Inhibition of hepatitis C virus-like particle binding to target cells by antiviral antibodies in acute and chronic hepatitis C
- PMID: 15308699
- PMCID: PMC506960
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.17.9030-9040.2004
Inhibition of hepatitis C virus-like particle binding to target cells by antiviral antibodies in acute and chronic hepatitis C
Abstract
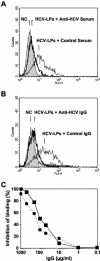
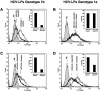
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a leading cause of chronic viral hepatitis worldwide. The study of antibody-mediated virus neutralization has been hampered by the lack of an efficient and high-throughput cell culture system for the study of virus neutralization. The HCV structural proteins have been shown to assemble into noninfectious HCV-like particles (HCV-LPs). Similar to serum-derived virions, HCV-LPs bind and enter human hepatocytes and hepatoma cell lines. In this study, we developed an HCV-LP-based model system for a systematic functional analysis of antiviral antibodies from patients with acute or chronic hepatitis C. We demonstrate that cellular HCV-LP binding was specifically inhibited by antiviral antibodies from patients with acute or chronic hepatitis C in a dose-dependent manner. Using a library of homologous overlapping envelope peptides covering the entire HCV envelope, we identified an epitope in the N-terminal E2 region (SQKIQLVNTNGSWHI; amino acid positions 408 to 422) as one target of human antiviral antibodies inhibiting cellular particle binding. Using a large panel of serum samples from patients with acute and chronic hepatitis C, we demonstrated that the presence of antibodies with inhibition of binding activity was not associated with viral clearance. In conclusion, antibody-mediated inhibition of cellular HCV-LP binding represents a convenient system for the functional characterization of human anti-HCV antibodies, allowing the mapping of envelope neutralization epitopes targeted by naturally occurring antiviral antibodies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antibodies against hepatitis C virus-like particles and viral clearance in acute and chronic hepatitis C.Hepatology. 2000 Sep;32(3):610-7. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2000.9876. Hepatology. 2000. PMID: 10960457
-
Antibodies directed to envelope proteins of hepatitis C virus outside of hypervariable region 1.Virology. 1998 Apr 10;243(2):313-21. doi: 10.1006/viro.1998.9069. Virology. 1998. PMID: 9568031
-
High titers of antibodies inhibiting the binding of envelope to human cells correlate with natural resolution of chronic hepatitis C.Hepatology. 1998 Oct;28(4):1117-20. doi: 10.1002/hep.510280429. Hepatology. 1998. PMID: 9755251
-
Virus-neutralizing antibodies to hepatitis C virus.J Viral Hepat. 2013 Jun;20(6):369-76. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12094. Epub 2013 Apr 4. J Viral Hepat. 2013. PMID: 23647953 Review.
-
Hepatitis C virus (HCV): a review of immunological aspects.Int Rev Immunol. 2008;27(6):497-517. doi: 10.1080/08830180802432178. Int Rev Immunol. 2008. PMID: 19065353 Review.
Cited by
-
Viral and cellular determinants of the hepatitis C virus envelope-heparan sulfate interaction.J Virol. 2006 Nov;80(21):10579-90. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00941-06. Epub 2006 Aug 23. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16928753 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive immunity to the hepatitis C virus.Adv Virus Res. 2010;78:43-86. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385032-4.00002-1. Adv Virus Res. 2010. PMID: 21040831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis C virus is a weak inducer of interferon alpha in plasmacytoid dendritic cells in comparison with influenza and human herpesvirus type-1.PLoS One. 2009;4(2):e4319. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004319. Epub 2009 Feb 2. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19183807 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid induction of virus-neutralizing antibodies and viral clearance in a single-source outbreak of hepatitis C.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Apr 3;104(14):6025-30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0607026104. Epub 2007 Mar 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17392433 Free PMC article.
-
New therapeutic opportunities for hepatitis C based on small RNA.World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Sep 7;13(33):4431-6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i33.4431. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17724797 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bartenschlager, R., and V. Lohmann. 2000. Replication of hepatitis C virus. J. Gen. Virol. 81:1631-1648. - PubMed
-
- Barth, H., C. Schafer, M. I. Adah, F. Zhang, R. J. Linhardt, H. Toyoda, A. Kinoshita-Toyoda, T. Toida, T. H. Van Kuppevelt, E. Depla, F. Von Weizsacker, H. E. Blum, and T. F. Baumert. 2003. Cellular binding of hepatitis C virus envelope glycoprotein E2 requires cell surface heparan sulfate. J. Biol. Chem. 278:41003-41012. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

