Cellular stresses induce the nuclear accumulation of importin alpha and cause a conventional nuclear import block
- PMID: 15184398
- PMCID: PMC2172376
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200312008
Cellular stresses induce the nuclear accumulation of importin alpha and cause a conventional nuclear import block
Abstract
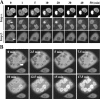
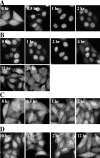
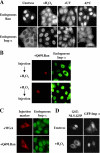
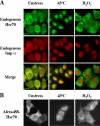
We report here that importin alpha accumulates reversibly in the nucleus in response to cellular stresses including UV irradiation, oxidative stress, and heat shock. The nuclear accumulation of importin alpha appears to be triggered by a collapse in the Ran gradient, resulting in the suppression of the nuclear export of importin alpha. In addition, nuclear retention and the importin beta/Ran-independent import of importin alpha also facilitate its rapid nuclear accumulation. The findings herein show that the classical nuclear import pathway is down-regulated via the removal of importin alpha from the cytoplasm in response to stress. Moreover, whereas the nuclear accumulation of heat shock cognate 70 is more sensitive to heat shock than the other stresses, importin alpha is able to accumulate in the nucleus at all the stress conditions tested. These findings suggest that the stress-induced nuclear accumulation of importin alpha can be involved in a common physiological response to various stress conditions.
Copyright the Rockefeller University Press
Figures

Similar articles
-
Heat-shock induced nuclear retention and recycling inhibition of importin alpha.Genes Cells. 2004 May;9(5):429-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1356-9597.2004.00734.x. Genes Cells. 2004. PMID: 15147272
-
Multiple mechanisms promote the inhibition of classical nuclear import upon exposure to severe oxidative stress.Cell Death Differ. 2004 Aug;11(8):862-74. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401432. Cell Death Differ. 2004. PMID: 15088071
-
[Importin alpha and stress response].Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2006 Nov;51(14 Suppl):2187-8. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2006. PMID: 17471934 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Mechanism of the stress-induced collapse of the Ran distribution.Exp Cell Res. 2006 Feb 15;312(4):512-20. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.11.017. Exp Cell Res. 2006. PMID: 16368437
-
Importin alpha: a multipurpose nuclear-transport receptor.Trends Cell Biol. 2004 Sep;14(9):505-14. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2004.07.016. Trends Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15350979 Review.
Cited by
-
Thermal Stress and Nuclear Transport.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1461:61-78. doi: 10.1007/978-981-97-4584-5_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39289274 Review.
-
Two isoforms of Npap60 (Nup50) differentially regulate nuclear protein import.Mol Biol Cell. 2010 Feb 15;21(4):630-8. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-05-0374. Epub 2009 Dec 16. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20016008 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered allostery in light-regulated LOV-Turbo enables precise spatiotemporal control of proximity labeling in living cells.Nat Methods. 2023 Jun;20(6):908-917. doi: 10.1038/s41592-023-01880-5. Epub 2023 May 15. Nat Methods. 2023. PMID: 37188954 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Ivermectin and Atorvastatin on Nuclear Localization of Importin Alpha and Drug Target Expression Profiling in Host Cells from Nasopharyngeal Swabs of SARS-CoV-2- Positive Patients.Viruses. 2021 Oct 15;13(10):2084. doi: 10.3390/v13102084. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34696514 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear transport, oxidative stress, and neurodegeneration.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2011 Mar;4(3):215-29. Epub 2011 Feb 28. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21487518 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adam, S.A., and L. Gerace. 1991. Cytosolic proteins that specifically bind nuclear location signals are receptors for nuclear import. Cell. 66:837–847. - PubMed
-
- Carson, D.A., S. Seto, D.B. Wasson, and C.J. Carrera. 1986. DNA strand breaks, NAD metabolism, and programmed cell death. Exp. Cell Res. 164:273–281. - PubMed
-
- Chu, A., N. Matusiewicz, and U. Stochaj. 2001. Heat-induced nuclear accumulation of hsc70s is regulated by phosphorylation and inhibited in confluent cells. FASEB J. 15:1478–1480. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

