Innate immunity in the retina: Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling in human retinal pigment epithelial cells
- PMID: 15265658
- PMCID: PMC7119465
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2004.04.018
Innate immunity in the retina: Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling in human retinal pigment epithelial cells
Abstract
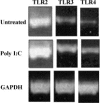
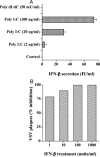
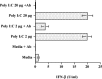
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are crucial components of innate immunity that participate in host defense against microbial pathogens. We evaluated the expression and function of TLRs in human retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells. Real time PCR analysis revealed gene expression for TLRs 1-7, 9, and 10 in RPE cells. TLRs 1 and 3 were the most highly expressed TLRs. Protein expression for TLRs 2, 3, and 4 was observed on RPE cells and this expression was augmented by treatment with poly I:C or interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma). TLR 3 is the receptor for dsRNA, an intermediate of virus replication. Because RPE cells express TLR 3 and are frequently the site of virus replication within the retina, we evaluated TLR 3 signaling. RPE cells treated with poly I:C produced IFN-beta but not IFN-alpha, and this was inhibited by the treatment of RPE cells with anti-TLR 3 antibody. Human recombinant IFN-beta was shown to be biologically active on RPE cells by inhibiting viral replication. Poly I:C treatment of RPE resulted in an increase in the production of IL-6, IL-8, MCP-1, and sICAM-1. The presence of TLRs on RPE cells and the resultant TLR signaling in RPE cells suggest that these molecules may play an important role in innate and adaptive immune responses within the retina.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Innate immunity in the human female reproductive tract: antiviral response of uterine epithelial cells to the TLR3 agonist poly(I:C).J Immunol. 2005 Jan 15;174(2):992-1002. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.2.992. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15634923
-
Distinct functions between toll-like receptors 3 and 9 in retinal pigment epithelial cells.Ophthalmic Res. 2007;39(3):155-63. doi: 10.1159/000103235. Epub 2007 May 25. Ophthalmic Res. 2007. PMID: 17534115
-
Preferential expression and function of Toll-like receptor 3 in human astrocytes.J Neuroimmunol. 2005 Feb;159(1-2):12-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2004.09.009. Epub 2004 Nov 11. J Neuroimmunol. 2005. PMID: 15652398
-
Recognition of pathogen-associated molecular patterns by TLR family.Immunol Lett. 2003 Jan 22;85(2):85-95. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2478(02)00228-6. Immunol Lett. 2003. PMID: 12527213 Review.
-
Evolution and integration of innate immune recognition systems: the Toll-like receptors.J Endotoxin Res. 2005;11(1):51-5. doi: 10.1179/096805105225006687. J Endotoxin Res. 2005. PMID: 15826379 Review.
Cited by
-
The unfolded protein response and diabetic retinopathy.J Diabetes Res. 2014;2014:160140. doi: 10.1155/2014/160140. Epub 2014 Oct 29. J Diabetes Res. 2014. PMID: 25530974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AMD Genetics in India: The Missing Links.Front Aging Neurosci. 2016 May 23;8:115. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2016.00115. eCollection 2016. Front Aging Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27252648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interferon-beta and adhesion molecules (E-selectin and s-intracellular adhesion molecule-1) are detected in sera from patients with retinal vasculitis and are induced in retinal vascular endothelial cells by Toll-like receptor 3 signalling.Clin Exp Immunol. 2007 Jan;147(1):71-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03253.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17177965 Free PMC article.
-
Immune regulation in the retina.Immunol Res. 2010 Jul;47(1-3):153-61. doi: 10.1007/s12026-009-8146-1. Immunol Res. 2010. PMID: 20082152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Short-interfering RNAs induce retinal degeneration via TLR3 and IRF3.Mol Ther. 2012 Jan;20(1):101-8. doi: 10.1038/mt.2011.212. Epub 2011 Oct 11. Mol Ther. 2012. PMID: 21988875 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexopoulou L, Holt A.C, Medzhitov R, Flavell R.A. Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature. 2001;413:732–738. - PubMed
-
- Banchereau J, Paczesny S, Blanco P, Bennett L, Pascual V, Fay J, Palucka A.K. Dendritic cells: controllers of the immune system and a new promise for immunotherapy. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2003;987:180–187. - PubMed
-
- Bodaghi B, Slobbe-van Drunen M.E, Topilko A, Perret E, Vossen R.C, van Dam-Mieras M.C, Zipeto D, Virelizier J.L, LeHoang P, Bruggeman C.A, Michelson S. Entry of human cytomegalovirus into retinal pigment epithelial and endothelial cells by endocytosis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1999;40:2598–2607. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

