Block of AMPA receptor desensitization by a point mutation outside the ligand-binding domain
- PMID: 15152033
- PMCID: PMC6729461
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0757-04.2004
Block of AMPA receptor desensitization by a point mutation outside the ligand-binding domain
Abstract
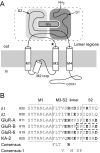
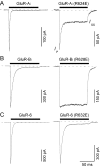
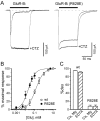
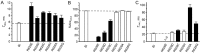
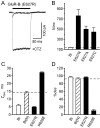
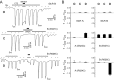
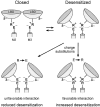
Desensitization of ionotropic glutamate receptors (GluRs), specifically the AMPA receptor subtype, shapes the postsynaptic response at certain synapses in the brain. All known mechanisms that alter desensitization, either pharmacological or mutational, are associated with the ligand-binding domain. Here we report that substitution of a conserved positively charged arginine (R) with a negatively charged glutamate in the linker between the pore-forming M3 segment and the S2 lobe, a region outside the ligand-binding domain, blocks desensitization in homomeric AMPA receptors composed of GluR-B(i) subunits. A charge-reversing substitution of a glutamate adjacent to this conserved R enhanced desensitization, consistent with these effects attributable to electrostatics. Homologous substitutions of the conserved R in GluR-B(o), GluR-A(i) and the kainate receptor GluR-6 subunits produced comparable but less visible effects on desensitization. Subunit specificity was also apparent for accessibility of substituted cysteines in the M3-S2 linker, suggesting that this part of the channel is not structurally identical in different GluRs. Additionally, reactivity with a sulfhydryl-specific reagent was state dependent, suggesting that the conformations of the nonconducting closed and desensitized states are different at the level of the M3-S2 linker. Our results therefore represent the first identification of elements outside the ligand-binding domain affecting desensitization in non-NMDA receptor channels and suggest that electrostatic interactions involving charged residues in the M3-S2 linker influence channel gating in a subunit- and subtype-specific manner.
Figures
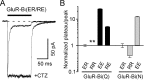
Similar articles
-
The outer pore of the glutamate receptor channel has 2-fold rotational symmetry.Neuron. 2004 Feb 5;41(3):367-78. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(04)00008-x. Neuron. 2004. PMID: 14766176
-
Identification of amino acid residues in GluR1 responsible for ligand binding and desensitization.J Neurosci. 2001 May 1;21(9):3052-62. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-09-03052.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11312290 Free PMC article.
-
A domain linking the AMPA receptor agonist binding site to the ion pore controls gating and causes lurcher properties when mutated.J Neurosci. 2007 Nov 7;27(45):12230-41. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3175-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17989289 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic manipulation of key determinants of ion flow in glutamate receptor channels in the mouse.Brain Res. 2001 Jul 13;907(1-2):233-43. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(01)02445-3. Brain Res. 2001. PMID: 11430906 Review.
-
Structure and mechanism of AMPA receptor - auxiliary protein complexes.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2019 Feb;54:104-111. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2019.01.011. Epub 2019 Feb 27. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2019. PMID: 30825796 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lupus autoantibodies act as positive allosteric modulators at GluN2A-containing NMDA receptors and impair spatial memory.Nat Commun. 2020 Mar 16;11(1):1403. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15224-w. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32179753 Free PMC article.
-
Neto proteins differentially modulate the gating properties of Drosophila NMJ glutamate receptors.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 26:2024.04.22.590603. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.22.590603. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Physiol. 2024 Dec;602(24):7043-7064. doi: 10.1113/JP287331. PMID: 38903091 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Dancing partners at the synapse: auxiliary subunits that shape kainate receptor function.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012 Oct;13(10):675-86. doi: 10.1038/nrn3335. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22948074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interface interactions modulating desensitization of the kainate-selective ionotropic glutamate receptor subunit GluR6.J Neurosci. 2006 Sep 27;26(39):10033-42. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2750-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17005866 Free PMC article.
-
A charge-inverting mutation in the "linker" region of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptors alters agonist binding and gating kinetics independently of allosteric modulators.J Biol Chem. 2014 Apr 11;289(15):10702-10714. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.526921. Epub 2014 Feb 18. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24550387 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armstrong N, Gouaux E (2000) Mechanisms for activation and antagonism of an AMPA-sensitive glutamate receptor: crystal structures of the GluR2 ligand binding core. Neuron 28: 165–181. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong N, Sun Y, Chen GQ, Gouaux E (1998) Structure of a glutamate-receptor ligand-binding core in complex with kainate. Nature 395: 913–917. - PubMed
-
- Beck C, Wollmuth LP, Seeburg PH, Sakmann B, Kuner T (1999) NMDAR channel segments forming the extracellular vestibule inferred from the accessibility of substituted cysteines. Neuron 22: 559–570. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
