Interactions between Sox9 and beta-catenin control chondrocyte differentiation
- PMID: 15132997
- PMCID: PMC406296
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1171104
Interactions between Sox9 and beta-catenin control chondrocyte differentiation
Abstract
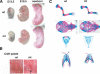
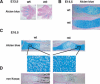
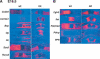
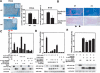
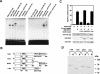
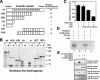
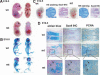
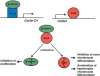
Chondrogenesis is a multistep process that is essential for endochondral bone formation. Previous results have indicated a role for beta-catenin and Wnt signaling in this pathway. Here we show the existence of physical and functional interactions between beta-catenin and Sox9, a transcription factor that is required in successive steps of chondrogenesis. In vivo, either overexpression of Sox9 or inactivation of beta-catenin in chondrocytes of mouse embryos produces a similar phenotype of dwarfism with decreased chondrocyte proliferation, delayed hypertrophic chondrocyte differentiation, and endochondral bone formation. Furthermore, either inactivation of Sox9 or stabilization of beta-catenin in chondrocytes also produces a similar phenotype of severe chondrodysplasia. Sox9 markedly inhibits activation of beta-catenin-dependent promoters and stimulates degradation of beta-catenin by the ubiquitination/proteasome pathway. Likewise, Sox9 inhibits beta-catenin-mediated secondary axis induction in Xenopus embryos. Beta-catenin physically interacts through its Armadillo repeats with the C-terminal transactivation domain of Sox9. We hypothesize that the inhibitory activity of Sox9 is caused by its ability to compete with Tcf/Lef for binding to beta-catenin, followed by degradation of beta-catenin. Our results strongly suggest that chondrogenesis is controlled by interactions between Sox9 and the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway.
Figures

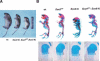


Similar articles
-
Canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling prevents osteoblasts from differentiating into chondrocytes.Dev Cell. 2005 May;8(5):727-38. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2005.02.013. Dev Cell. 2005. PMID: 15866163
-
Secreted frizzled related protein 1 regulates Wnt signaling for BMP2 induced chondrocyte differentiation.J Cell Physiol. 2006 Jul;208(1):87-96. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20637. J Cell Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16575902
-
Wnt induction of chondrocyte hypertrophy through the Runx2 transcription factor.J Cell Physiol. 2006 Jul;208(1):77-86. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20656. J Cell Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16575901
-
[Molecular mechanisms of cartilage formation and chondrocyte maturation].Clin Calcium. 2004 Jul;14(7):15-21. Clin Calcium. 2004. PMID: 15577071 Review. Japanese.
-
Transcriptional mechanisms of chondrocyte differentiation.Matrix Biol. 2000 Sep;19(5):389-94. doi: 10.1016/s0945-053x(00)00094-9. Matrix Biol. 2000. PMID: 10980415 Review.
Cited by
-
SOXC Transcription Factors Induce Cartilage Growth Plate Formation in Mouse Embryos by Promoting Noncanonical WNT Signaling.J Bone Miner Res. 2015 Sep;30(9):1560-71. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2504. Epub 2015 May 21. J Bone Miner Res. 2015. PMID: 25761772 Free PMC article.
-
SOX9 directly regulates IGFBP-4 in the intestinal epithelium.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2013 Jul 1;305(1):G74-83. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00086.2013. Epub 2013 May 9. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23660500 Free PMC article.
-
Acute stress disrupts intestinal homeostasis via GDNF-RET.Cell Prolif. 2020 Oct;53(10):e12889. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12889. Epub 2020 Aug 17. Cell Prolif. 2020. PMID: 32808420 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 2 (ROR2) and Indian hedgehog regulate digit outgrowth mediated by the phalanx-forming region.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Aug 10;107(32):14211-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1009314107. Epub 2010 Jul 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20660756 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt gene expression in the post-natal growth plate: regulation with chondrocyte differentiation.Bone. 2007 May;40(5):1361-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2007.01.005. Epub 2007 Jan 20. Bone. 2007. PMID: 17337262 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albrecht U., Eichele, G., Helms, J.A., and Lu, H.C. 1997. Visualization of gene expression patterns by in situ hybridization. In Molecular and cellular methods in developmental toxicology (ed. G.P. Daston), pp. 23-48. CRC Press, Boca Raton.
-
- Behrens J., von Kries, J.P., Kuhl, M., Bruhn, L., Wedlich, D., Grosschedl, R., and Birchmeier, W. 1996. Functional interaction of β-catenin with the transcription factor LEF-1. Nature 382: 638-642. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
