Recognition and processing of a nuclear-encoded polyprotein precursor by mitochondrial processing peptidase
- PMID: 15458388
- PMCID: PMC1134751
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20041396
Recognition and processing of a nuclear-encoded polyprotein precursor by mitochondrial processing peptidase
Abstract
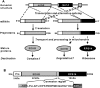
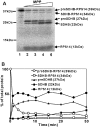
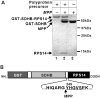
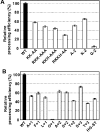
The nuclear-encoded protein RPS14 (ribosomal protein S14) of rice mitochondria is synthesized in the cytosol as a polyprotein consisting of a large N-terminal domain comprising preSDHB (succinate dehydrogenase B precursor) and the C-terminal RPS14. After the preSDHB-RPS14 polyprotein is transported into the mitochondrial matrix, the protein is processed into three peptides: the N-terminal prepeptide, the SDHB domain and the C-terminal mature RPS14. Here we report that the general MPP (mitochondrial processing peptidase) plays an essential role in processing of the polyprotein. Purified yeast MPP cleaved both the N-terminal presequence and the connector region between SDHB and RPS14. Moreover, the connector region was processed more rapidly than the presequence. When the site of cleavage between SDHB and RPS14 was determined, it was located in an MPP processing motif that has also been shown to be present in the N-terminal presequence. Mutational analyses around the cleavage site in the connector region suggested that MPP interacts with multiple sites in the region, possibly in a similar manner to the interaction with the N-terminal presequence. In addition, MPP preferentially recognized the unfolded structure of preSDHB-RPS14. In mitochondria, MPP may recognize the stretched polyprotein during passage of the precursor through the translocational apparatus in the inner membrane, and cleave the connecting region between the SDHB and RPS14 domains even before processing of the presequence.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The nuclear-encoded SDH2-RPS14 precursor is proteolytically processed between SDH2 and RPS14 to generate maize mitochondrial RPS14.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000 May 10;271(2):380-5. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2000.2644. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000. PMID: 10799306
-
A single nuclear transcript encoding mitochondrial RPS14 and SDHB of rice is processed by alternative splicing: common use of the same mitochondrial targeting signal for different proteins.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Aug 3;96(16):9207-11. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.16.9207. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10430921 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Profiling for Substrates of the Mitochondrial Presequence Processing Protease Reveals a Set of Nonsubstrate Proteins Increased upon Proteotoxic Stress.J Proteome Res. 2015 Nov 6;14(11):4550-63. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.5b00327. Epub 2015 Oct 21. J Proteome Res. 2015. PMID: 26446170
-
Mitochondrial processing peptidase: multiple-site recognition of precursor proteins.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999 Nov 30;265(3):611-6. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.1703. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999. PMID: 10600469 Review.
-
The mitochondrial processing peptidase: function and specificity.Experientia. 1996 Dec 15;52(12):1077-82. doi: 10.1007/BF01952105. Experientia. 1996. PMID: 8988249 Review.
Cited by
-
More than just a ticket canceller: the mitochondrial processing peptidase tailors complex precursor proteins at internal cleavage sites.Mol Biol Cell. 2020 Nov 15;31(24):2657-2668. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E20-08-0524. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Mol Biol Cell. 2020. PMID: 32997570 Free PMC article.
-
Sequential processing of a mitochondrial tandem protein: insights into protein import in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Eukaryot Cell. 2006 Jul;5(7):997-1006. doi: 10.1128/EC.00092-06. Eukaryot Cell. 2006. PMID: 16835444 Free PMC article.
-
Organelle-dependent polyprotein designs enable stoichiometric expression of nitrogen fixation components targeted to mitochondria.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Aug 22;120(34):e2305142120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2305142120. Epub 2023 Aug 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37585462 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic profiling of the mitochondrial ribosome identifies Atp25 as a composite mitochondrial precursor protein.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Oct 15;27(20):3031-3039. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-07-0513. Epub 2016 Aug 31. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27582385 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hartl F.-U., Pfanner N., Nicholson D. W., Neupert W. Mitochondrial protein import. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1989;988:1–45. - PubMed
-
- Baker K. P., Shatz G. Mitochondrial proteins essential for viability mediate protein import into yeast mitochondria. Nature (London) 1991;349:205–208. - PubMed
-
- Ryan K. R., Jensen R. E. Protein translocation across mitochondrial membranes: what a long, strange trip it is. Cell. 1995;83:517–519. - PubMed
-
- Schatz G. The protein import system of mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:31763–31766. - PubMed
-
- Neupert W. Protein import into mitochondria. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1997;66:863–917. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

