SNAP-23 functions in docking/fusion of granules at low Ca2+
- PMID: 14742706
- PMCID: PMC379287
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e03-09-0684
SNAP-23 functions in docking/fusion of granules at low Ca2+
Abstract
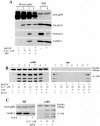
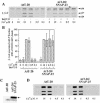
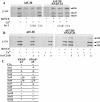
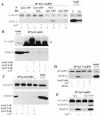
Ca(2+)-triggered exocytosis of secretory granules mediates the release of hormones from endocrine cells and neurons. The plasma membrane protein synaptosome-associated protein of 25 kDa (SNAP-25) is thought to be a key component of the membrane fusion apparatus that mediates exocytosis in neurons. Recently, homologues of SNAP-25 have been identified, including SNAP-23, which is expressed in many tissues, albeit at different levels. At present, little is known concerning functional differences among members of this family of proteins. Using an in vitro assay, we show here that SNAP-25 and SNAP-23 mediate the docking of secretory granules with the plasma membrane at high (1 microM) and low (100 nM) Ca(2+) levels, respectively, by interacting with different members of the synaptotagmin family. In intact endocrine cells, expression of exogenous SNAP-23 leads to high levels of hormone secretion under basal conditions. Thus, the relative expression levels of SNAP-25 and SNAP-23 might control the mode (regulated vs. basal) of granule release by forming docking complexes at different Ca(2+) thresholds.
Figures

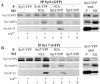

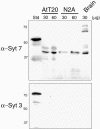
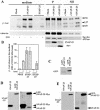
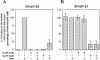
Similar articles
-
Identification of SNAREs involved in synaptotagmin VII-regulated lysosomal exocytosis.J Biol Chem. 2004 May 7;279(19):20471-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M400798200. Epub 2004 Mar 1. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14993220
-
Differential phosphorylation of syntaxin and synaptosome-associated protein of 25 kDa (SNAP-25) isoforms.J Neurochem. 1999 Feb;72(2):614-24. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1999.0720614.x. J Neurochem. 1999. PMID: 9930733
-
R-type voltage-gated Ca(2+) channel interacts with synaptic proteins and recruits synaptotagmin to the plasma membrane of Xenopus oocytes.Neuroscience. 2004;128(4):831-41. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.07.027. Neuroscience. 2004. PMID: 15464290
-
Interactions between presynaptic calcium channels and proteins implicated in synaptic vesicle trafficking and exocytosis.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1998 Aug;30(4):347-56. doi: 10.1023/a:1021937605818. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1998. PMID: 9758331 Review.
-
Function of the t-SNARE SNAP-23 and secretory carrier membrane proteins (SCAMPs) in exocytosis in mast cells.Mol Immunol. 2002 Sep;38(16-18):1337-40. doi: 10.1016/s0161-5890(02)00084-6. Mol Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12217404 Review.
Cited by
-
The calcium-sensing protein synaptotagmin 7 is expressed on different endosomal compartments in endocrine, neuroendocrine cells or neurons but not on large dense core vesicles.Histochem Cell Biol. 2007 Jun;127(6):625-32. doi: 10.1007/s00418-007-0271-0. Epub 2007 Feb 3. Histochem Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17277932
-
The role of non-canonical SNAREs in synaptic vesicle recycling.Cell Logist. 2012 Jan 1;2(1):20-27. doi: 10.4161/cl.20114. Cell Logist. 2012. PMID: 22645707 Free PMC article.
-
Selected SNARE proteins are essential for the polarized membrane insertion of igf-1 receptor and the regulation of initial axonal outgrowth in neurons.Cell Discov. 2015 Sep 1;1:15023. doi: 10.1038/celldisc.2015.23. eCollection 2015. Cell Discov. 2015. PMID: 27462422 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane-Binding Cooperativity and Coinsertion by C2AB Tandem Domains of Synaptotagmins 1 and 7.Biophys J. 2019 Mar 19;116(6):1025-1036. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2019.01.035. Epub 2019 Feb 5. Biophys J. 2019. PMID: 30795874 Free PMC article.
-
Vesicle-associated membrane protein-2 (VAMP2) mediates cAMP-stimulated renin release in mouse juxtaglomerular cells.J Biol Chem. 2011 Aug 12;286(32):28608-18. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.225839. Epub 2011 Jun 27. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21708949 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Binz, T., Blasi, J., Yamasaki, S., Baumeister, A., Link, E., Sudhof, T.C., Jahn, R., and Niemann, H. (1994). Proteolysis of SNAP-25 by types E and A botulinal neurotoxins. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 1617-1620. - PubMed
-
- Bittner, M.A., and Holz, R.W. (1992). Kinetic analysis of secretion from permeabilized adrenal chromaffin cells reveals distinct components. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 16219-16225. - PubMed
-
- Borgonovo, B., Cocucci, E., Racchetti, G., Podini, P., Bachi, A., and Meldolesi, J. (2002). Regulated exocytosis: a novel, widely expressed system. Nat. Cell Biol. 4, 955-962. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

