The modified wobble nucleoside uridine-5-oxyacetic acid in tRNAPro(cmo5UGG) promotes reading of all four proline codons in vivo
- PMID: 15383682
- PMCID: PMC1370651
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.7106404
The modified wobble nucleoside uridine-5-oxyacetic acid in tRNAPro(cmo5UGG) promotes reading of all four proline codons in vivo
Abstract
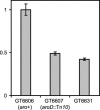
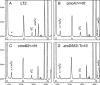
In Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium five of the eight family codon boxes are decoded by a tRNA having the modified nucleoside uridine-5-oxyacetic acid (cmo5U) as a wobble nucleoside present in position 34 of the tRNA. In the proline family codon box, one (tRNAProcmo5UGG) of the three tRNAs that reads the four proline codons has cmo5U34. According to theoretical predictions and several results obtained in vitro, cmo5U34 should base pair with A, G, and U in the third position of the codon but not with C. To analyze the function of cmo5U34 in tRNAProcmo5UGG in vivo, we first identified two genes (cmoA and cmoB) involved in the synthesis of cmo5U34. The null mutation cmoB2 results in tRNA having 5-hydroxyuridine (ho5U34) instead of cmo5U34, whereas the null mutation cmoA1 results in the accumulation of 5-methoxyuridine (mo5U34) and ho5U34 in tRNA. The results suggest that the synthesis of cmo5U34 occurs as follows: U34 -->(?) ho5U -->(CmoB) mo5U -->(CmoA?) cmo5U. We introduced the cmoA1 or the cmoB2 null mutations into a strain that only had tRNAProcmo5UGG and thus lacked the other two proline-specific tRNAs normally present in the cell. From analysis of growth rates of various strains and of the frequency of +1 frameshifting at a CCC-U site we conclude: (1) unexpectedly, tRNAProcmo5UGG is able to read all four proline codons; (2) the presence of ho5U34 instead of cmo5U34 in this tRNA reduces the efficiency with which it reads all four codons; and (3) the fully modified nucleoside is especially important for reading proline codons ending with U or C.
Copyright 2004 RNA Society
Figures

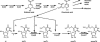
Similar articles
-
The wobble hypothesis revisited: uridine-5-oxyacetic acid is critical for reading of G-ending codons.RNA. 2007 Dec;13(12):2151-64. doi: 10.1261/rna.731007. Epub 2007 Oct 17. RNA. 2007. PMID: 17942742 Free PMC article.
-
A cytosolic tRNA with an unmodified adenosine in the wobble position reads a codon ending with the non-complementary nucleoside cytidine.J Mol Biol. 2002 Apr 5;317(4):481-92. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2002.5435. J Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 11955004
-
Deficiency of 1-methylguanosine in tRNA from Salmonella typhimurium induces frameshifting by quadruplet translocation.J Mol Biol. 1993 Aug 5;232(3):756-65. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1429. J Mol Biol. 1993. PMID: 7689113
-
tRNA's wobble decoding of the genome: 40 years of modification.J Mol Biol. 2007 Feb 9;366(1):1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.11.046. Epub 2006 Nov 15. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17187822 Review.
-
tRNA residues that have coevolved with their anticodon to ensure uniform and accurate codon recognition.Biochimie. 2006 Aug;88(8):943-50. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2006.06.005. Epub 2006 Jun 23. Biochimie. 2006. PMID: 16828219 Review.
Cited by
-
S-Adenosyl-S-carboxymethyl-L-homocysteine: a novel cofactor found in the putative tRNA-modifying enzyme CmoA.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013 Jun;69(Pt 6):1090-8. doi: 10.1107/S0907444913004939. Epub 2013 May 15. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013. PMID: 23695253 Free PMC article.
-
Codon-Specific Translation by m1G37 Methylation of tRNA.Front Genet. 2019 Jan 10;9:713. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00713. eCollection 2018. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 30687389 Free PMC article.
-
Two groups of phenylalanine biosynthetic operon leader peptides genes: a high level of apparently incidental frameshifting in decoding Escherichia coli pheL.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Apr;39(8):3079-92. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq1272. Epub 2010 Dec 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21177642 Free PMC article.
-
TrmD: A Methyl Transferase for tRNA Methylation With m1G37.Enzymes. 2017;41:89-115. doi: 10.1016/bs.enz.2017.03.003. Epub 2017 Apr 12. Enzymes. 2017. PMID: 28601227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
S-Adenosylmethionine: more than just a methyl donor.Nat Prod Rep. 2023 Sep 20;40(9):1521-1549. doi: 10.1039/d2np00086e. Nat Prod Rep. 2023. PMID: 36891755 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agris, P.F., Sierzputowska-Gracz, H., Smith, W., Malkiewicz, A., Sochacka, E., and Nawrot, B. 1992. Thiolation of uridine carbon-2 restricts the motional dynamics of the transfer RNA wobble position nucleoside. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 114: 2652–2656.
-
- Atkins, J.F. and Ryce, S. 1974. UGA and non-triplet suppressor reading of the genetic code. Nature 249: 527–530. - PubMed
-
- Björk, G.R. 1980. A novel link between the biosynthesis of aromatic amino acids and transfer RNA modification in Escherichia coli. J.Mol. Biol. 140: 391–410. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
