Inhibitory regulation of constitutive transient receptor potential-like cation channels in rabbit ear artery myocytes
- PMID: 15297579
- PMCID: PMC1665202
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.071738
Inhibitory regulation of constitutive transient receptor potential-like cation channels in rabbit ear artery myocytes
Abstract
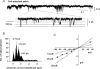
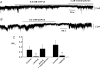
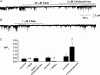
In the present study we have investigated an inhibitory pathway regulating a constitutively active Ca(2+)-permeable non-selective cation conductance (I(cat)) in rabbit ear artery smooth muscle cells. Constitutive single channel activity of I(cat) was recorded in cell-attached and inside-out patches with similar unitary conductance values. In inside-out patches with relatively high constitutive activity the G-protein activator GTPgammaS inhibited channel activity which was reversed by the protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor chelerythrine indicating a G-protein pathway inhibits channel activity via PKC. Spontaneous channel activity was also suppressed by the G-protein inhibitor GDPbetaS suggesting a G-protein is also involved in initiation of constitutive channel activity. Bath application of antibodies to G(alphaq)/G(alpha11) enhanced channel activity whereas anti-G(alpha1-3)/G(alphao) antibodies decreased basal channel activity which suggests that G(alphaq)/G(alpha11) and G(alphaiota)/G(alphao) proteins initiate, respectively, the inhibitory and excitatory cascades. The phospholipase C (PLC) inhibitor U73122 increased spontaneous activity which implies a role for PLC in the inhibitory pathway. Bath application of the diacylycerol (DAG) analogue 1-oeoyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycerol (OAG) decreased the probability of channel opening (NP(o)) and this was reversed by chelerythrine. Application of the PKC activator phorbol 12, 13-dibutyrate (PDBu) and chelerythrine, respectively, decreased and increased NP(o). These data indicate that spontaneously active cation channels are inhibited by a tonic inhibitory pathway involving G(alphaq)/G(alpha11)-mediated stimulation of PLC to generate DAG which activates PKC to inhibit channel opening. There were some patches with relatively low NP(o) and it was evident that the inhibitory pathway was particularly marked in these cases. Moreover in the latter patches GTPgammaS and OAG caused marked increases in NP(o). Together with inhibitory effects of GDPbetaS and anti-G(alpha1-3)/G(alphao) antibodies the results suggest that there is constitutive G(alphai)/G(alphao) protein activity leading to channel opening via a DAG-mediated but PKC-independent mechanism. Finally, with whole-cell recording it is shown that noradrenaline increases I(cat) and the noradrenaline-evoked response is markedly potentiated by PKC inhibition. This latter observation shows that PKC also limits agonist-evoked I(cat) in these arterial myocytes.
Figures

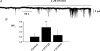


Similar articles
-
Role of phospholipase D and diacylglycerol in activating constitutive TRPC-like cation channels in rabbit ear artery myocytes.J Physiol. 2005 Aug 1;566(Pt 3):769-80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.090852. Epub 2005 May 26. J Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15919706 Free PMC article.
-
Properties of a constitutively active Ca2+-permeable non-selective cation channel in rabbit ear artery myocytes.J Physiol. 2003 May 15;549(Pt 1):143-56. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.038190. Epub 2003 Apr 4. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12679370 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II activates two cation conductances with distinct TRPC1 and TRPC6 channel properties in rabbit mesenteric artery myocytes.J Physiol. 2006 Dec 1;577(Pt 2):479-95. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.119305. Epub 2006 Sep 14. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16973707 Free PMC article.
-
Control of TRPC and store-operated channels by protein kinase C.Novartis Found Symp. 2004;258:172-85; discussion 185-8, 263-6. Novartis Found Symp. 2004. PMID: 15104182 Review.
-
Receptor-operated Ca2(+)-permeable nonselective cation channels in vascular smooth muscle: a physiologic perspective.J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2002 May;13(5):493-501. doi: 10.1046/j.1540-8167.2002.00493.x. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2002. PMID: 12030534 Review.
Cited by
-
Transient receptor potential channels in the vasculature.Physiol Rev. 2015 Apr;95(2):645-90. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00026.2014. Physiol Rev. 2015. PMID: 25834234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of phospholipase D and diacylglycerol in activating constitutive TRPC-like cation channels in rabbit ear artery myocytes.J Physiol. 2005 Aug 1;566(Pt 3):769-80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.090852. Epub 2005 May 26. J Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15919706 Free PMC article.
-
TRPC3 properties of a native constitutively active Ca2+-permeable cation channel in rabbit ear artery myocytes.J Physiol. 2006 Mar 1;571(Pt 2):361-9. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.102780. Epub 2006 Jan 5. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16396924 Free PMC article.
-
Obligatory role for PKCδ in PIP2 -mediated activation of store-operated TRPC1 channels in vascular smooth muscle cells.J Physiol. 2020 Sep;598(18):3911-3925. doi: 10.1113/JP279947. Epub 2020 Jul 21. J Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32627185 Free PMC article.
-
Isoform-selective physical coupling of TRPC3 channels to IP3 receptors in smooth muscle cells regulates arterial contractility.Circ Res. 2010 May 28;106(10):1603-12. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.216804. Epub 2010 Apr 8. Circ Res. 2010. PMID: 20378853 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Colquhoun D. Practical analysis of single channel recordes. In: Standen NB, Gray PTA, Whitaker MJ, editors. Microelectrode Techniques. Cambridge: The Company of Biologists; 1987. pp. 83–104.
-
- Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981;391:85–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

