MicroRNA profiling reveals distinct signatures in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemias
- PMID: 15284443
- PMCID: PMC511048
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0404432101
MicroRNA profiling reveals distinct signatures in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemias
Abstract
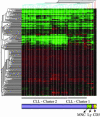
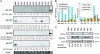
Little is known about the expression levels or function of micro-RNAs (miRNAs) in normal and neoplastic cells, although it is becoming clear that miRNAs play important roles in the regulation of gene expression during development [Ambros, V. (2003) Cell 113, 673-676; McManus, M. T. (2003) Semin. Cancer Biol. 13, 253-258]. We now report the genomewide expression profiling of miRNAs in human B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) by using a microarray containing hundreds of human precursor and mature miRNA oligonucleotide probes. This approach allowed us to identify significant differences in miRNome expression between CLL samples and normal CD5+ B cells; data were confirmed by Northern blot analyses and real-time RT-PCR. At least two distinct clusters of CLL samples can be identified that were associated with the presence or absence of Zap-70 expression, a predictor of early disease progression. Two miRNA signatures were associated with the presence or absence of mutations in the expressed Ig variableregion genes or with deletions at 13q14, respectively. These data suggest that miRNA expression patterns have relevance to the biological and clinical behavior of this leukemia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ZAP-70 expression identifies a chronic lymphocytic leukemia subtype with unmutated immunoglobulin genes, inferior clinical outcome, and distinct gene expression profile.Blood. 2003 Jun 15;101(12):4944-51. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-10-3306. Epub 2003 Feb 20. Blood. 2003. PMID: 12595313
-
Expression of ZAP-70 protein correlates with disease stage in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and is associated with, but not generally restricted to, non-mutated Ig VH status.Leuk Lymphoma. 2004 Oct;45(10):2037-45. doi: 10.1080/10428190410001714016. Leuk Lymphoma. 2004. PMID: 15370248
-
A MicroRNA signature associated with prognosis and progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.N Engl J Med. 2005 Oct 27;353(17):1793-801. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa050995. N Engl J Med. 2005. PMID: 16251535
-
New insights into the pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Semin Cancer Biol. 2010 Dec;20(6):377-83. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2010.10.012. Epub 2010 Oct 26. Semin Cancer Biol. 2010. PMID: 21029776 Review.
-
Molecular pathogenesis of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: analysis of 13q14 chromosomal deletions.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2000;252:275-84. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-57284-5_28. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2000. PMID: 11125485 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic regulation of miRNA-211 by MMP-9 governs glioma cell apoptosis, chemosensitivity and radiosensitivity.Oncotarget. 2012 Nov;3(11):1439-54. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.683. Oncotarget. 2012. PMID: 23183822 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-181b: new perspective to evaluate disease progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Oncotarget. 2012 Feb;3(2):195-202. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.448. Oncotarget. 2012. PMID: 22350310 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and Profiling of MicroRNA-containing Exosomes from Human Bile.J Vis Exp. 2016 Jun 13;(112):54036. doi: 10.3791/54036. J Vis Exp. 2016. PMID: 27341293 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies to Modulate MicroRNA Functions for the Treatment of Cancer or Organ Injury.Pharmacol Rev. 2020 Jul;72(3):639-667. doi: 10.1124/pr.119.019026. Pharmacol Rev. 2020. PMID: 32554488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CLL cells respond to B-Cell receptor stimulation with a microRNA/mRNA signature associated with MYC activation and cell cycle progression.PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e60275. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060275. Epub 2013 Apr 1. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23560086 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moss, E. G. (2003) in MicroRNAs in Noncoding RNAs: Molecular Biology and Molecular Medicine), eds. Barciszewski, J. & Erdmann, V. (Landes Bioscience, Georgetown, TX), pp. 98–114.
-
- Bartel, D. P. (2004) Cell 116, 281–297. - PubMed
-
- Ambros, V. (2003) Cell 113, 673–676. - PubMed
-
- Chen, C. Z., Li, L., Lodish, H. F. & Bartel, D. P. (2004) Science 303, 83–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

