15301857
-
Biotin protein ligase as you like it: Either extraordinarily specific or promiscuous protein biotinylation.Proteins. 2024 Apr;92(4):435-448. doi: 10.1002/prot.26642. Epub 2023 Nov 23. Proteins. 2024. PMID: 37997490 Review.
-
[Progress in research and application of the biotin ligase BirA and its mutants in pathogen-host interaction].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2024 Jul 25;40(7):1981-1996. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.230855. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 39044570 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Immobilized enzyme cascade for targeted glycosylation.Nat Chem Biol. 2024 Jun;20(6):732-741. doi: 10.1038/s41589-023-01539-4. Epub 2024 Feb 6. Nat Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 38321209 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging insights and challenges for understanding T cell function through the proteome.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 16;13:1028366. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1028366. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36466897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proximity extracellular protein-protein interaction analysis of EGFR using AirID-conjugated fragment of antigen binding.Nat Commun. 2023 Dec 14;14(1):8301. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43931-7. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 38097606 Free PMC article.
-
Proximity-Dependent In Vivo Biotin Labeling for Interactome Mapping in Marchantia polymorpha.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2581:295-308. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2784-6_21. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36413326
-
Halo-seq: An RNA Proximity Labeling Method for the Isolation and Analysis of Subcellular RNA Populations.Curr Protoc. 2022 May;2(5):e424. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.424. Curr Protoc. 2022. PMID: 35532287 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barker, D.F. and Campbell, A.M. 1981. Genetic and biochemical characterization of the birA gene and its product: Evidence for a direct role of biotin holoenzyme synthetase in repression of the biotin operon in Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 146 469–492. - PubMed
-
- Beckett, D. and Matthews, B.W. 1997. Escherichia coli repressor of biotin biosynthesis. Methods Enzymol. 279 362–376. - PubMed
-
- Brown, P.H., Cronan, J.E., Grotli, M., and Beckett, D. 2004. The biotin repressor: Modulation of allostery by corepressor analogs. J. Mol. Biol. 337 857–869. - PubMed
-
- Chapman-Smith, A. and Cronan Jr., J.E. 1999. The enzymatic biotinylation of proteins: A post-translational modification of exceptional specificity. Trends Biochem. Sci. 24 359–363. - PubMed
-
- Chapman-Smith, A., Morris, T.W., Wallace, J.C., and Cronan Jr., J.E. 1999. Molecular recognition in a post-translational modification of exceptional specificity. Mutants of the biotinylated domain of acetyl-CoA carboxylase defective in recognition by biotin protein ligase. J. Biol. Chem. 274 1449–1457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

