Truncated mutants of the putative Wnt receptor LRP6/Arrow can stabilize beta-catenin independently of Frizzled proteins
- PMID: 15064719
- PMCID: PMC2494703
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207642
Truncated mutants of the putative Wnt receptor LRP6/Arrow can stabilize beta-catenin independently of Frizzled proteins
Abstract
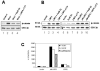
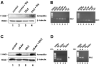
Secreted signaling proteins of the Wnt family are known to regulate a diverse range of developmental processes, and their signaling pathway through beta-catenin is frequently activated in cancer. The identification of both Frizzled and LRP5/6 (LRP: low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein) proteins as components of cell-surface receptors for Wnt proteins has raised questions about their individual functions. We have investigated this issue through a structure-function analysis of Frizzled and LRP proteins that have been implicated in Wnt1 signaling. Consistent with other reports, we find that LRP6/Arrow proteins deleted for their extracellular domain are able to activate the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Importantly, our results demonstrate that this signaling from LRP6/Arrow derivatives can occur in a Frizzled- and ligand-independent manner. Furthermore, we show that the PPSP motifs within the intracellular domain of LRP6 are required for signaling. In contrast to results with LRP6, overexpression of Frizzled proteins did not activate the pathway. Based on evidence of ligand binding to both Frizzled and LRP6, current models suggest that both proteins are components of a Wnt receptor complex that signals to beta-catenin. In light of these models, our data imply that LRP5/6/Arrow proteins constitute the distal signal-initiating component of these receptors. The results also support the notion that LRP5/6 are candidate oncogenes.
Copyright 2004 Nature Publishing Group
Figures


Similar articles
-
Wnt/Wingless signaling through beta-catenin requires the function of both LRP/Arrow and frizzled classes of receptors.BMC Cell Biol. 2003 May 2;4:4. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-4-4. BMC Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12729465 Free PMC article.
-
A novel set of Wnt-Frizzled fusion proteins identifies receptor components that activate beta -catenin-dependent signaling.J Biol Chem. 2002 Sep 20;277(38):34727-35. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M204989200. Epub 2002 Jul 16. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12121999
-
Head inducer Dickkopf-1 is a ligand for Wnt coreceptor LRP6.Curr Biol. 2001 Jun 26;11(12):951-61. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(01)00290-1. Curr Biol. 2001. PMID: 11448771
-
LDL receptor-related proteins 5 and 6 in Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: arrows point the way.Development. 2004 Apr;131(8):1663-77. doi: 10.1242/dev.01117. Development. 2004. PMID: 15084453 Review.
-
Wnt signaling and osteoblastogenesis.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2006 Jun;7(1-2):33-9. doi: 10.1007/s11154-006-9002-4. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2006. PMID: 16960757 Review.
Cited by
-
Near-membrane ensemble elongation in the proline-rich LRP6 intracellular domain may explain the mysterious initiation of the Wnt signaling pathway.BMC Bioinformatics. 2011;12 Suppl 13(Suppl 13):S13. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-S13-S13. Epub 2011 Nov 30. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 22372892 Free PMC article.
-
A Role for the WNT Co-Receptor LRP6 in Pathogenesis and Therapy of Epithelial Cancers.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Aug 13;11(8):1162. doi: 10.3390/cancers11081162. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31412666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ror2 modulates the canonical Wnt signaling in lung epithelial cells through cooperation with Fzd2.BMC Mol Biol. 2008 Jan 23;9:11. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-9-11. BMC Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18215320 Free PMC article.
-
Wingless/Wnt signal transduction requires distinct initiation and amplification steps that both depend on Arrow/LRP.Dev Biol. 2007 Jun 1;306(1):94-111. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.03.005. Epub 2007 Mar 13. Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17433287 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Rare LRP5 Variants in a Cohort of Males with Impaired Bone Mass.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 7;22(19):10834. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910834. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34639175 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bafico A, Liu G, Yaniv A, Gazit A, Aaronson SA. Nature Cell Biology. 2001;3:683–686. - PubMed
-
- Bhanot P, Brink M, Harryman Samos C, Hsieh J-C, Wang Y-S, Macke JP, Andrew D, Nathans J, Nusse R. Nature. 1996;382:225–230. - PubMed
-
- Bhanot P, Fish M, Jemison JA, Nusse R, Nathans J, Cadigan KM. Development. 1999;126:4175–4186. - PubMed
-
- Binari RC, Staveley BE, Johnson WA, Godavarti R, Sasisekharan R, Manoukian AS. Development. 1997;124:2623–2632. - PubMed
-
- Boutros M, Mihaly J, Bouwmeester T, Mlodzik M. Science. 2000;288:1825–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

