Mutated MESP2 causes spondylocostal dysostosis in humans
- PMID: 15122512
- PMCID: PMC1182088
- DOI: 10.1086/421053
Mutated MESP2 causes spondylocostal dysostosis in humans
Abstract
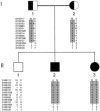
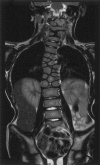
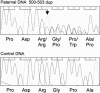
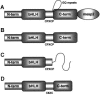
Spondylocostal dysostosis (SCD) is a term given to a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by abnormal vertebral segmentation (AVS). We have previously identified mutations in the Delta-like 3 (DLL3) gene as a major cause of autosomal recessive spondylocostal dysostosis. DLL3 encodes a ligand for the Notch receptor and, when mutated, defective somitogenesis occurs resulting in a consistent and distinctive pattern of AVS affecting the entire spine. From our study cohort of cases of AVS, we have identified individuals and families with abnormal segmentation of the entire spine but no mutations in DLL3, and, in some of these, linkage to the DLL3 locus at 19q13.1 has been excluded. Within this group, the radiological phenotype differs mildly from that of DLL3 mutation-positive SCD and is variable, suggesting further heterogeneity. Using a genomewide scanning strategy in one consanguineous family with two affected children, we demonstrated linkage to 15q21.3-15q26.1 and furthermore identified a 4-bp duplication mutation in the human MESP2 gene that codes for a basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor. No MESP2 mutations were found in a further 7 patients with related radiological phenotypes in whom abnormal segmentation affected all vertebrae, nor in a further 12 patients with diverse phenotypes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel mutations in DLL3, a somitogenesis gene encoding a ligand for the Notch signalling pathway, cause a consistent pattern of abnormal vertebral segmentation in spondylocostal dysostosis.J Med Genet. 2003 May;40(5):333-9. doi: 10.1136/jmg.40.5.333. J Med Genet. 2003. PMID: 12746394 Free PMC article.
-
Autosomal dominant spondylocostal dysostosis in three generations of a Macedonian family: Negative mutation analysis of DLL3, MESP2, HES7, and LFNG.Am J Med Genet A. 2010 Jun;152A(6):1378-82. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.33471. Am J Med Genet A. 2010. PMID: 20503311
-
Molecular genetic prenatal diagnosis for a case of autosomal recessive spondylocostal dysostosis.Prenat Diagn. 2003 Jul;23(7):575-9. doi: 10.1002/pd.643. Prenat Diagn. 2003. PMID: 12868087
-
Defective somitogenesis and abnormal vertebral segmentation in man.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;638:164-89. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-09606-3_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 21038776 Review.
-
Abnormal vertebral segmentation and the notch signaling pathway in man.Dev Dyn. 2007 Jun;236(6):1456-74. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21182. Dev Dyn. 2007. PMID: 17497699 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular landscape of congenital vertebral malformations: recent discoveries and future directions.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2024 Jan 30;19(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s13023-024-03040-0. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2024. PMID: 38291488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tbx16 regulates hox gene activation in mesodermal progenitor cells.Nat Chem Biol. 2016 Sep;12(9):694-701. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2124. Epub 2016 Jul 4. Nat Chem Biol. 2016. PMID: 27376691 Free PMC article.
-
Notch signaling in skeletal health and disease.Eur J Endocrinol. 2013 May 8;168(6):R95-103. doi: 10.1530/EJE-13-0115. Print 2013 Jun. Eur J Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23554451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Notch signaling pathway: architecture, disease, and therapeutics.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Mar 24;7(1):95. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-00934-y. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 35332121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two novel missense mutations in HAIRY-AND-ENHANCER-OF-SPLIT-7 in a family with spondylocostal dysostosis.Eur J Hum Genet. 2010 Jun;18(6):674-9. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2009.241. Epub 2010 Jan 20. Eur J Hum Genet. 2010. PMID: 20087400 Free PMC article.
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Human Genome Working Draft, The, http://genome.ucsc.edu/
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/
References
-
- Dunwoodie SL, Clements M, Sparrow DB, Sa X, Conlon RA, Beddington RS (2002) Axial skeletal defects caused by mutation in the spondylocostal dysplasia/pudgy gene Dll3 are associated with disruption of the segmentation clock within the presomitic mesoderm. Development 129:1795–1806 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

