Endocytosis and sorting of ErbB2 and the site of action of cancer therapeutics trastuzumab and geldanamycin
- PMID: 15385631
- PMCID: PMC532009
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-07-0591
Endocytosis and sorting of ErbB2 and the site of action of cancer therapeutics trastuzumab and geldanamycin
Abstract
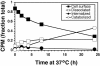
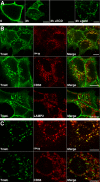
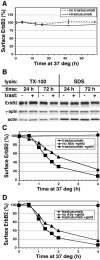
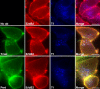
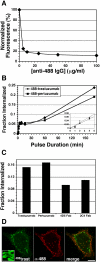
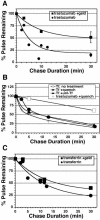
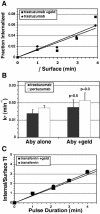
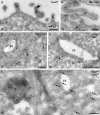
ErbB2 is a transmembrane tyrosine kinase whose surface overexpression is linked to tumorigenesis and poor prognosis in breast cancer patients. Two models have emerged that account for the high surface distribution of ErbB2. In one model, the surface pool is dynamic and governed by a balance between endocytosis and recycling, whereas in the other it is retained, static, and excluded from endocytosis. These models have contrasting implications for how ErbB2 exerts its biological function and how cancer therapies might down-regulate surface ErbB2, such as the antibody trastuzumab (Herceptin) or the Hsp90 inhibitor geldanamycin. Little is known, however, about how these treatments affect ErbB2 endocytic trafficking. To investigate this issue, we examined breast carcinoma cells by immunofluorescence and quantitative immunoelectron microscopy and developed imaging and trafficking kinetics assays using cell surface fluorescence quenching. Surprisingly, trastuzumab does not influence ErbB2 distribution but instead recycles passively with internalized ErbB2. By contrast, geldanamycin down-regulates surface ErbB2 through improved degradative sorting in endosomes exclusively rather than through increased endocytosis. These results reveal substantial dynamism in the surface ErbB2 pool and clearly demonstrate the significance of endosomal sorting in the maintenance of ErbB2 surface distribution, a critical feature of its biological function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A combination of Trastuzumab and 17-AAG induces enhanced ubiquitinylation and lysosomal pathway-dependent ErbB2 degradation and cytotoxicity in ErbB2-overexpressing breast cancer cells.Cancer Biol Ther. 2008 Oct;7(10):1630-40. doi: 10.4161/cbt.7.10.6585. Epub 2008 Oct 9. Cancer Biol Ther. 2008. PMID: 18769124 Free PMC article.
-
The deubiquitylase USP2 maintains ErbB2 abundance via counteracting endocytic degradation and represents a therapeutic target in ErbB2-positive breast cancer.Cell Death Differ. 2020 Sep;27(9):2710-2725. doi: 10.1038/s41418-020-0538-8. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Cell Death Differ. 2020. PMID: 32327714 Free PMC article.
-
Hsp90 inhibitor 17-AAG reduces ErbB2 levels and inhibits proliferation of the trastuzumab resistant breast tumor cell line JIMT-1.Immunol Lett. 2006 Apr 15;104(1-2):146-55. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2005.11.018. Epub 2005 Dec 12. Immunol Lett. 2006. PMID: 16384610
-
The ErbB2 signaling network as a target for breast cancer therapy.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2006 Jan;11(1):13-25. doi: 10.1007/s10911-006-9009-1. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2006. PMID: 16947083 Review.
-
[Management of metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer: present and future].Bull Cancer. 2010 Mar;97(3):365-83. doi: 10.1684/bdc.2010.1040. Bull Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20176546 Review. French.
Cited by
-
The Huntington disease protein accelerates breast tumour development and metastasis through ErbB2/HER2 signalling.EMBO Mol Med. 2013 Feb;5(2):309-25. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201201546. Epub 2013 Jan 9. EMBO Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23300147 Free PMC article.
-
Geldanamycin Enhances Retrograde Transport of Shiga Toxin in HEp-2 Cells.PLoS One. 2015 May 27;10(5):e0129214. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129214. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26017782 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Resistance to Trastuzumab and Novel Therapeutic Strategies in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer.Int J Breast Cancer. 2012;2012:415170. doi: 10.1155/2012/415170. Epub 2012 May 9. Int J Breast Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22649737 Free PMC article.
-
Increased signalling of EGFR and IGF1R, and deregulation of PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway are related with trastuzumab resistance in HER2 breast carcinomas.Br J Cancer. 2012 Apr 10;106(8):1367-73. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2012.85. Epub 2012 Mar 27. Br J Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22454081 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering a HER2-specific antibody-drug conjugate to increase lysosomal delivery and therapeutic efficacy.Nat Biotechnol. 2019 May;37(5):523-526. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0073-7. Epub 2019 Apr 1. Nat Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30936563 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agus, D.B. et al. (2002). Targeting ligand-activated ErbB2 signaling inhibits breast and prostate tumor growth. Cancer Cell 2, 127–137. - PubMed
-
- Bargmann, C.I., Hung, M.C., and Weinberg, R.A. (1986). Multiple independent activations of the neu oncogene by a point mutation altering the transmembrane domain of p185. Cell 45, 649–657. - PubMed
-
- Baselga, J., and Albanell, J. (2001). Mechanism of action of anti-HER2 monoclonal antibodies. Ann. Oncol. 12(Suppl 1), S35–S41. - PubMed
-
- Baulida, J., Kraus, M.H., Alimandi, M., Di Fiore, P.P., and Carpenter, G. (1996). All ErbB receptors other than the epidermal growth factor receptor are endocytosis impaired. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 5251–5257. - PubMed
-
- Benz, C.C., Scott, G.K., Sarup, J.C., Johnson, R.M., Tripathy, D., Coronado, E., Shepard, H.M., and Osborne, C.K. (1993). Estrogen-dependent, tamoxifen-resistant tumorigenic growth of MCF-7 cells transfected with HER2/neu. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 24, 85–95. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

