Helicase Motif III in SecA is essential for coupling preprotein binding to translocation ATPase
- PMID: 15272299
- PMCID: PMC1299117
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400206
Helicase Motif III in SecA is essential for coupling preprotein binding to translocation ATPase
Abstract
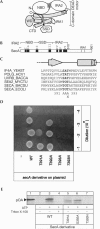
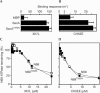
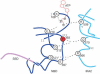
The SecA ATPase is a protein translocase motor and a superfamily 2 (SF2) RNA helicase. The ATPase catalytic core ('DEAD motor') contains the seven conserved SF2 motifs. Here, we demonstrate that Motif III is essential for SecA-mediated protein translocation and viability. SecA Motif III mutants can bind ligands (nucleotide, the SecYEG translocase 'channel', signal and mature preprotein domains), can catalyse basal and SecYEG-stimulated ATP hydrolysis and can be activated for catalysis. However, Motif III mutation specifically blocks the preprotein-stimulated 'translocation ATPase' at a step of the reaction pathway that lies downstream of ligand binding. A functional Motif III is required for optimal ligand-driven conformational changes and kinetic parameters that underlie optimal preprotein-modulated nucleotide cycling at the SecA DEAD motor. We propose that helicase Motif III couples preprotein binding to the SecA translocation ATPase and that catalytic activation of SF2 enzymes through Motif-III-mediated action is essential for both polypeptide and nucleic-acid substrates.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Analysis of the isolated SecA DEAD motor suggests a mechanism for chemical-mechanical coupling.J Mol Biol. 2008 Nov 7;383(2):380-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.08.022. Epub 2008 Aug 22. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18761349
-
Identification of the preprotein binding domain of SecA.J Biol Chem. 2005 Dec 30;280(52):43209-17. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M509990200. Epub 2005 Oct 21. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16243836
-
Nucleotide control of interdomain interactions in the conformational reaction cycle of SecA.Science. 2002 Sep 20;297(5589):2018-26. doi: 10.1126/science.1074424. Science. 2002. PMID: 12242434
-
SecA-mediated targeting and translocation of secretory proteins.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Aug;1843(8):1466-74. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.02.014. Epub 2014 Feb 25. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24583121 Review.
-
Structure and function of SecA, the preprotein translocase nanomotor.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Nov 11;1694(1-3):67-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2004.06.003. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15546658 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of Streptococcus gordonii SecA2 as a paralogue of SecA.J Bacteriol. 2009 Jun;191(11):3482-91. doi: 10.1128/JB.00365-09. Epub 2009 Apr 10. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19363114 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of mycobacterial 3'-to-5' RNA:DNA helicase Lhr bound to a ssDNA tracking strand highlights distinctive features of a novel family of bacterial helicases.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 9;46(1):442-455. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1163. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29165676 Free PMC article.
-
Using a low denaturant model to explore the conformational features of translocation-active SecA.Biochemistry. 2012 Feb 21;51(7):1369-79. doi: 10.1021/bi201793e. Epub 2012 Feb 8. Biochemistry. 2012. PMID: 22304380 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly of the translocase motor onto the preprotein-conducting channel.Mol Microbiol. 2008 Oct;70(2):311-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06402.x. Epub 2008 Aug 22. Mol Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18761620 Free PMC article.
-
DNA-mediated coupling of ATPase, translocase and nuclease activities of a Type ISP restriction-modification enzyme.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Mar 18;48(5):2594-2603. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 31974580 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baud C, Karamanou S, Sianidis G, Vrontou E, Politou AS, Economou A (2002) Allosteric communication between signal peptides and the SecA protein DEAD motor ATPase domain. J Biol Chem 277: 13724–13731 - PubMed
-
- Caruthers JM, McKay DB (2002) Helicase structure and mechanism. Curr Opin Struct Biol 12: 123–133 - PubMed
-
- Cho HS, Ha NC, Kang LW, Chung KM, Back SH, Jang SK (1998) Crystal structure of RNA helicase from genotype 1b hepatitis C virus. A feasible mechanism of unwinding duplex RNA. J Biol Chem 273: 15045–15052 - PubMed
-
- Hartl FU, Lecker S, Schiebel E, Hendrick JP, Wickner W (1990) The binding of SecB to SecA to SecY/E mediates preprotein targeting to the E. coli membrane. Cell 63: 269–279 - PubMed
-
- Hunt JF, Weinkauf S, Henry L, Fak JJ, McNicholas P, Oliver DB, Deisenhofer J (2002) Nucleotide control of interdomain interactions in the conformational reaction cycle of SecA. Science 297: 2018–2026 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

