SPAK kinase is a substrate and target of PKCtheta in T-cell receptor-induced AP-1 activation pathway
- PMID: 14988727
- PMCID: PMC380980
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600125
SPAK kinase is a substrate and target of PKCtheta in T-cell receptor-induced AP-1 activation pathway
Abstract
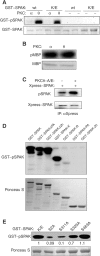
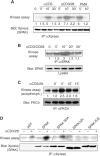
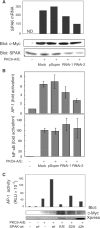
Protein kinase C-theta (PKCtheta) plays an important role in T-cell activation via stimulation of AP-1 and NF-kappaB. Here we report the isolation of SPAK, a Ste20-related upstream mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), as a PKCtheta-interacting kinase. SPAK interacted with PKCtheta (but not with PKCalpha) via its 99 COOH-terminal residues. TCR/CD28 costimulation enhanced this association and stimulated the catalytic activity of SPAK. Recombinant SPAK was phosphorylated on Ser-311 in its kinase domain by PKCtheta, but not by PKCalpha. The magnitude and duration of TCR/CD28-induced endogenous SPAK activation were markedly impaired in PKCtheta-deficient T cells. Transfected SPAK synergized with constitutively active PKCtheta to activate AP-1, but not NF-kappaB. This synergistic activity, as well as the receptor-induced SPAK activation, required the PKCtheta-interacting region of SPAK, and Ser-311 mutation greatly reduced these activities of SPAK. Conversely, a SPAK-specific RNAi or a dominant-negative SPAK mutant inhibited PKCtheta- and TCR/CD28-induced AP-1, but not NF-kappaB, activation. These results define SPAK as a substrate and target of PKCtheta in a TCR/CD28-induced signaling pathway leading selectively to AP-1 (but not NF-kappaB) activation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
NF-kappa B activation induced by T cell receptor/CD28 costimulation is mediated by protein kinase C-theta.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Mar 28;97(7):3394-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.7.3394. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10716728 Free PMC article.
-
Role for protein kinase Ctheta (PKCtheta) in TCR/CD28-mediated signaling through the canonical but not the non-canonical pathway for NF-kappaB activation.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jan 14;280(2):1217-23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M409492200. Epub 2004 Nov 9. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15536066
-
Positive feedback regulation of PLCgamma1/Ca(2+) signaling by PKCtheta in restimulated T cells via a Tec kinase-dependent pathway.Eur J Immunol. 2004 Jul;34(7):2001-11. doi: 10.1002/eji.200324625. Eur J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15214048
-
Protein kinase Ctheta: a new essential superstar on the T-cell stage.Immunol Today. 2000 Nov;21(11):567-73. doi: 10.1016/s0167-5699(00)01749-7. Immunol Today. 2000. PMID: 11094261 Review.
-
NF-kappaB activation pathways induced by T cell costimulation.FASEB J. 2003 Dec;17(15):2187-93. doi: 10.1096/fj.02-1100rev. FASEB J. 2003. PMID: 14656980 Review.
Cited by
-
Intervention of PKC-θ as an immunosuppressive regimen.Front Immunol. 2012 Aug 2;3:225. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00225. eCollection 2012. Front Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22876242 Free PMC article.
-
Excess Salt Intake Activates IL-21-Dominant Autoimmune Diabetogenesis via a Salt-Regulated Ste20-Related Proline/Alanine-Rich Kinase in CD4 T Cells.Diabetes. 2024 Apr 1;73(4):592-603. doi: 10.2337/db23-0599. Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38241027 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid raft targeting of hematopoietic protein tyrosine phosphatase by protein kinase C theta-mediated phosphorylation.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Mar;26(5):1806-16. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.5.1806-1816.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16479000 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and biochemical insights into the activation mechanisms of germinal center kinase OSR1.J Biol Chem. 2014 Dec 26;289(52):35969-78. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.592097. Epub 2014 Nov 11. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25389294 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic silencing of Stk39 in B-cell lymphoma inhibits apoptosis from genotoxic stress.Am J Pathol. 2009 Oct;175(4):1653-61. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.090091. Epub 2009 Aug 28. Am J Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19717643 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altman A, Isakov N, Baier G (2000) PKCθ: a new essential superstar on the T cell stage. Immunol Today 21: 567–573 - PubMed
-
- Arendt CW, Albrecht B, Soos TJ, Littman DR (2002) Protein kinase C-θ: signaling from the center of the T-cell synapse. Curr Opin Immunol 14: 323–330 - PubMed
-
- Avraham A, Jung S, Samuels Y, Seger R, Nen-Neriah Y (1998) Co-stimulation-dependent activation of a JNK-kinase in T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol 28: 2320–2330 - PubMed
-
- Bi K, Tanaka Y, Coudronniere N, Hong S, Sugie K, van Stipdonk MJB, Altman A (2001) Antigen-induced translocation of PKC-θ to membrane rafts is required for T cell activation. Nat Immunol 2: 556–563 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

