Yeast expression and DNA immunization of hepatitis B virus S gene with second-loop deletion of alpha determinant region
- PMID: 15378779
- PMCID: PMC4576258
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i20.2989
Yeast expression and DNA immunization of hepatitis B virus S gene with second-loop deletion of alpha determinant region
Abstract
Aim: Immune escape mutations of HBV often occur in the dominant epitope, the second-loop of the a determinant of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg). To let the hosts respond to the subdominant epitopes in HBsAg may be an effective way to decrease the prevalence of immune escape mutants. For this reason, a man-made clone of HBV S gene with the second-loop deletion was constructed. Its antigenicity was evaluated by yeast expression analysis and DNA immunization in mice.
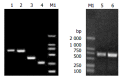
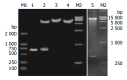
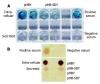
Methods: HBV S gene with deleted second-loop, amino acids from 139 to 145, was generated using splicing by overlap extension. HBV deleted S gene was then cloned into the yeast expression vector pPIC9 and the mammalian expression vector pcDNA3 to generate pHB-SDY and pHB-SD, respectively. The complete S gene was cloned into the same vectors as controls. The deleted recombinant HBsAg expressed in yeasts was detected using Abbott IMx HBsAg test kits, enzyme-linked immunoadsorbent assay (ELISA) and immune dot blotting to evaluate its antigenicity in vitro. The anti-HBs responses to DNA immunization in BALB/c mice were detected using Abbott IMx AUSAB test kits to evaluate the antigenicity of that recombinant protein in vivo.
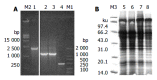
Results: Both deleted and complete HBsAg were successfully expressed in yeasts. They were intracellular expressions. The deleted HBsAg could not be detected by ELISA, in which the monoclonal anti-HBs against the alpha determinant was used, but could be detected by Abbott IMx and immune dot blotting, in which multiple monoclonal anti-HBs and polyclonal anti-HBs were used, respectively. The activity of the deleted HBsAg detected by Abbott IMx was much lower than that of complete HBsAg (the ratio of sample value/cut off value, 106+/-26.7 vs 1 814.4+/-776.3, P<0.01, t = 5.02). The anti-HBs response of pHB-SD to DNA immunization was lower than that of complete HBV S gene vector pHB (the positive rate 2/10 vs 6/10, 4.56+/-3.52 mIU/mL vs 27.60+/-17.3 mIU/mL, P = 0.02, t = 2.7).
Conclusions: HBsAg with deleted second-loop of the alpha determinant still has antigenicity, and can also raise weak anti-HBs response in mice to DNA immunization, suggesting that it is possible to develop a subdominant vaccine for preventing infections of immune escape mutants of HBV.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Construction of exogenous multiple epitopes of helper T lymphocytes and DNA immunization of its chimeric plasmid with HBV pre-S2/S gene.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Oct 15;10(20):2979-83. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i20.2979. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15378777 Free PMC article.
-
A novel hepatitis B virus variant S 129 (Gln-->Leu): lack of correlation between antigenicity and immunogenicity.J Med Virol. 1999 Dec;59(4):424-30. J Med Virol. 1999. PMID: 10534722
-
Vaccine- and hepatitis B immune globulin-induced escape mutations of hepatitis B virus surface antigen.J Biomed Sci. 2001 May-Jun;8(3):237-47. doi: 10.1007/BF02256597. J Biomed Sci. 2001. PMID: 11385295 Review.
-
Cloning, protein expression and immunogenicity of HBs-murine IL-18 fusion DNA vaccine.Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2007 Dec;25(4):233-42. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2007. PMID: 18402297
-
Hepatitis B virus vaccine breakthrough infection: surveillance of S gene mutants of HBV.Acta Virol. 2018;62(2):115-121. doi: 10.4149/av_2018_210. Acta Virol. 2018. PMID: 29895151 Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatitis B virus S gene escape mutants.Asian J Transfus Sci. 2007 Jul;1(2):62-70. doi: 10.4103/0973-6247.33445. Asian J Transfus Sci. 2007. PMID: 21938236 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kao JH, Chen DS. Global control of hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet Infect Dis. 2002;2:395–403. - PubMed
-
- Huang P, Ye G, Zhong J, Sha Q. Assessment of current epidemiological status of viral hepatitis in Guangdong Province, China. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2002;33:832–836. - PubMed
-
- Kane MA. Global control of primary hepatocellular carcinoma with hepatitis B vaccine: the contributions of research in Taiwan. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2003;12:2–3. - PubMed
-
- Tao Q, Feng B. Prevention and therapy of hepatitis B. Chin Med J (Engl) 1999;112:942–946. - PubMed
-
- André FE, Zuckerman AJ. Review: protective efficacy of hepatitis B vaccines in neonates. J Med Virol. 1994;44:144–151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

