Absence of BLM leads to accumulation of chromosomal DNA breaks during both unperturbed and disrupted S phases
- PMID: 15197177
- PMCID: PMC2172405
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200402095
Absence of BLM leads to accumulation of chromosomal DNA breaks during both unperturbed and disrupted S phases
Abstract
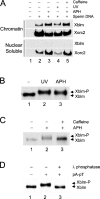
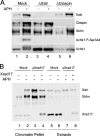
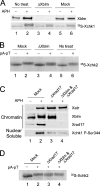
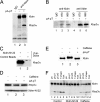
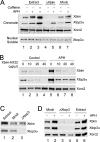
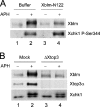
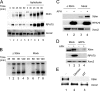
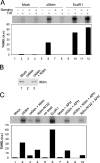
Bloom's syndrome (BS), a disorder associated with genomic instability and cancer predisposition, results from defects in the Bloom's helicase (BLM) protein. In BS cells, chromosomal abnormalities such as sister chromatid exchanges occur at highly elevated rates. Using Xenopus egg extracts, we have studied Xenopus BLM (Xblm) during both unperturbed and disrupted DNA replication cycles. Xblm binds to replicating chromatin and becomes highly phosphorylated in the presence of DNA replication blocks. This phosphorylation depends on Xenopus ATR (Xatr) and Xenopus Rad17 (Xrad17), but not Claspin. Xblm and Xenopus topoisomerase IIIalpha (Xtop3alpha) interact in a regulated manner and associate with replicating chromatin interdependently. Immunodepletion of Xblm from egg extracts results in accumulation of chromosomal DNA breaks during both normal and perturbed DNA replication cycles. Disruption of the interaction between Xblm and Xtop3alpha has similar effects. The occurrence of DNA damage in the absence of Xblm, even without any exogenous insult to the DNA, may help to explain the genesis of chromosomal defects in BS cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bloom helicase is involved in DNA surveillance in early S phase in vertebrate cells.Oncogene. 2001 Mar 8;20(10):1143-51. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204195. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11313858
-
The function of Xenopus Bloom's syndrome protein homolog (xBLM) in DNA replication.Genes Dev. 2000 Oct 15;14(20):2570-5. doi: 10.1101/gad.822400. Genes Dev. 2000. PMID: 11040210 Free PMC article.
-
Werner and Bloom helicases are involved in DNA repair in a complementary fashion.Oncogene. 2002 Jan 31;21(6):954-63. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205143. Oncogene. 2002. PMID: 11840341
-
Role of the BLM helicase in replication fork management.DNA Repair (Amst). 2007 Jul 1;6(7):936-44. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2007.02.007. Epub 2007 Mar 23. DNA Repair (Amst). 2007. PMID: 17363339 Review.
-
Bloom syndrome, genomic instability and cancer: the SOS-like hypothesis.Cancer Lett. 2006 May 8;236(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2005.04.023. Epub 2005 Jun 13. Cancer Lett. 2006. PMID: 15950375 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA structure-induced recruitment and activation of the Fanconi anemia pathway protein FANCD2.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Jun;27(12):4283-92. doi: 10.1128/MCB.02196-06. Epub 2007 Apr 9. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17420278 Free PMC article.
-
Hpz1 modulates the G1-S transition in fission yeast.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44539. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044539. Epub 2012 Sep 6. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22970243 Free PMC article.
-
ATM and ATR promote Mre11 dependent restart of collapsed replication forks and prevent accumulation of DNA breaks.EMBO J. 2006 Apr 19;25(8):1764-74. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601045. Epub 2006 Apr 6. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16601701 Free PMC article.
-
RecQ helicases: guardian angels of the DNA replication fork.Chromosoma. 2008 Jun;117(3):219-33. doi: 10.1007/s00412-007-0142-4. Epub 2008 Jan 11. Chromosoma. 2008. PMID: 18188578 Review.
-
Phosphorylation of BLM, dissociation from topoisomerase IIIalpha, and colocalization with gamma-H2AX after topoisomerase I-induced replication damage.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Oct;25(20):8925-37. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.20.8925-8937.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16199871 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ababou, M., S. Dutertre, Y. Lecluse, R. Onclercq, B. Chatton, and M. Amor-Gueret. 2000. ATM-dependent phosphorylation and accumulation of endogenous BLM protein in response to ionizing radiation. Oncogene. 19:5955–5963. - PubMed
-
- Abraham, R.T. 2001. Cell cycle checkpoint signaling through the ATM and ATR kinases. Genes Dev. 15:2177–2196. - PubMed
-
- Adams, M.D., M. McVey, and J.J. Sekelsky. 2003. Drosophila BLM in double-strand break repair by synthesis-dependent strand annealing. Science. 299:265–267. - PubMed
-
- Bartek, J., J. Falck, and J. Lukas. 2001. CHK2 kinase–a busy messenger. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2:877–886. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

