Molecular evidence for rhesus lymphocryptovirus infection of epithelial cells in immunosuppressed rhesus macaques
- PMID: 15016868
- PMCID: PMC371085
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.78.7.3455-3461.2004
Molecular evidence for rhesus lymphocryptovirus infection of epithelial cells in immunosuppressed rhesus macaques
Abstract
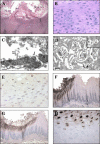
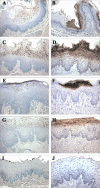
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a human oncogenic herpesvirus associated with epithelial cell and B-cell malignancies. EBV infection of B lymphocytes is essential for acute and persistent EBV infection in humans; however, the role of epithelial cell infection in the normal EBV life cycle remains controversial. The rhesus lymphocryptovirus (LCV) is an EBV-related herpesvirus that naturally infects rhesus macaques and can be used experimentally to model persistent B-cell infection and B-cell lymphomagenesis. We now show that the rhesus LCV can infect epithelial cells in immunosuppressed rhesus macaques and can induce epithelial cell lesions resembling oral hairy leukoplakia in AIDS patients. Electron microscopy, immunohistochemistry, and DNA-RNA in situ hybridization were used to identify the presence of a lytic rhesus LCV infection in these proliferative, hyperkeratotic, or parakeratotic epithelial cell lesions. These studies demonstrate that the rhesus LCV has tropism for epithelial cells, in addition to B cells, and is a relevant animal model system for studying the role of epithelial cell infection in EBV pathogenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr Virus gp350 Can Functionally Replace the Rhesus Lymphocryptovirus Major Membrane Glycoprotein and Does Not Restrict Infection of Rhesus Macaques.J Virol. 2015 Nov 11;90(3):1222-30. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02531-15. Print 2016 Feb 1. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26559839 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental rhesus lymphocryptovirus infection in immunosuppressed macaques: an animal model for Epstein-Barr virus pathogenesis in the immunosuppressed host.Blood. 2004 Sep 1;104(5):1482-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-01-0342. Epub 2004 May 18. Blood. 2004. PMID: 15150077
-
Cloning of the rhesus lymphocryptovirus viral capsid antigen and Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNA homologues and use in diagnosis of acute and persistent infections.J Clin Microbiol. 2000 Sep;38(9):3219-25. doi: 10.1128/JCM.38.9.3219-3225.2000. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10970361 Free PMC article.
-
Non-human Primate Lymphocryptoviruses: Past, Present, and Future.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;391:385-405. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22834-1_13. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26428382 Review.
-
A new animal model for Epstein-Barr virus pathogenesis.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2001;258:201-19. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-56515-1_13. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11443863 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Simian herpesviruses and their risk to humans.Vaccine. 2010 May 26;28 Suppl 2:B78-84. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.11.026. Vaccine. 2010. PMID: 20510749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus gp350 Can Functionally Replace the Rhesus Lymphocryptovirus Major Membrane Glycoprotein and Does Not Restrict Infection of Rhesus Macaques.J Virol. 2015 Nov 11;90(3):1222-30. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02531-15. Print 2016 Feb 1. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26559839 Free PMC article.
-
Animal Models for Gammaherpesvirus Infections: Recent Development in the Analysis of Virus-Induced Pathogenesis.Pathogens. 2020 Feb 12;9(2):116. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9020116. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 32059472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macaque homologs of EBV and KSHV show uniquely different associations with simian AIDS-related lymphomas.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(10):e1002962. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002962. Epub 2012 Oct 4. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 23055934 Free PMC article.
-
Pathologic characteristics of infectious diseases in macaque monkeys used in biomedical and toxicologic studies.J Toxicol Pathol. 2023 Apr;36(2):95-122. doi: 10.1293/tox.2022-0089. Epub 2023 Feb 13. J Toxicol Pathol. 2023. PMID: 37101957 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baskin, G. B., E. D. Roberts, D. Kuebler, L. N. Martin, B. Blauw, J. Heeney, and C. Zurcher. 1995. Squamous epithelial proliferative lesions associated with rhesus Epstein-Barr virus in simian immunodeficiency virus-infected rhesus monkeys. J. Infect. Dis. 172:535-539. - PubMed
-
- Chien, K., R. Van de Velde, and R. Heusser. 1982. A one-step method for re-embedding paraffin embedded specimens for electron microscopy, p. 356-357. In G. W. Bailey (ed.), Fortieth Annual Proceedings of the EMSA Meeting. Claitor’s Publishing Co., Baton Rouge, La.
-
- Du, Z., S. M. Lang, V. G. Sasseville, A. A. Lackner, P. O. Ilyinskii, M. D. Daniel, J. U. Jung, and R. C. Desrosiers. 1995. Identification of a nef allele that causes lymphocyte activation and acute disease in macaque monkeys. Cell 82:665-674. - PubMed
-
- Faulkner, G. C., S. R. Burrows, R. Khanna, D. J. Moss, A. G. Bird, D. H. Crawford, J. W. Gratama, M. A. Oosterveer, F. E. Zwaan, J. Lepoutre, G. Klein, and I. Ernberg. 1999. X-linked agammaglobulinemia patients are not infected with Epstein-Barr virus: implications for the biology of the virus. J. Virol. 73:1555-1564. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

