In search of RNase P RNA from microbial genomes
- PMID: 15337843
- PMCID: PMC1370640
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.7970404
In search of RNase P RNA from microbial genomes
Abstract
A simple procedure has been developed to quickly retrieve and validate the DNA sequence encoding the RNA subunit of ribonuclease P (RNase P RNA) from microbial genomes. RNase P RNA sequences were identified from 94% of bacterial and archaeal complete genomes where previously no RNase P RNA was annotated. A sequence was found in camelpox virus, highly conserved in all orthopoxviruses (including smallpox virus), which could fold into a putative RNase P RNA in terms of conserved primary features and secondary structure. New structure features of RNase P RNA that enable one to distinguish bacteria from archaea and eukarya were found. This RNA is yet another RNA that can be a molecular criterion to divide the living world into three domains (bacteria, archaea, and eukarya). The catalytic center of this RNA, and its detection from some environmental whole genome shotgun sequences, is also discussed.
Copyright 2004 RNA Society
Figures
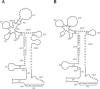
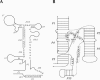
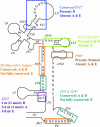
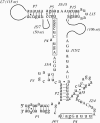
Similar articles
-
Deciphering RNA structural diversity and systematic phylogeny from microbial metagenomes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(7):2283-94. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm057. Epub 2007 Mar 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17389640 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of putative RNase P RNA from orthopoxviruses.J Mol Biol. 2005 Dec 2;354(3):529-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.09.020. Epub 2005 Sep 29. J Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 16253270
-
Archaeal-bacterial chimeric RNase P RNAs: towards understanding RNA's architecture, function and evolution.Chembiochem. 2011 Jul 4;12(10):1536-43. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201100054. Epub 2011 May 13. Chembiochem. 2011. PMID: 21574237
-
The enigma of ribonuclease P evolution.Trends Genet. 2003 Oct;19(10):561-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2003.08.007. Trends Genet. 2003. PMID: 14550630 Review.
-
The RNase P family.RNA Biol. 2009 Sep-Oct;6(4):362-9. doi: 10.4161/rna.6.4.9241. Epub 2009 Sep 9. RNA Biol. 2009. PMID: 19738420 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery, structure, mechanisms, and evolution of protein-only RNase P enzymes.J Biol Chem. 2024 Mar;300(3):105731. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.105731. Epub 2024 Feb 8. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38336295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A noncoding RNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is an RNase P substrate.RNA. 2007 May;13(5):682-90. doi: 10.1261/rna.460607. Epub 2007 Mar 22. RNA. 2007. PMID: 17379814 Free PMC article.
-
Transfer RNA processing in archaea: unusual pathways and enzymes.FEBS Lett. 2010 Jan 21;584(2):303-9. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.10.067. FEBS Lett. 2010. PMID: 19878676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of Sinorhizobium meliloti sRNA genes and experimental detection in strain 2011.BMC Genomics. 2008 Sep 16;9:416. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-416. BMC Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18793445 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary patterns of non-coding RNAs.Theory Biosci. 2005 Apr;123(4):301-69. doi: 10.1016/j.thbio.2005.01.002. Theory Biosci. 2005. PMID: 18202870
References
-
- Birkenheuer, A.J., Breitschwerdt, E.B., Alleman, A.R., and Pitulle, C. 2002. Differentiation of Haemobartonella canis and Mycoplasma haemofelis on the basis of comparative analysis of gene sequences. Am. J. Vet. Res. 63: 1385–1388. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
