Defects in secretion, aggregation, and thrombus formation in platelets from mice lacking Akt2
- PMID: 14755341
- PMCID: PMC324545
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI20267
Defects in secretion, aggregation, and thrombus formation in platelets from mice lacking Akt2
Abstract
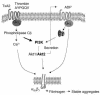
Prior studies have shown that PI3Ks play a necessary but incompletely defined role in platelet activation. One potential effector for PI3K is the serine/threonine kinase, Akt, whose contribution to platelet activation was explored here. Two isoforms of Akt were detected in mouse platelets, with expression of Akt2 being greater than Akt1. Deletion of the gene encoding Akt2 impaired platelet aggregation, fibrinogen binding, and granule secretion, especially in response to low concentrations of agonists that activate the G(q)-coupled receptors for thrombin and thromboxane A(2). Loss of Akt2 also impaired arterial thrombus formation and stability in vivo, despite having little effect on platelet responses to collagen and ADP. In contrast, reducing Akt1 expression had no effect except when Akt2 was also deleted. Activation of Akt by thrombin was abolished by deletion of Galpha(q) but was relatively unaffected by deletion of Galpha(i2), which abolished Akt activation by ADP. From these results we conclude that Akt2 is a necessary component of PI3K-dependent signaling downstream of G(q)-coupled receptors, promoting thrombus growth and stability in part by supporting secretion. The contribution of Akt1 is less evident except in the setting in which Akt2 is absent.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Receptor-interacting protein kinase 3 promotes platelet activation and thrombosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Mar 14;114(11):2964-2969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1610963114. Epub 2017 Feb 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28242694 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired platelet responses to thrombin and collagen in AKT-1-deficient mice.Blood. 2004 Sep 15;104(6):1703-10. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-10-3428. Epub 2004 Apr 22. Blood. 2004. PMID: 15105289 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance to thromboembolism in PI3Kgamma-deficient mice.FASEB J. 2001 Sep;15(11):2019-21. doi: 10.1096/fj.00-0810fje. Epub 2001 Jul 9. FASEB J. 2001. PMID: 11511514
-
Role of the growth arrest-specific gene 6 (gas6) product in thrombus stabilization.Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2006 May-Jun;36(3):373-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2005.12.038. Epub 2006 Mar 29. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2006. PMID: 16564713 Review.
-
PI3K/Akt in platelet integrin signaling and implications in thrombosis.Adv Biol Regul. 2015 Sep;59:36-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2015.06.001. Epub 2015 Jun 19. Adv Biol Regul. 2015. PMID: 26159296 Review.
Cited by
-
Brevianamide F Exerts Antithrombotic Effects by Modulating the MAPK Signaling Pathway and Coagulation Cascade.Mar Drugs. 2024 Sep 26;22(10):439. doi: 10.3390/md22100439. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39452847 Free PMC article.
-
Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase enhance C-type lectin-like receptor 2-mediated platelet activation by inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3α/β.J Thromb Haemost. 2015 Jun;13(6):1139-50. doi: 10.1111/jth.12954. Epub 2015 May 9. J Thromb Haemost. 2015. PMID: 25858425 Free PMC article.
-
P2Y12 receptor: platelet thrombus formation and medical interventions.Int J Hematol. 2012 Nov;96(5):572-87. doi: 10.1007/s12185-012-1188-5. Epub 2012 Oct 1. Int J Hematol. 2012. PMID: 23054651 Review.
-
A G(i) -independent mechanism mediating Akt phosphorylation in platelets.J Thromb Haemost. 2010 Sep;8(9):2032-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2010.03969.x. J Thromb Haemost. 2010. PMID: 20586915 Free PMC article.
-
Akt1 is necessary for the vascular maturation and angiogenesis during cutaneous wound healing.Angiogenesis. 2008;11(3):277-88. doi: 10.1007/s10456-008-9111-7. Epub 2008 Apr 16. Angiogenesis. 2008. PMID: 18415691 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Trumel C, et al. A key role of adenosine diphosphate in the irreversible platelet aggregation induced by the PAR1-activating peptide through the late activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Blood. 1999;94:4156–4165. - PubMed
-
- Kim S, et al. Protease-activated receptors 1 and 4 do not stimulate G(i) signaling pathways in the absence of secreted ADP and cause human platelet aggregation independently of G(i) signaling. Blood. 2002;99:3629–3636. - PubMed
-
- Dangelmaier C, Jin J, Smith JB, Kunapuli SP. Potentiation of thromboxane A2-induced platelet secretion by Gi signaling through the phosphoinositide-3 kinase pathway. Thromb. Haemost. 2001;85:341–348. - PubMed
-
- Li Z, et al. Two waves of platelet secretion induced by thromboxane A2 receptor and a critical role for phosphoinositide 3-kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:30725–30731. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

