Differential cell killing by lymphomagenic murine leukemia viruses occurs independently of p53 activation and mitochondrial damage
- PMID: 15113890
- PMCID: PMC400358
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.78.10.5088-5096.2004
Differential cell killing by lymphomagenic murine leukemia viruses occurs independently of p53 activation and mitochondrial damage
Abstract
Upon inoculation into AKR mice, mink cell focus-forming murine leukemia virus (MCF MLV) accelerates thymic lymphoma formation. During the preleukemic phase of disease, we observed the induction of apoptosis in thymic lymphocytes. A similar induction of apoptosis was observed for cultured mink epithelial cells after MCF13 MLV infection. In this study, the relevance of viral pathogenicity to cell killing was determined by testing the susceptibility of various cell types from different species to lymphomagenic MLVs. We observed that the cytopathic effect of lymphomagenic MLVs was restricted to mink cells. Southern blot analysis of MLV-infected cells revealed an accumulation of the linear form of unintegrated viral DNA, particularly in mink cells after MCF13 MLV infection. Thus, a strong correlation was observed between viral superinfection, which results in the accumulation of high levels of unintegrated viral DNA, and cell killing. Immunoblot analysis for MCF13 MLV-infected mink epithelial cells did not show a significant change in total p53 levels or its phosphorylated form at Ser-15 compared with that in mock-treated cells. Moreover, a time course analysis for mink epithelial cells infected with MCF13 MLV did not reveal mitochondrial depolarization or a significant change in Bax levels. These results demonstrate that MCF13 MLV induces apoptosis preferentially in cells in which superinfection occurs, and the mechanism involved is independent of p53 activation and mitochondrial damage.
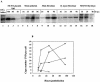
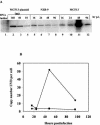
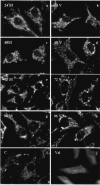
Figures



Similar articles
-
Up-regulation of a cellular protein at the translational level by a retrovirus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Apr 8;105(14):5543-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0710526105. Epub 2008 Mar 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18378896 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of murine leukemia virus envelope protein is sufficient for the induction of apoptosis.J Virol. 2008 Mar;82(5):2586-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02291-07. Epub 2007 Dec 12. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18077710 Free PMC article.
-
Mink epithelial cell killing by pathogenic murine leukemia viruses involves endoplasmic reticulum stress.J Virol. 2004 Nov;78(21):12071-4. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.21.12071-12074.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15479849 Free PMC article.
-
Mink cell focus-forming murine leukemia virus killing of mink cells involves apoptosis and superinfection.J Virol. 2001 Jul;75(13):6007-15. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.13.6007-6015.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11390602 Free PMC article.
-
Mink cell focus-forming murine leukemia virus infection induces apoptosis of thymic lymphocytes.J Virol. 2000 Sep;74(17):8119-26. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.17.8119-8126.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10933722 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Up-regulation of a cellular protein at the translational level by a retrovirus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Apr 8;105(14):5543-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0710526105. Epub 2008 Mar 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18378896 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of murine leukemia virus envelope protein is sufficient for the induction of apoptosis.J Virol. 2008 Mar;82(5):2586-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02291-07. Epub 2007 Dec 12. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18077710 Free PMC article.
-
Mink epithelial cell killing by pathogenic murine leukemia viruses involves endoplasmic reticulum stress.J Virol. 2004 Nov;78(21):12071-4. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.21.12071-12074.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15479849 Free PMC article.
-
The prostate cancer-associated human retrovirus XMRV lacks direct transforming activity but can induce low rates of transformation in cultured cells.J Virol. 2010 Feb;84(4):1874-80. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01941-09. Epub 2009 Dec 9. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20007266 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashkenazi, A., and V. M. Dixit. 1998. Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science 281:1305-1308. - PubMed
-
- Bernardi, P., L. Scorrano, R. Colonna, V. Petronilli, and F. Di Lisa. 1999. Mitochondria and cell death. Mechanistic aspects and methodological issues. Eur. J. Biochem. 264:687-701. - PubMed
-
- Castedo, M., T. Roumier, J. Blanco, K. F. Ferri, J. Barretina, L. A. Tintignac, K. Andreau, J. L. Perfettini, A. Amendola, R. Nardacci, P. Leduc, D. E. Ingber, S. Druillennec, B. Roques, S. A. Leibovitch, M. Vilella-Bach, J. Chen, J. A. Este, N. Modjtahedi, M. Piacentini, and G. Kroemer. 2002. Sequential involvement of Cdk1, mTOR and p53 in apoptosis induced by the HIV-1 envelope. EMBO J. 21:4070-4080. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

