Characterization of the murine alpha interferon gene family
- PMID: 15254193
- PMCID: PMC446145
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.15.8219-8228.2004
Characterization of the murine alpha interferon gene family
Abstract
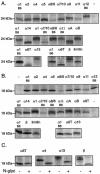
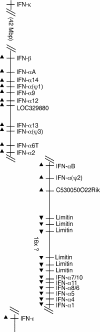
Mouse and human genomes carry more than a dozen genes coding for closely related alpha interferon (IFN-alpha) subtypes. IFN-alpha, as well as IFN-beta, IFN-kappa, IFN-epsilon, and limitin, are thought to bind the same receptor, raising the question of whether different IFN subtypes possess specific functions. As some confusion existed in the identity and characteristics of mouse IFN-alpha subtypes, the availability of data from the mouse genome sequence prompted us to characterize the murine IFN-alpha family. A total of 14 IFN-alpha genes were detected in the mouse genome, in addition to three IFN-alpha pseudogenes. Four IFN-alpha genes (IFN-alpha1, IFN-alpha7/10, IFN-alpha8/6, and IFN-alpha11) exhibited surprising allelic divergence between 129/Sv and C57BL/6 mice. All IFN-alpha subtypes were found to be stable at pH 2 and to exhibit antiviral activity. Interestingly, some IFN subtypes (IFN-alpha4, IFN-alpha11, IFN-alpha12, IFN-beta, and limitin) showed higher biological activity levels than others, whereas IFN-alpha7/10 exhibited lower activity. Most murine IFN-alpha turned out to be N-glycosylated. However, no correlation was found between N-glycosylation and activity. The various IFN-alpha subtypes displayed a good correlation between their antiviral and antiproliferative potencies, suggesting that IFN-alpha subtypes did not diverge primarily to acquire specific biological activities but probably evolved to acquire specific expression patterns. In L929 cells, IFN genes activated in response to poly(I*C) transfection or to viral infection were, however, similar.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Characterization of the porcine alpha interferon multigene family.Gene. 2006 Nov 1;382:28-38. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2006.06.013. Epub 2006 Jun 29. Gene. 2006. PMID: 16901658
-
Antiviral activities of individual murine IFN-alpha subtypes in vivo: intramuscular injection of IFN expression constructs reduces cytomegalovirus replication.J Immunol. 1998 Mar 15;160(6):2932-9. J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9510197
-
Characterization of murine interferon-alpha 12 (MuIFN-alpha12): biological activities and gene expression.Cytokine. 2007 Feb;37(2):138-49. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2007.03.002. Epub 2007 Apr 23. Cytokine. 2007. PMID: 17451966
-
Biologic activities of natural and synthetic type I interferons.Semin Oncol. 1997 Jun;24(3 Suppl 9):S9-63-S9-69. Semin Oncol. 1997. PMID: 9208874 Review.
-
Interferon-zeta/limitin: novel type I interferon that displays a narrow range of biological activity.Int J Hematol. 2004 Nov;80(4):325-31. doi: 10.1532/ijh97.04087. Int J Hematol. 2004. PMID: 15615256 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Dendritic Cells During Infections Caused by Highly Prevalent Viruses.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 16;11:1513. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01513. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32765522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type I Interferon-Mediated Regulation of Antiviral Capabilities of Neutrophils.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 29;22(9):4726. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094726. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33946935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interferon Alpha, but Not Interferon Beta, Acts Early To Control Chronic Chikungunya Virus Pathogenesis.J Virol. 2022 Jan 12;96(1):e0114321. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01143-21. Epub 2021 Oct 20. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 34668781 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of a Virus-Like Nanoparticle As Treatment for a Chronic Viral Infection Is Hindered by IRAK1 Regulation and Antibody Interference.Front Immunol. 2018 Jan 4;8:1885. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01885. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29354118 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutically targeting type I interferon directly to XCR1+ dendritic cells reveals the role of cDC1s in anti-drug antibodies.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 24;14:1272055. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1272055. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37942313 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adolf, G. R., I. Maurer-Fogy, I. Kalsner, and K. Cantell. 1990. Purification and characterization of natural human interferon omega 1. Two alternative cleavage sites for the signal peptidase. J. Biol. Chem. 265:9290-9295. - PubMed
-
- Aguet, M., M. Grobke, and P. Dreiding. 1984. Various human interferon alpha subclasses cross-react with common receptors: their binding affinities correlate with their specific biological activities. Virology 132:211-216. - PubMed
-
- Barnes, B. J., A. E. Field, and P. M. Pitha-Rowe. 2003. Virus-induced heterodimer formation between IRF-5 and IRF-7 modulates assembly of the IFNA enhanceosome in vivo and transcriptional activity of IFNA genes. J. Biol. Chem. 278:16630-16641. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

