Cdc14p/FEAR pathway controls segregation of nucleolus in S. cerevisiae by facilitating condensin targeting to rDNA chromatin in anaphase
- PMID: 15190202
- PMCID: PMC2673102
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.3.7.1003
Cdc14p/FEAR pathway controls segregation of nucleolus in S. cerevisiae by facilitating condensin targeting to rDNA chromatin in anaphase
Abstract
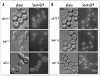
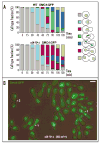
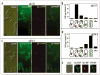
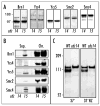
The condensin complex is the chief molecular machine of mitotic chromosome condensation. Nucleolar concentration of condensin in mitosis was previously shown to correlate with proficiency of rDNA condensation and segregation. To uncover the mechanisms facilitating this targeting we conducted a screen for mutants that impair mitotic condensin congression to the nucleolus. Mutants in the cdc14, esp1 and cdc5 genes, which encode FEAR-network components, showed the most prominent defects in mitotic condensin localization. We established that Cdc14p activity released by the FEAR pathway was required for proper condensin-to-rDNA targeting in anaphase. The MEN pathway was dispensable for condensin-to-rDNA targeting, however MEN-mediated release of Cdc14p later in anaphase allowed for proper, albeit delayed, condensin targeting to rDNA and successful segregation of nucleolus in the slk19 FEAR mutant. Although condensin was physically dislodged from rDNA in the cdc14 mutant, it was properly assembled, phosphorylated and chromatin-bound, suggesting that condensin was mis-targeted but active. This study identifies a novel pathway promoting condensin targeting to a specific chromosomal address, the rDNA locus.
Figures
Comment in
-
Cdc14p regulates condensin binding to rDNA.Cell Cycle. 2009 Apr 15;8(8):1114. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.8.8469. Epub 2009 Apr 15. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19305166 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Cdc14 and condensin control the dissolution of cohesin-independent chromosome linkages at repeated DNA.Cell. 2004 May 14;117(4):455-69. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00413-1. Cell. 2004. PMID: 15137939
-
Cdc14 phosphatase induces rDNA condensation and resolves cohesin-independent cohesion during budding yeast anaphase.Cell. 2004 May 14;117(4):471-82. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00415-5. Cell. 2004. PMID: 15137940
-
Putting the brake on FEAR: Tof2 promotes the biphasic release of Cdc14 phosphatase during mitotic exit.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Jan;20(1):245-55. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-08-0879. Epub 2008 Oct 15. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 18923139 Free PMC article.
-
A case of selfish nucleolar segregation.Cell Cycle. 2005 Jan;4(1):113-7. doi: 10.4161/cc.4.1.1488. Epub 2005 Jan 21. Cell Cycle. 2005. PMID: 15655374 Review.
-
Cdc14 and the temporal coordination between mitotic exit and chromosome segregation.Cell Cycle. 2005 Jan;4(1):109-12. doi: 10.4161/cc.4.1.1356. Epub 2005 Jan 10. Cell Cycle. 2005. PMID: 15611663 Review.
Cited by
-
Nucleolar and Ribosomal DNA Structure under Stress: Yeast Lessons for Aging and Cancer.Cells. 2019 Jul 26;8(8):779. doi: 10.3390/cells8080779. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31357498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ribosomal DNA metaphase loop of Saccharomyces cerevisiae gets condensed upon heat stress in a Cdc14-independent TORC1-dependent manner.Cell Cycle. 2018;17(2):200-215. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2017.1407890. Epub 2018 Jan 21. Cell Cycle. 2018. PMID: 29166821 Free PMC article.
-
Histone variant H2A.Z and linker histone H1 influence chromosome condensation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2024 Apr 3;226(4):iyae022. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyae022. Genetics. 2024. PMID: 38366024
-
Diverse mitotic and interphase functions of condensins in Drosophila.Genetics. 2006 Feb;172(2):991-1008. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.050567. Epub 2005 Nov 4. Genetics. 2006. PMID: 16272408 Free PMC article.
-
Resolution of human ribosomal DNA occurs in anaphase, dependent on tankyrase 1, condensin II, and topoisomerase IIα.Genes Dev. 2019 Mar 1;33(5-6):276-281. doi: 10.1101/gad.321836.118. Epub 2019 Feb 25. Genes Dev. 2019. PMID: 30804226 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Swedlow JR, Hirano T. The making of the mitotic chromosome: modern insights into classical questions. Mol Cell. 2003;11:557–69. - PubMed
-
- Hudson DF, Vagnarelli P, Gassmann R, Earnshaw WC. Condensin is required for nonhistone protein assembly and structural integrity of vertebrate mitotic chromosomes. Dev Cell. 2003;5:323–36. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
