Transcriptional complexes engaged by apo-estrogen receptor-alpha isoforms have divergent outcomes
- PMID: 15343269
- PMCID: PMC517616
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600377
Transcriptional complexes engaged by apo-estrogen receptor-alpha isoforms have divergent outcomes
Abstract
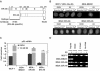
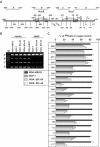
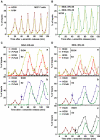
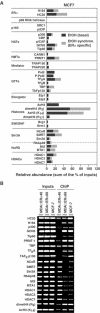
Unliganded (apo-) estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha, NR3A1) is classically considered as transcriptionally unproductive. Reassessing this paradigm demonstrated that apo-human ERalpha (ERalpha66) and its N-terminally truncated isoform (ERalpha46) are both predominantly nuclear transcription factors that cycle on the endogenous estrogen-responsive pS2 gene promoter in vivo. Importantly, isoform-specific consequences occur in terms of poising the promoter for transcription, as evaluated by determining (i) the engagement of several cofactors and the resulting nucleosomal organization; and (ii) the CpG methylation state of the pS2 promoter. Although transcriptionally unproductive, cycling of apo-ERalpha66 prepares the promoter to respond to ligand, through sequentially targeting chromatin remodeling complexes and general transcription factors. Additionally, apo-ERalpha46 recruits corepressors, following engagement of cofactors identical to those recruited by apo-ERalpha66. Together, these data describe differential activities of ERalpha isoforms. Furthermore, they depict the maintenance of a promoter in a repressed state as a cyclical process that is intrinsically dependent on initial poising of the promoter.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MUC1 gene overexpressed in breast cancer: structure and transcriptional activity of the MUC1 promoter and role of estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) in regulation of the MUC1 gene expression.Mol Cancer. 2006 Nov 5;5:57. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-5-57. Mol Cancer. 2006. PMID: 17083744 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen receptor regulates insulin-like growth factor-I receptor gene expression in breast tumor cells: involvement of transcription factor Sp1.J Endocrinol. 2006 Dec;191(3):605-12. doi: 10.1677/joe.1.07016. J Endocrinol. 2006. PMID: 17170218
-
Marking time: the dynamic role of chromatin and covalent modification in transcription.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 Jan;41(1):155-63. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2008.08.028. Epub 2008 Sep 2. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 18805503 Review.
-
Estrogen receptor-alpha directs ordered, cyclical, and combinatorial recruitment of cofactors on a natural target promoter.Cell. 2003 Dec 12;115(6):751-63. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00934-6. Cell. 2003. PMID: 14675539
-
Methylation analysis of the promoter F of estrogen receptor alpha gene: effects on the level of transcription on human osteoblastic cells.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2004 Jun;91(1-2):1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2004.02.005. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15261302
Cited by
-
Histone hyperacetylation during SV40 transcription is regulated by p300 and RNA polymerase II translocation.J Mol Biol. 2007 Aug 24;371(4):1022-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.06.080. Epub 2007 Jul 3. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17658552 Free PMC article.
-
Multivalent engagement of chromatin modifications by linked binding modules.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Dec;8(12):983-94. doi: 10.1038/nrm2298. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 18037899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endocrine disruptors fludioxonil and fenhexamid stimulate miR-21 expression in breast cancer cells.Toxicol Sci. 2013 Jan;131(1):71-83. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfs290. Epub 2012 Oct 10. Toxicol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23052036 Free PMC article.
-
A tale of two estrogen receptors (ERs): how differential ER-estrogen responsive element interactions contribute to subtype-specific transcriptional responses.Nucl Recept Signal. 2006;4:e015. doi: 10.1621/nrs.04015. Epub 2006 Jul 7. Nucl Recept Signal. 2006. PMID: 16862221 Free PMC article.
-
A role for methyl-CpG binding domain protein 2 in the modulation of the estrogen response of pS2/TFF1 gene.PLoS One. 2010 Mar 12;5(3):e9665. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009665. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20300195 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barkhem T, Haldosén LA, Gustafsson JA, Nilsson S (2002) Transcriptional synergism on the pS2 gene promoter between a p160 coactivator and ERα depends on the coactivator subtype, the type of ERE, and the promoter context. Mol Endocrinol 16: 2571–2581 - PubMed
-
- Belandia B, Parker MG (2003) Nuclear receptors: a rendezvous for chromatin remodeling factors. Cell 114: 277–280 - PubMed
-
- Bian Z, Nilsson S, Gustafsson JA (2001) Selective estrogen receptor modulators and coronary heart disease. Trends Cardiovasc Med 11: 196–202 - PubMed
-
- Bird A (2002) DNA methylation patterns and epigenetic memory. Genes Dev 16: 6–21 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

