Direct Toll-like receptor 2 mediated co-stimulation of T cells in the mouse system as a basis for chronic inflammatory joint disease
- PMID: 15380043
- PMCID: PMC546283
- DOI: 10.1186/ar1212
Direct Toll-like receptor 2 mediated co-stimulation of T cells in the mouse system as a basis for chronic inflammatory joint disease
Abstract
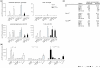
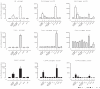
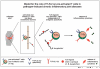
The pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory joint diseases such as adult and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and Lyme arthritis is still poorly understood. Central to the various hypotheses in this respect is the notable involvement of T and B cells. Here we develop the premise that the nominal antigen-independent, polyclonal activation of preactivated T cells via Toll-like receptor (TLR)-2 has a pivotal role in the initiation and perpetuation of pathogen-induced chronic inflammatory joint disease. We support this with the following evidence. Both naive and effector T cells express TLR-2. A prototypic lipoprotein, Lip-OspA, from the etiological agent of Lyme disease, namely Borrelia burgdorferi, but not its delipidated form or lipopolysaccharide, was able to provide direct antigen-nonspecific co-stimulatory signals to both antigen-sensitized naive T cells and cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) lines via TLR-2. Lip-OspA induced the proliferation and interferon (IFN)-gamma secretion of purified, anti-CD3-sensitized, naive T cells from C57BL/6 mice but not from TLR-2-deficient mice. Induction of proliferation and IFN-gamma secretion of CTL lines by Lip-OspA was independent of T cell receptor (TCR) engagement but was considerably enhanced after suboptimal TCR activation and was inhibitable by monoclonal antibodies against TLR-2.
Figures
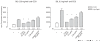
Similar articles
-
The outer surface lipoprotein OspA of Borrelia burgdorferi provides co-stimulatory signals to normal human peripheral CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes.Eur J Immunol. 1996 Oct;26(10):2299-303. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830261005. Eur J Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8898937
-
Hyporesponsiveness to vaccination with Borrelia burgdorferi OspA in humans and in TLR1- and TLR2-deficient mice.Nat Med. 2002 Aug;8(8):878-84. doi: 10.1038/nm732. Epub 2002 Jul 1. Nat Med. 2002. PMID: 12091878 Clinical Trial.
-
Cutting edge: inflammatory signaling by Borrelia burgdorferi lipoproteins is mediated by toll-like receptor 2.J Immunol. 1999 Sep 1;163(5):2382-6. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10452971
-
Chemokines and Toll-like receptors in Lyme disease pathogenesis.Trends Mol Med. 2005 Mar;11(3):114-20. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2005.01.003. Trends Mol Med. 2005. PMID: 15760769 Review.
-
Expression and function of Toll-like receptor on T cells.Cell Immunol. 2005 Feb;233(2):85-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2005.04.019. Cell Immunol. 2005. Retraction in: Cell Immunol. 2013 Feb;281(2):170. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2013.04.002. PMID: 15950961 Retracted. Review.
Cited by
-
Toll-like receptors, Notch ligands, and cytokines drive the chronicity of lung inflammation.Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2007 Dec;4(8):635-41. doi: 10.1513/pats.200706-067TH. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2007. PMID: 18073395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Toll-like receptor signals in T-cell neoplasms.Future Oncol. 2011 Feb;7(2):309-20. doi: 10.2217/fon.10.185. Future Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21345147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of immune responses through direct activation of Toll-like receptors to T cells.Clin Exp Immunol. 2010 May;160(2):168-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04091.x. Epub 2010 Jan 29. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20128825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction of Experimental Arthritis by Borrelial Lipoprotein and CpG Motifs: Are Toll-Like Receptors 2, 4, 9 or CD-14 Involved?Open Rheumatol J. 2011;5:18-23. doi: 10.2174/1874312901105010018. Epub 2011 Jul 19. Open Rheumatol J. 2011. PMID: 21804904 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of IRAK1/4 sensitizes T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia to chemotherapies.J Clin Invest. 2015 Mar 2;125(3):1081-97. doi: 10.1172/JCI75821. Epub 2015 Feb 2. J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 25642772 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Silman AJ, Hochberg MC. Rheumatoid Arthritis. In: Silman AJ, Hochberg MC, editor. In Epidemiology of the Rheumatic Diseases. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2001. pp. 31–71.
-
- Hirschfeld M, Kirschning CJ, Schwandner R, Wesche H, Weis JH, Wooten RM, Weis JJ. Cutting edge: inflammatory signaling by Borrelia burgdorferi lipoproteins is mediated by toll-like receptor 2. J Immunol. 1999;163:2382–2386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

