Heme oxygenase-1 modulates early inflammatory responses: evidence from the heme oxygenase-1-deficient mouse
- PMID: 15331427
- PMCID: PMC1618611
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63365-2
Heme oxygenase-1 modulates early inflammatory responses: evidence from the heme oxygenase-1-deficient mouse
Erratum in
- Am J Pathol. 2006 Feb;168(2):714
Abstract
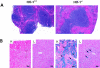
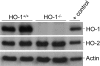
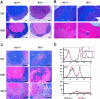
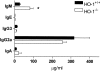
Induction of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) is protective in tissue injury in models of allograft rejection and vascular inflammation through either prevention of oxidative damage or via immunomodulatory effects. To examine the specific role of HO-1 in modulating the immune response, we examined the differences in immune phenotype between HO-1 knockout (HO-1(-/-)) and wild-type (HO-1(+/+)) mice. Consistent with previous findings, marked splenomegaly and fibrosis were observed in HO-1(-/-) mice. The lymph nodes of HO-1-deficient mice demonstrated a relative paucity of CD3- and B220-positive cells, but no such abnormalities were observed in the thymus. Flow cytometric analysis of isolated splenocytes demonstrated no differences in the proportions of T lymphocytes, B lymphocytes or monocytes/macrophages between the HO-1(-/-) and HO-1(+/+) mice. Significantly higher baseline serum IgM levels were observed in HO-1(-/-) versus HO-1(+/+) mice. Under mitogen stimulation with either lipopolysaccharide or anti-CD3/anti-CD28, HO-1(-/-) splenocytes secreted disproportionately higher levels of pro-inflammatory Th1 cytokines as compared to those from HO-1(+/+) mice. These findings demonstrate significant differences in the immune phenotype between the HO-1(-/-) and the HO-1(+/+) mice. The absence of HO-1 correlates with a Th1-weighted shift in cytokine responses suggesting a general pro-inflammatory tendency associated with HO-1 deficiency.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heme oxygenase-1 modulates the allo-immune response by promoting activation-induced cell death of T cells.FASEB J. 2005 Mar;19(3):458-60. doi: 10.1096/fj.04-2217fje. Epub 2005 Jan 7. FASEB J. 2005. PMID: 15640283
-
Graft protective effects of heme oxygenase 1 in mouse tracheal transplant-related obliterative bronchiolitis.Transplantation. 2003 Aug 27;76(4):650-6. doi: 10.1097/01.TP.0000080069.61917.18. Transplantation. 2003. PMID: 12973103
-
Interdependence of lipoxin A4 and heme-oxygenase in counter-regulating inflammation during corneal wound healing.FASEB J. 2007 Jul;21(9):2257-66. doi: 10.1096/fj.06-7918com. Epub 2007 Mar 23. FASEB J. 2007. PMID: 17384141
-
Heme oxygenase: recent advances in understanding its regulation and role.Proc Assoc Am Physicians. 1999 Sep-Oct;111(5):438-47. Proc Assoc Am Physicians. 1999. PMID: 10519165 Review.
-
Alteration in heme oxygenase-1 and nitric oxide synthase-2 gene expression during endotoxemia in cyclooxygenase-2-deficient mice.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2004 Oct;6(5):850-7. doi: 10.1089/ars.2004.6.850. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2004. PMID: 15345145 Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammation-induced alterations in maternal-fetal Heme Oxygenase (HO) are associated with sustained innate immune cell dysregulation in mouse offspring.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 4;16(6):e0252642. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252642. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34086785 Free PMC article.
-
Heme oxygenase-1 in protozoan infections: A tale of resistance and disease tolerance.PLoS Pathog. 2020 Jul 21;16(7):e1008599. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008599. eCollection 2020 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32692767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heme oxygenase-1 expression protects the heart from acute injury caused by inducible Cre recombinase.Lab Invest. 2013 Aug;93(8):868-79. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2013.74. Epub 2013 Jun 3. Lab Invest. 2013. PMID: 23732814 Free PMC article.
-
Gastric antisecretory and antiulcer activity of bovine hemoglobin.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Jun 7;19(21):3291-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i21.3291. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23745031 Free PMC article.
-
Heme Oxygenase-1 Regulates Myeloid Cell Trafficking in AKI.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015 Sep;26(9):2139-51. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2014080770. Epub 2015 Feb 12. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25677389 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Otterbein LE, Soares MP, Yamashita K, Bach FH. Heme oxygenase-1: unleashing the protective properties of heme. Trends Immunol. 2003;24:449–455. - PubMed
-
- Katori M, Busuttil RW, Kupiec-Weglinski JW. Heme oxygenase-1 system in organ transplantation. Transplantation. 2002;74:905–912. - PubMed
-
- Ishikawa K. Heme oxygenase-1 against vascular insufficiency: roles of atherosclerotic disorders. Curr Pharm Des. 2003;9:2489–2497. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

