The proteosome inhibitor MG132 attenuates retinoic acid receptor trans-activation and enhances trans-repression of nuclear factor kappaB. Potential relevance to chemo-preventive interventions with retinoids
- PMID: 15035668
- PMCID: PMC398417
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-3-8
The proteosome inhibitor MG132 attenuates retinoic acid receptor trans-activation and enhances trans-repression of nuclear factor kappaB. Potential relevance to chemo-preventive interventions with retinoids
Abstract
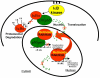
Background: Nuclear factor kappa B (NFkappaB) is a pro-malignant transcription factor with reciprocal effects on pro-metastatic and anti-metastatic gene expression. Interestingly, NFkappaB blockade results in the reciprocal induction of retinoic acid receptors (RARs). Given the established property of RARs as negative regulators of malignant progression, we postulated that reciprocal interactions between NFkappaB and RARs constitute a signaling module in metastatic gene expression and malignant progression. Using Line 1 tumor cells as a model for signal regulation of metastatic gene expression, we investigated the reciprocal interactions between NFkappaB and RARs in response to the pan-RAR agonist, all-trans retinoic acid (at-RA) and the pan-RAR antagonist, AGN193109.
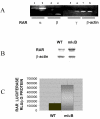
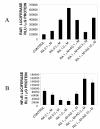
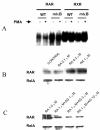
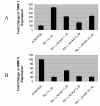
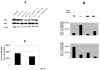
Results: At-RA [0.1-1 microM] dose-dependently activated RAR and coordinately trans-repressed NFkappaB, while AGN193109 [1-10 microM] dose-dependently antagonized the effects of at-RA. At-RA and AGN193109 reciprocally regulate pro-metastatic matrix metalloprotease 9 (MMP 9) and its endogenous inhibitor, the tissue inhibitor of metalloprotease 1 (TIMP 1), in a manner consistent with the putative roles of NFkappaB and RAR in malignant progression. Activation of RAR concurs with its ubiquitination and proteosomal degradation. Accordingly, the proteosome inhibitor, MG132 [5 microM], blocked RAR degradation, quelled RAR trans-activation and enhanced RAR trans-repression of NFkappaB.
Conclusion: We conclude that reciprocal interactions between NFkappaB and RARs constitute a signaling module in metastatic gene expression and malignant progression and propose that the dissociative effect of proteosome inhibitors could be harnessed towards enhancing the anticancer activity of retinoids.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of trans-retinoic acid-resistant human breast cancer cell growth by retinoid X receptor-selective retinoids.Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Nov;17(11):6598-608. doi: 10.1128/MCB.17.11.6598. Mol Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9343423 Free PMC article.
-
Conformationally defined 6-s-trans-retinoic acid analogs. 3. Structure-activity relationships for nuclear receptor binding, transcriptional activity, and cancer chemopreventive activity.J Med Chem. 1996 Sep 13;39(19):3625-35. doi: 10.1021/jm9603126. J Med Chem. 1996. PMID: 8809153
-
Critical role of both retinoid nuclear receptors and retinoid-X-receptors in mediating growth inhibition of ovarian cancer cells by all-trans retinoic acid.Oncogene. 1998 Dec 3;17(22):2839-49. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202208. Oncogene. 1998. PMID: 9879990
-
[Mechanism of action of retinoids in a new therapeutic approach to acute promyelocytic leukemia].Bull Cancer. 1992;79(7):697-704. Bull Cancer. 1992. PMID: 1334741 Review. French.
-
Dynamic and combinatorial control of gene expression by nuclear retinoic acid receptors (RARs).Nucl Recept Signal. 2009 May 8;7:e005. doi: 10.1621/nrs.07005. Nucl Recept Signal. 2009. PMID: 19471584 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of keratin expression by retinoids.Dermatoendocrinol. 2011 Jul;3(3):136-40. doi: 10.4161/derm.3.3.15026. Epub 2011 Jul 1. Dermatoendocrinol. 2011. PMID: 22110773 Free PMC article.
-
Latent membrane protein 1 regulates STAT1 through NF-kappaB-dependent interferon secretion in Epstein-Barr virus-immortalized B cells.J Virol. 2005 Apr;79(8):4936-43. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.8.4936-4943.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15795279 Free PMC article.
-
The Ski protein can inhibit ligand induced RARalpha and HDAC3 degradation in the retinoic acid signaling pathway.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009 May 22;383(1):119-24. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.03.141. Epub 2009 Mar 31. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009. PMID: 19341714 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoic acid decreases adherence of murine myeloid dendritic cells and increases production of matrix metalloproteinase-9.J Nutr. 2008 Aug;138(8):1512-9. doi: 10.1093/jn/138.8.1512. J Nutr. 2008. PMID: 18641199 Free PMC article.
-
Promoter context determines the role of proteasome in ligand-dependent occupancy of retinoic acid responsive elements.Epigenetics. 2011 Feb;6(2):202-11. doi: 10.4161/epi.6.2.13658. Epub 2011 Feb 1. Epigenetics. 2011. PMID: 20948287 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baeuerle PA, Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-κB transcription factor. Cell. 1988;53:211–217. - PubMed
-
- Denhardt DT. Oncogene-initiated aberrant signaling engenders the metastatic phenotype: synergistic transcription factor interactions are targets for cancer therapy. Crit Rev Oncog. 1996;7:261–291. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

