Distinct roles of hippocampal de novo protein synthesis and actin rearrangement in extinction of contextual fear
- PMID: 14985438
- PMCID: PMC6730386
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5112-03.2004
Distinct roles of hippocampal de novo protein synthesis and actin rearrangement in extinction of contextual fear
Abstract
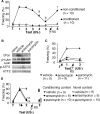
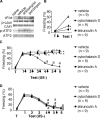
It is believed that de novo protein synthesis is fundamentally linked to synaptic changes in neuronal circuits involved in acquisition and extinction of conditioned responses. Recent studies show that neuronal plasticity may be also altered by cytoskeletal rearrangement independently of protein synthesis. We investigated the role of these processes in the hippocampus during acquisition and extinction of context-dependent conditioned fear in mice. Intrahippocampal injections of the protein synthesis inhibitors anisomycin and puromycin, or of the actin rearrangement inhibitors cytochalasin D and latrunculin A, prevented the acquisition of context-dependent fear. Unexpectedly, anisomycin and puromycin enhanced extinction without erasing the fear memory. In contrast, cytochalasin D and latrunculin A prevented extinction of context-dependent freezing. On the basis of these findings, it is suggested that certain hippocampal mechanisms mediating extinction of conditioned contextual fear are inhibited by protein synthesis and involve actin rearrangement. Such mechanisms might predominantly elicit modifications of hippocampal circuits that store the conditioning memory.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential involvement of protein synthesis and actin rearrangement in the reacquisition of contextual fear conditioning.Hippocampus. 2012 Mar;22(3):494-500. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20915. Epub 2011 Jan 14. Hippocampus. 2012. PMID: 21240917
-
Different requirements for protein synthesis in acquisition and extinction of spatial preferences and context-evoked fear.J Neurosci. 2001 Aug 1;21(15):5773-80. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-15-05773.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11466449 Free PMC article.
-
AMPA receptors control fear extinction through an Arc-dependent mechanism.Learn Mem. 2017 Jul 17;24(8):375-380. doi: 10.1101/lm.045013.117. Print 2017 Aug. Learn Mem. 2017. PMID: 28716957 Free PMC article.
-
The role of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons in fear and extinction memory.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2016 Sep;133:39-52. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2016.06.001. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2016. PMID: 27264248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of fear learning and extinction: synaptic plasticity-fear memory connection.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Jan;236(1):163-182. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-5104-4. Epub 2018 Nov 10. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30415278 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Spontaneous recovery from extinction depends on the reconsolidation of the acquisition memory in an appetitive learning paradigm in the honeybee (Apis mellifera).J Neurosci. 2005 May 4;25(18):4485-92. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0117-05.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15872095 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent disruption of an established morphine conditioned place preference.J Neurosci. 2006 Mar 15;26(11):3010-20. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4818-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16540579 Free PMC article.
-
Stability of recent and remote contextual fear memory.Learn Mem. 2006 Jul-Aug;13(4):451-7. doi: 10.1101/lm.183406. Learn Mem. 2006. PMID: 16882861 Free PMC article.
-
Extinction of remotely acquired fear depends on an inhibitory NR2B/PKA pathway in the retrosplenial cortex.J Neurosci. 2013 Dec 11;33(50):19492-8. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3338-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24336715 Free PMC article.
-
Segregated populations of hippocampal principal CA1 neurons mediating conditioning and extinction of contextual fear.J Neurosci. 2009 Mar 18;29(11):3387-94. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5619-08.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19295145 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anokhin KV, Tiunova AA, Rose SP (2002) Reminder effects - reconsolidation or retrieval deficit? Pharmacological dissection with protein synthesis inhibitors following reminder for a passive-avoidance task in young chicks. Eur J Neurosci 15: 1759-1765. - PubMed
-
- Antonova I, Arancio O, Trillat AC, Wang HG, Zablow L, Udo H, Kandel ER, Hawkins RD (2001) Rapid increase in clusters of presynaptic proteins at onset of long-lasting potentiation. Science 294: 1547-1550. - PubMed
-
- Berman DE, Dudai Y (2001) Memory extinction, learning anew, and learning the new: dissociations in the molecular machinery of learning in cortex. Science 291: 2417-2419. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard RJ, Blanchard DC (1969) Crouching as an index of fear. J Comp Physiol Psychol 67: 370-375. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
