53BP1 is required for class switch recombination
- PMID: 15159415
- PMCID: PMC2172356
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200403021
53BP1 is required for class switch recombination
Abstract
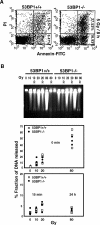
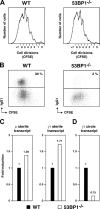
53BP1 participates early in the DNA damage response and is involved in cell cycle checkpoint control. Moreover, the phenotype of mice and cells deficient in 53BP1 suggests a defect in DNA repair (Ward et al., 2003b). Therefore, we asked whether or not 53BP1 would be required for the efficient repair of DNA double strand breaks. Our data indicate that homologous recombination by gene conversion does not depend on 53BP1. Moreover, 53BP1-deficient mice support normal V(D)J recombination, indicating that 53BP1 is not required for "classic" nonhomologous end joining. However, class switch recombination is severely impaired in the absence of 53BP1, suggesting that 53BP1 facilitates DNA end joining in a way that is not required or redundant for the efficient closing of RAG-induced strand breaks. These findings are similar to those observed in mice or cells deficient in the tumor suppressors ATM and H2AX, further suggesting that the functions of ATM, H2AX, and 53BP1 are closely linked.
Figures


Similar articles
-
p53 binding protein 1 (53BP1) is an early participant in the cellular response to DNA double-strand breaks.J Cell Biol. 2000 Dec 25;151(7):1381-90. doi: 10.1083/jcb.151.7.1381. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11134068 Free PMC article.
-
53BP1 facilitates long-range DNA end-joining during V(D)J recombination.Nature. 2008 Nov 27;456(7221):529-33. doi: 10.1038/nature07476. Epub 2008 Oct 19. Nature. 2008. PMID: 18931658 Free PMC article.
-
Overlapping functions between XLF repair protein and 53BP1 DNA damage response factor in end joining and lymphocyte development.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Mar 6;109(10):3903-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1120160109. Epub 2012 Feb 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22355127 Free PMC article.
-
53BP1-mediated DNA double strand break repair: insert bad pun here.DNA Repair (Amst). 2011 Oct 10;10(10):1071-6. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2011.07.012. Epub 2011 Aug 24. DNA Repair (Amst). 2011. PMID: 21868291 Review.
-
Recombination at double-strand breaks and DNA ends: conserved mechanisms from phage to humans.Mol Cell. 2001 Dec;8(6):1163-74. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(01)00419-1. Mol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11779493 Review.
Cited by
-
The 53BP1 homolog in C. elegans influences DNA repair and promotes apoptosis in response to ionizing radiation.PLoS One. 2013 May 8;8(5):e64028. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064028. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23667696 Free PMC article.
-
53BP1 regulates DNA resection and the choice between classical and alternative end joining during class switch recombination.J Exp Med. 2010 Apr 12;207(4):855-65. doi: 10.1084/jem.20100244. Epub 2010 Apr 5. J Exp Med. 2010. PMID: 20368578 Free PMC article.
-
Moving Mountains-The BRCA1 Promotion of DNA Resection.Front Mol Biosci. 2019 Sep 3;6:79. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2019.00079. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Biosci. 2019. PMID: 31552267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Parp3 promotes long-range end joining in murine cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Oct 2;115(40):10076-10081. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1801591115. Epub 2018 Sep 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30213852 Free PMC article.
-
AID produces DNA double-strand breaks in non-Ig genes and mature B cell lymphomas with reciprocal chromosome translocations.Mol Cell. 2009 Nov 25;36(4):631-41. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.11.007. Mol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19941823 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham, R.T. 2002. Checkpoint signalling: focusing on 53BP1. Nat. Cell Biol. 4:E277–E279. - PubMed
-
- Bassing, C.H., W. Swat, and F.W. Alt. 2002. The mechanism and regulation of chromosomal V(D)J recombination. Cell. 109:S45–S55. - PubMed
-
- Burma, S., B.P. Chen, M. Murphy, A. Kurimasa, and D.J. Chen. 2001. ATM phosphorylates histone H2AX in response to DNA double-strand breaks. J. Biol. Chem. 276:42462–42467. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

