Specificity of microRNA target selection in translational repression
- PMID: 15014042
- PMCID: PMC374233
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1184404
Specificity of microRNA target selection in translational repression
Abstract
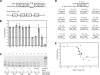
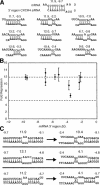
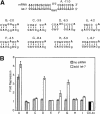
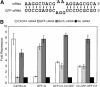
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of noncoding RNAs found in organisms as evolutionarily distant as plants and mammals, yet most of the mRNAs they regulate are unknown. Here we show that the ability of an miRNA to translationally repress a target mRNA is largely dictated by the free energy of binding of the first eight nucleotides in the 5' region of the miRNA. However, G:U wobble base-pairing in this region interferes with activity beyond that predicted on the basis of thermodynamic stability. Furthermore, an mRNA can be simultaneously repressed by more than one miRNA species. The level of repression achieved is dependent on both the amount of mRNA and the amount of available miRNA complexes. Thus, predicted miRNA:mRNA interactions must be viewed in the context of other potential interactions and cellular conditions.
Figures


Comment in
-
Great expectations of small RNAs.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Oct;11(10):676. doi: 10.1038/nrm2987. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20861869 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Analysis of microRNA-target interactions by a target structure based hybridization model.Pac Symp Biocomput. 2008:64-74. Pac Symp Biocomput. 2008. PMID: 18232104
-
Is the Efficiency of RNA Silencing Evolutionarily Regulated?Int J Mol Sci. 2016 May 12;17(5):719. doi: 10.3390/ijms17050719. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27187367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miRNA Targeting: Growing beyond the Seed.Trends Genet. 2019 Mar;35(3):215-222. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2018.12.005. Epub 2019 Jan 9. Trends Genet. 2019. PMID: 30638669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complementarity to an miRNA seed region is sufficient to induce moderate repression of a target transcript in the unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.Plant J. 2013 Dec;76(6):1045-56. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12354. Plant J. 2013. PMID: 24127635
-
MicroRNA targeting specificity in mammals: determinants beyond seed pairing.Mol Cell. 2007 Jul 6;27(1):91-105. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.06.017. Mol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17612493 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Influence of 3'UTRs on MicroRNA Function Inferred from Human SNP Data.Comp Funct Genomics. 2011;2011:910769. doi: 10.1155/2011/910769. Epub 2011 Oct 25. Comp Funct Genomics. 2011. PMID: 22110399 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-101 (miR-101) post-transcriptionally regulates the expression of EP4 receptor in colon cancers.Cancer Biol Ther. 2012 Feb 1;13(3):175-83. doi: 10.4161/cbt.13.3.18874. Cancer Biol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22353936 Free PMC article.
-
A pathogenic mechanism in Huntington's disease involves small CAG-repeated RNAs with neurotoxic activity.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(2):e1002481. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002481. Epub 2012 Feb 23. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 22383888 Free PMC article.
-
How Does Protein Nutrition Affect the Epigenetic Changes in Pig? A Review.Animals (Basel). 2021 Feb 19;11(2):544. doi: 10.3390/ani11020544. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33669864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Let-7b regulates the expression of the growth hormone receptor gene in deletion-type dwarf chickens.BMC Genomics. 2012 Jul 10;13:306. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-306. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22781587 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrahante J.E., Daul, A.L., Li, M., Volk, M.L., Tennessen, J.M., Miller, E.A., and Rougvie, A.E. 2003. The Caenorhabditis elegans hunchback-like gene lin-57/hbl-1 controls developmental time and is regulated by microRNAs. Dev. Cell 4: 625–637. - PubMed
-
- Bartel D.P. 2004. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism and function. Cell 116: 281–297. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein E., Caudy, A.A., Hammond, S.M., and Hannon, G.J. 2001. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature 409: 363–366. - PubMed
-
- Brennecke J., Hipfner, D.R., Stark, A., Russell, R.B., and Cohen, S.M. 2003. bantam encodes a developmentally regulated microRNA that controls cell proliferation and regulates the proapoptotic gene hid in Drosophila. Cell 113: 25–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
