Parkin counteracts symptoms in a Drosophila model of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 15090075
- PMCID: PMC419346
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-5-14
Parkin counteracts symptoms in a Drosophila model of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
Background: Parkinson's disease, a prevalent neurodegenerative disease, is characterized by the reduction of dopaminergic neurons resulting in the loss of motor control, resting tremor, the formation of neuronal inclusions and ultimately premature death. Two inherited forms of PD have been linked to mutations in the alpha-synuclein and parkin genes. The parkin protein functions as an ubiquitin ligase targeting specific proteins for degradation. Expression of human alpha-synuclein in Drosophila neurons recapitulates the loss of motor control, the development of neuronal inclusions, degeneration of dopaminergic neurons and the ommatidial array to provide an excellent genetic model of PD.
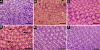
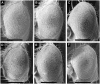
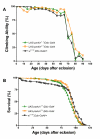
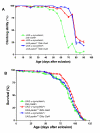
Results: To investigate the role of parkin, we have generated transgenic Drosophila that conditionally express parkin under the control of the yeast UAS enhancer. While expression of parkin has little consequence, co-expression of parkin with alpha-synuclein in the dopaminergic neurons suppresses the alpha-synuclein-induced premature loss of climbing ability. In addition directed expression of parkin in the eye counteracts the alpha-synuclein-induced degeneration of the ommatidial array. These results show that parkin suppresses the PD-like symptoms observed in the alpha-synuclein-dependent Drosophila model of PD.
Conclusion: The highly conserved parkin E3 ubiquitin ligase can suppress the damaging effects of human alpha-synuclein. These results are consistent with a role for parkin in targeting alpha-synuclein to the proteasome. If this relationship is conserved in humans, this suggests that up-regulation of parkin should suppress alpha-synucleinopathic PD. The development of therapies that regulate parkin activity may be crucial in the treatment of PD.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mutant alpha-synuclein-induced degeneration is reduced by parkin in a fly model of Parkinson's disease.Genome. 2006 May;49(5):505-10. doi: 10.1139/g06-011. Genome. 2006. PMID: 16767175
-
Lentiviral vector delivery of parkin prevents dopaminergic degeneration in an alpha-synuclein rat model of Parkinson's disease.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Dec 14;101(50):17510-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0405313101. Epub 2004 Dec 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15576511 Free PMC article.
-
Pink1 suppresses alpha-synuclein-induced phenotypes in a Drosophila model of Parkinson's disease.Genome. 2008 Dec;51(12):1040-6. doi: 10.1139/G08-085. Genome. 2008. PMID: 19088817
-
Ubiquitin-proteasome system and Parkinson's diseases.Exp Neurol. 2005 Feb;191 Suppl 1:S17-27. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2004.08.021. Exp Neurol. 2005. PMID: 15629758 Review.
-
The cast of molecular characters in Parkinson's disease: felons, conspirators, and suspects.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003 Jun;991:80-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb07465.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003. PMID: 12846976 Review.
Cited by
-
C3KO mouse expression analysis: downregulation of the muscular dystrophy Ky protein and alterations in muscle aging.Neurogenetics. 2012 Nov;13(4):347-57. doi: 10.1007/s10048-012-0336-7. Epub 2012 Jul 22. Neurogenetics. 2012. PMID: 22820870
-
Role of the ubiquitin proteasome system in Parkinson's disease.BMC Biochem. 2007 Nov 22;8 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S13. doi: 10.1186/1471-2091-8-S1-S13. BMC Biochem. 2007. PMID: 18047737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Studies of neurodegenerative diseases using Drosophila and the development of novel approaches for their analysis.Fly (Austin). 2022 Dec;16(1):275-298. doi: 10.1080/19336934.2022.2087484. Fly (Austin). 2022. PMID: 35765969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targets for neuroprotection in Parkinson's disease.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Jul;1792(7):676-87. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2008.09.009. Epub 2008 Oct 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 18930814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding and treating neurodegeneration: insights from the flies.Age (Dordr). 2005 Sep;27(3):225-39. doi: 10.1007/s11357-005-2917-y. Epub 2005 Dec 31. Age (Dordr). 2005. PMID: 23598655 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parkinson J. An essay on the Shaking Palsy. In: Gowers W R, editor. A Manual of Diseases of the Nervous System. 2. Philadelphia, Blakiston; 1817. pp. 6366–6657.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

