Flagellin acting via TLR5 is the major activator of key signaling pathways leading to NF-kappa B and proinflammatory gene program activation in intestinal epithelial cells
- PMID: 15324458
- PMCID: PMC516440
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-4-33
Flagellin acting via TLR5 is the major activator of key signaling pathways leading to NF-kappa B and proinflammatory gene program activation in intestinal epithelial cells
Abstract
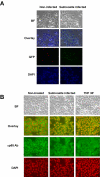
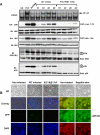
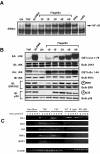
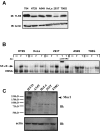
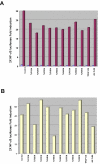
Background: Infection of intestinal epithelial cells by pathogenic Salmonella leads to activation of signaling cascades that ultimately initiate the proinflammatory gene program. The transcription factor NF-kappa B is a key regulator/activator of this gene program and is potently activated. We explored the mechanism by which Salmonella activates NF-kappa B during infection of cultured intestinal epithelial cells and found that flagellin produced by the bacteria and contained on them leads to NF-kappa B activation in all the cells; invasion of cells by the bacteria is not required to activate NF-kappa B.
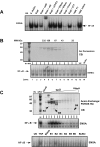
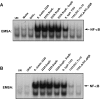
Results: Purified flagellin activated the mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK), stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK) and I kappa B kinase (IKK) signaling pathways that lead to expression of the proinflammatory gene program in a temporal fashion nearly identical to that of infection of intestinal epithelial cells by Salmonella. Flagellin expression was required for Salmonella invasion of host cells and it activated NF-kappa B via toll-like receptor 5 (TLR5). Surprisingly, a number of cell lines found to be unresponsive to flagellin express TLR5 and expression of exogenous TLR5 in these cells induces NF-kappa B activity in response to flagellin challenge although not robustly. Conversely, overexpression of dominant-negative TLR5 alleles only partially blocks NF-kappa B activation by flagellin. These observations are consistent with the possibility of either a very stable TLR5 signaling complex, the existence of a low abundance flagellin co-receptor or required adapter, or both.
Conclusion: These collective results provide the evidence that flagellin acts as the main determinant of Salmonella mediated NF-kappa B and proinflammatory signaling and gene activation by this flagellated pathogen. In addition, expression of the fli C gene appears to play an important role in the proper functioning of the TTSS since mutants that fail to express fli C are defective in expressing a subset of Sip proteins and fail to invade host cells. Flagellin added in trans cannot restore the ability of the fli C mutant bacteria to invade intestinal epithelial cells. Lastly, TLR5 expression in weak and non-responding cells indicates that additional factors may be required for efficient signal propagation in response to flagellin recognition.
Figures


Similar articles
-
TLR5-mediated activation of p38 MAPK regulates epithelial IL-8 expression via posttranscriptional mechanism.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003 Aug;285(2):G282-90. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00503.2002. Epub 2003 Apr 17. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12702497
-
Toll-like receptor (TLR) 2 and TLR5, but not TLR4, are required for Helicobacter pylori-induced NF-kappa B activation and chemokine expression by epithelial cells.J Biol Chem. 2003 Aug 29;278(35):32552-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M305536200. Epub 2003 Jun 13. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12807870
-
In vitro and ex vivo activation of the TLR5 signaling pathway in intestinal epithelial cells by a commensal Escherichia coli strain.J Biol Chem. 2004 Oct 8;279(41):42984-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M405410200. Epub 2004 Aug 9. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15302888
-
AsialoGM1 and TLR5 cooperate in flagellin-induced nucleotide signaling to activate Erk1/2.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006 Jun;34(6):653-60. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2005-0441OC. Epub 2006 Jan 26. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16439799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Signal transduction of Toll-like receptors].Nihon Rinsho. 2005 Apr;63 Suppl 4:109-14. Nihon Rinsho. 2005. PMID: 15861643 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Activation of NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression by Salmonella flagellins FliC and FljB.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007 Mar 30;355(1):280-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.01.148. Epub 2007 Feb 5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007. PMID: 17292856 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenicity and Competitive Fitness of Salmonella enterica Serovar 4,[5],12:i:- Compared to Salmonella Typhimurium and Salmonella Derby in Swine.Front Vet Sci. 2020 Jan 30;6:502. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2019.00502. eCollection 2019. Front Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 32083096 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-1 beta secretion is activated comparably by FliC and FljB flagellins but differentially by wild-type and DNA adenine methylase-deficient salmonella.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2008 Nov;28(11):661-6. doi: 10.1089/jir.2008.0022. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2008. PMID: 18844581 Free PMC article.
-
NF-kB as a key player in regulation of cellular radiation responses and identification of radiation countermeasures.Discoveries (Craiova). 2015 Mar 31;3(1):e35. doi: 10.15190/d.2015.27. Discoveries (Craiova). 2015. PMID: 32309561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SPI1 Regulates the Progression of Ankylosing Spondylitis by Modulating TLR5 via NF-κB Signaling.Inflammation. 2023 Oct;46(5):1697-1708. doi: 10.1007/s10753-023-01834-1. Epub 2023 Jun 6. Inflammation. 2023. PMID: 37277671
References
-
- Elewaut D, DiDonato JA, Kim JM, Truong F, Eckmann L, Kagnoff MF. NF-kappa B is a central regulator of the intestinal epithelial cell innate immune response induced by infection with enteroinvasive bacteria. J Immunol. 1999;163:1457–1466. - PubMed
-
- Witthoft T, Eckmann L, Kim JM, Kagnoff MF. Enteroinvasive bacteria directly activate expression of iNOS and NO production in human colon epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1998;275:G564–G571. - PubMed
-
- Eckmann L, Stenson WF, Savidge TC, Lowe DC, Barrett KE, Fierer J, Smith JR, Kagnoff MF. Role of intestinal epithelial cells in the host secretory response to infection by invasive bacteria. Bacterial entry induces epithelial prostaglandin h synthase-2 expression and prostaglandin E2 and F2 alpha production. J Clin Invest. 1997;100:296–309. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

