Dose escalation of infliximab in clinical practice: improvements seen may be explained by a regression-like effect
- PMID: 15020338
- PMCID: PMC1754945
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2003.010967
Dose escalation of infliximab in clinical practice: improvements seen may be explained by a regression-like effect
Abstract
Objective: To determine whether increased infliximab doses result in better clinical outcome in rheumatic diseases.
Methods: Subjects were 124 patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with biological agents at a single institute. Index cases were 44 patients whose infliximab doses had been increased. Controls were patients treated with infliximab without dose increase (n = 44), and patients treated with etanercept (n = 36). Disease activity score (DAS28), ACR28 swollen joint counts, and numerical ACR responses were compared before and after dose increases. For the controls, the point at which the DAS28 value showed any increase (despite infliximab/etanercept treatment) was used as the reference time point. Comparisons were made between three sets of outcomes: best outcome achieved before the dose increase (cases) or before the reference time point (controls); outcomes at this point; and best outcomes after this point.
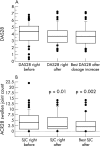
Results: Following dose increase, disease activity showed modest but statistically significant improvements. The improvement achieved after dosage escalation was equal to, but not better than, the best values before dose escalation. While this finding could be interpreted as "recapturing" the previous response, similar improvements were seen in both control groups. Thus the same pattern of worsening and subsequent improvement was seen with or without the infliximab dose increase.
Conclusions: Clinical improvement with increased infliximab dose, and the impression that a previous response can be "recaptured" with higher doses, cannot be taken at face value, as similar improvements occurred in two control groups. The use of infliximab at doses higher than 3 mg/kg needs to be evaluated further.
Figures
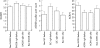

Similar articles
-
Differences in biologic dose-escalation, non-biologic and steroid intensification among three anti-TNF agents: evidence from clinical practice.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2011 Jan-Feb;29(1):26-34. Epub 2011 Feb 23. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 21345289
-
Dose escalation of the anti-TNF-alpha agents in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. A systematic review.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007 Mar;46(3):529-32. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kel326. Epub 2006 Sep 29. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007. PMID: 17012439 Review.
-
Infliximab efficacy in rheumatoid arthritis after an inadequate response to etanercept or adalimumab: results of a target-driven active switch study.Curr Med Res Opin. 2014 Nov;30(11):2139-49. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2014.942416. Epub 2014 Jul 30. Curr Med Res Opin. 2014. PMID: 25050591 Clinical Trial.
-
A dose adjustment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis not optimally responding to a standard dose of infliximab of 3 mg/kg every 8 weeks can be effective: a Belgian prospective study.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005 Apr;44(4):465-8. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keh494. Epub 2005 Feb 3. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005. PMID: 15695306
-
Efficacy of treatment intensification with adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review of cohort studies with focus on dose.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2013 Oct;43(2):144-51. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2013.01.007. Epub 2013 Jul 6. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2013. PMID: 23838092 Review.
Cited by
-
Updated consensus statement on biological agents for the treatment of rheumatic diseases, 2007.Ann Rheum Dis. 2007 Nov;66 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):iii2-22. doi: 10.1136/ard.2007.081430. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007. PMID: 17934088 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Unresolved issues in biologic therapy for rheumatoid arthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011 Apr;7(4):205-15. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2011.22. Epub 2011 Mar 8. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 21386796 Review.
-
Rheumatoid arthritis: strategies in the management of patients showing an inadequate response to TNFalpha antagonists.Drugs. 2008;68(5):591-606. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200868050-00003. Drugs. 2008. PMID: 18370440 Review.
-
Swedish registers to examine drug safety and clinical issues in RA.Ann Rheum Dis. 2006 Jun;65(6):707-12. doi: 10.1136/ard.2005.045872. Epub 2006 Jan 13. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006. PMID: 16414975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Updated consensus statement on biological agents, specifically tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) blocking agents and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra), for the treatment of rheumatic diseases, 2004.Ann Rheum Dis. 2004 Nov;63 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):ii2-ii12. doi: 10.1136/ard.2004.029272. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004. PMID: 15479866 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
