Purification and functional reconstitution of N- and C-halves of the MscL channel
- PMID: 15041653
- PMCID: PMC1304064
- DOI: 10.1016/S0006-3495(04)74272-1
Purification and functional reconstitution of N- and C-halves of the MscL channel
Abstract
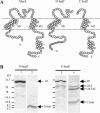
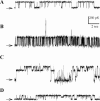
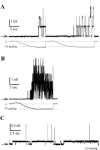
MscL is a mechanosensitive channel gated by membrane tension in the lipid bilayer alone. Its structure, known from x-ray crystallography, indicates that it is a homopentamer. Each subunit comprises two transmembrane segments TM1 and TM2 connected by a periplasmic loop. The closed pore is lined by five TM1 helices. We expressed in Escherichia coli and purified two halves of the protein, each containing one of the transmembrane segments. Their electrophysiological activity was studied by the patch-clamp recording upon reconstitution in artificial liposomes. The TM2 moiety had no electrophysiological activity, whereas the TM1 half formed channels, which were not affected by membrane tension and varied in conductance between 50 and 350 pS in 100 mM KCl. Coreconstitution of the two halves of MscL however, yielded mechanosensitive channels having the same conductance as the native MscL (1500 pS), but exhibiting increased sensitivity to pressure. Our results confirm the current view on the functional role of TM1 and TM2 helices in the MscL gating and emphasize the importance of helix-helix interactions for the assembly and functional properties of the channel protein. In addition, the results indicate a crucial role of the periplasmic loop for the channel mechanosensitivity.
Figures
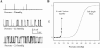
Similar articles
-
Mechanical coupling of the multiple structural elements of the large-conductance mechanosensitive channel during expansion.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Aug 25;112(34):10726-31. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1503202112. Epub 2015 Aug 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26261325 Free PMC article.
-
Purification and functional reconstitution of the recombinant large mechanosensitive ion channel (MscL) of Escherichia coli.J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 4;270(31):18329-34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.31.18329. J Biol Chem. 1995. PMID: 7543101
-
The role of the periplasmic loop residue glutamine 65 for MscL mechanosensitivity.Eur Biophys J. 2005 Jul;34(5):403-12. doi: 10.1007/s00249-005-0476-x. Epub 2005 Apr 6. Eur Biophys J. 2005. PMID: 15812636
-
MscL: channeling membrane tension.Pflugers Arch. 2015 Jan;467(1):15-25. doi: 10.1007/s00424-014-1535-x. Epub 2014 May 27. Pflugers Arch. 2015. PMID: 24859800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanosensitive channels in bacteria as membrane tension reporters.FASEB J. 1999;13 Suppl:S55-61. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.13.9001.s55. FASEB J. 1999. PMID: 10352145 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional similarities between heterogeneously and homogenously expressed MscL constructs.Eur Biophys J. 2015 Oct;44(7):589-98. doi: 10.1007/s00249-015-1062-5. Epub 2015 Aug 2. Eur Biophys J. 2015. PMID: 26233759
-
Gain-of-function mutations reveal expanded intermediate states and a sequential action of two gates in MscL.J Gen Physiol. 2005 Feb;125(2):155-70. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200409118. J Gen Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15684093 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanosensitive channels: insights from continuum-based simulations.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2008;52(1):1-18. doi: 10.1007/s12013-008-9024-5. Epub 2008 Sep 12. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2008. PMID: 18787764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human PIEZO1 Ion Channel Functions as a Split Protein.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 10;11(3):e0151289. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151289. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26963637 Free PMC article.
-
Scanning MscL Channels with Targeted Post-Translational Modifications for Functional Alterations.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 14;10(9):e0137994. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137994. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26368283 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ajouz, B., C. Berrier, M. Besnard, B. Martinac, and A. Ghazi. 2000. Contributions of the different extramembranous domains of the mechanosensitive ion channel MscL to its response to membrane tension. J. Biol. Chem. 275:1015–1022. - PubMed
-
- Berrier, C., M. Besnard, and A. Ghazi. 1997. Electrophysiological characteristics of the PhoE porin channel from Escherichia coli. Implications for the existence of a superfamily of ion channels. J. Membr. Biol. 156:105–115. - PubMed
-
- Berrier, C., A. Coulombe, C. Houssin, and A. Ghazi. 1989. A patch-clamp study of ion channels of inner and outer membranes and of contact zones of E. coli, fused into giant liposomes. Pressure-activated channels are localized in the inner membrane. FEBS Lett. 259:27–32. - PubMed
-
- Berrier, C., A. Coulombe, I. Szabo, M. Zoratti, and A. Ghazi. 1992. Gadolinium ion inhibits loss of metabolites induced by osmotic shock and large stretch-activated channels in bacteria. Eur. J. Biochem. 206:559–565. - PubMed
-
- Betanzos, M., C. S. Chiang, H. R. Guy, and S. Sukharev. 2002. A large iris-like expansion of a mechanosensitive channel protein induced by tension. Nat. Struct. Biol. 9:704–710. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

