Postsynaptic density 95 controls AMPA receptor incorporation during long-term potentiation and experience-driven synaptic plasticity
- PMID: 14749436
- PMCID: PMC6729816
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4733-03.2004
Postsynaptic density 95 controls AMPA receptor incorporation during long-term potentiation and experience-driven synaptic plasticity
Abstract
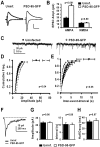
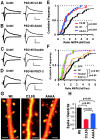
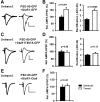
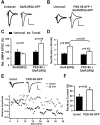
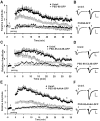
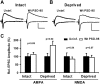
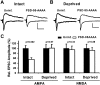
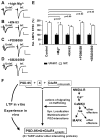
The regulated delivery of AMPA-type glutamate receptors (AMPARs) to synapses is an important mechanism underlying synaptic plasticity. Here, we ask whether the synaptic scaffolding protein PSD-95 (postsynaptic density 95) participates in AMPAR incorporation during two forms of synaptic plasticity. In hippocampal slice cultures, the expression of PSD-95-green fluorescent protein (PSD-95-GFP) increases AMPAR currents by selectively delivering glutamate receptor 1 (GluR1)-containing receptors to synapses, thus mimicking long-term potentiation (LTP). Mutational analysis shows that the N terminal of PSD-95 including the first two PDZ [PSD-95/Discs large (Dlg)/zona occludens-1 (ZO-1)] domains is necessary and sufficient to mediate this effect. Further supporting a role in synaptic plasticity, wild-type PSD-95 occludes LTP and dominant negative forms block LTP. Moreover, we demonstrate that PSD-95 also participates in AMPAR delivery during experience-driven plasticity in vivo. In the barrel cortex from experience-deprived animals, the expression of PSD-95-GFP selectively increases AMPAR currents, mimicking experience-driven plasticity. In nondeprived animals, PSD-95-GFP produces no additional potentiation, indicating common mechanisms between PSD-95-mediated potentiation and experience-driven synaptic strengthening. A dominant negative form of PSD-95 blocks experience-driven potentiation of synapses. Pharmacological analysis in slice cultures reveals that PSD-95 acts downstream of other signaling pathways involved in LTP. We conclude that PSD-95 controls activity-dependent AMPAR incorporation at synapses via PDZ interactions not only during LTP in vitro but also during experience-driven synaptic strengthening by natural stimuli in vivo.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Postsynaptic density-95 mimics and occludes hippocampal long-term potentiation and enhances long-term depression.J Neurosci. 2003 Jul 2;23(13):5503-6. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-13-05503.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12843250 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of the postsynaptic density-95 (PSD-95)/discs large/zona occludens-1 binding site of stargazin regulates binding to PSD-95 and synaptic targeting of AMPA receptors.J Neurosci. 2002 Jul 15;22(14):5791-6. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-14-05791.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12122038 Free PMC article.
-
Quaternary structure, protein dynamics, and synaptic function of SAP97 controlled by L27 domain interactions.Neuron. 2004 Oct 28;44(3):453-67. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2004.10.012. Neuron. 2004. PMID: 15504326
-
Regulation of neuronal PKA signaling through AKAP targeting dynamics.Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Jul;85(7):627-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2006.01.010. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16504338 Review.
-
Regulation of AMPA receptor surface diffusion by PSD-95 slots.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2012 Jun;22(3):453-60. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2011.10.010. Epub 2011 Nov 1. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2012. PMID: 22051694 Review.
Cited by
-
PKMζ is necessary and sufficient for synaptic clustering of PSD-95.Hippocampus. 2012 Jul;22(7):1501-7. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20996. Epub 2011 Dec 23. Hippocampus. 2012. PMID: 22378468 Free PMC article.
-
Postsynaptic BDNF-TrkB signaling in synapse maturation, plasticity, and disease.Dev Neurobiol. 2010 Apr;70(5):304-22. doi: 10.1002/dneu.20765. Dev Neurobiol. 2010. PMID: 20186705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Homeostatic synaptic plasticity as a metaplasticity mechanism - a molecular and cellular perspective.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2019 Feb;54:44-53. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2018.08.010. Epub 2018 Sep 11. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30212714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intranasal delivery of pro-resolving lipid mediators rescues memory and gamma oscillation impairment in AppNL-G-F/NL-G-F mice.Commun Biol. 2022 Mar 21;5(1):245. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03169-3. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 35314851 Free PMC article.
-
The role of SAP97 in synaptic glutamate receptor dynamics.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Feb 23;107(8):3805-10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0914422107. Epub 2010 Feb 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20133708 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aoki C, Miko I, Oviedo H, Mikeladze-Dvali T, Alexandre L, Sweeney N, Bredt DS (2001) Electron microscopic immunocytochemical detection of PSD-95, PSD-93, SAP-102, and SAP-97 at postsynaptic, presynaptic, and nonsynaptic sites of adult and neonatal rat visual cortex. Synapse 40: 239–257. - PubMed
-
- Arnold DB, Clapham DE (1999) Molecular determinants for subcellular localization of PSD-95 with an interacting K+ channel. Neuron 23: 149–157. - PubMed
-
- Barria A, Malinow R (2002) Subunit-specific NMDA receptor trafficking to synapses. Neuron 35: 345–353. - PubMed
-
- Barria A, Muller D, Derkach V, Griffith LC, Soderling TR (1997) Regulatory phosphorylation of AMPA-type glutamate receptors by CaM-KII during long-term potentiation. Science 276: 2042–2045. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
