Inhibitory effect of ubiquitin-proteasome pathway on proliferation of esophageal carcinoma cells
- PMID: 15334669
- PMCID: PMC4572101
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i19.2779
Inhibitory effect of ubiquitin-proteasome pathway on proliferation of esophageal carcinoma cells
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the inhibitory effect of ubiquitin-proteasome pathway (UPP) on proliferation of esophageal carcinoma cells.
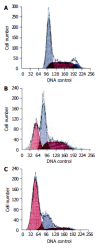
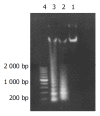
Methods: Esophageal carcinoma cell strain EC9706 was treated with MG-132 to inhibit its UPP specificity. Cell growth suppression was evaluated with 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazole-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. DNA synthesis was evaluated by (3)H-thymidine ((3)H-TdR) incorporation. Morphologic changes of cells were observed under microscope. Activity of telomerase was examined by telomeric repeat amplification protocol (TRAP) of PCR-ELISA. Cell cycle and apoptosis were detected by flow cytometry (FCM). DNA fragment analysis was used to confirm the presence of apoptosis. Expression of p27(kip1) was detected by immunocytochemical technique.
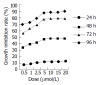
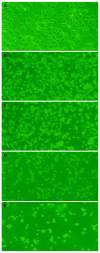
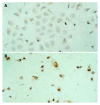
Results: After exposed to MG-132, the growth and value of (3)H-TdR incorporation of EC9706 cells were obviously inhibited. Cells became round, small and exfoliative under microscope. TRAP PCR-ELISA showed that light absorption of cells gradually decreased after exposed to 5 micromol/L of MG-132 for 24, 48, 72 and 96 h (P<0.01). The percentage of cells at G(0)/G(1) phase was increased and that at S and G(2)/M was decreased (P<0.01). The rate of apoptotic cells treated with 5 micromol/L of MG-132 for 48 and 96 h was 31.7% and 66.4%, respectively. Agarose electrophoresis showed marked ladders. In addition, the positive signals of p27(kip1) were located in cytoplasm and nuclei in MG-132 group in contrast to cytoplasm staining in control group.
Conclusion: MG-132 can obviously inhibit proliferation of EC9706 cells and induce apoptosis. The mechanisms include upregulation of p27(kip1) expression, G(1) arrest and depression of telomerase activity. The results indicate that inhibiting UPP is a novel strategy for esophageal carcinoma therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MG-132 inhibits telomerase activity, induces apoptosis and G(1) arrest associated with upregulated p27kip1 expression and downregulated survivin expression in gastric carcinoma cells.Cancer Invest. 2008 Dec;26(10):1032-6. doi: 10.1080/07357900802104997. Cancer Invest. 2008. PMID: 19093261
-
Bile salts inhibit growth and induce apoptosis of human esophageal cancer cell line.World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Sep 7;11(33):5109-16. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i33.5109. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 16127738 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of bufalin on cellular proliferation and apoptosis in human esophageal squamous carcinoma EC9706 cells].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2012 Dec;34(6):556-62. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.2012.06.004. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2012. PMID: 23286398 Chinese.
-
[Effect of downregulation of Tiam1 by siRNA on esophageal squamous cell carcinoma EC9706 cells].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2014 Apr;36(4):250-6. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 24989909 Chinese.
-
[Proliferation inhibition and apoptosis onset in human ovarian carcinoma cell line SKOV3 induced by Genistein].Ai Zheng. 2003 Jun;22(6):586-91. Ai Zheng. 2003. PMID: 12948406 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Effect of silencing of high mobility group A2 gene on gastric cancer MKN-45 cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Feb 28;19(8):1239-46. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i8.1239. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23482887 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying reproducible cancer-associated highly expressed genes with important functional significances using multiple datasets.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 31;6:36227. doi: 10.1038/srep36227. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27796338 Free PMC article.
-
The Mechanistic Links Between Proteasome Activity, Aging and Age-related Diseases.Curr Genomics. 2014 Feb;15(1):38-51. doi: 10.2174/138920291501140306113344. Curr Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24653662 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of p27mt gene on apoptosis of the colorectal cancer cell line Lovo.World J Gastroenterol. 2009 Jun 14;15(22):2794-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.2794. World J Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 19522032 Free PMC article.
-
Protein clearance strategies for disease intervention.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2022 Feb;129(2):141-172. doi: 10.1007/s00702-021-02431-y. Epub 2021 Oct 23. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2022. PMID: 34689261 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhang WG, Wu QM, Wang XH, Xie GJ, Yu JP. Relationship between expression of survivin gene and biological characteris-tics in human esophageal carcinoma. J Chinese Physician. 2003;5:1378–1380.
-
- Wu QM, Li SB, Wang Q, Wang DH, Li XB, Liu CZ. The expres-sion of COX-2 in esophageal carcinoma and its relation to clinicopathologic characteristics. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2001;9:11–14.
-
- Li SB, Wu QM, Wang Q, Wang XH, Xie GJ. Effects of adenovi-rus-mediated human COX-2 antisense RNA on synthesis of DNA and proteins in esophgeal carcinoma cell line. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2003;11:517–521.
-
- King RW, Deshaies RJ, Peters JM, Kirschner MW. How proteolysis drives the cell cycle. Science. 1996;274:1652–1659. - PubMed
-
- Fuchs SY. The role of ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in oncogenic signaling. Cancer Biol Ther. 2002;1:337–341. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

