RF2b, a rice bZIP transcription activator, interacts with RF2a and is involved in symptom development of rice tungro disease
- PMID: 14704272
- PMCID: PMC327209
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0307687100
RF2b, a rice bZIP transcription activator, interacts with RF2a and is involved in symptom development of rice tungro disease
Abstract
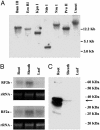
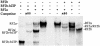
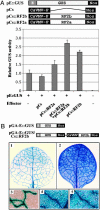
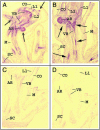
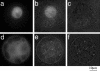
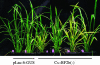
The phloem-specific promoter of rice tungro bacilliform virus (RTBV) is regulated in part by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins that bind to Box II, an essential cis element. Previous studies demonstrated that the bZIP protein RF2a is involved in transcriptional regulation of the RTBV promoter. Here we report the identification and functional characterization of a second bZIP protein, RF2b. RF2b, identified by its interaction with RF2a, binds to Box II in in vitro assays as a homodimer and as RF2a/RF2b heterodimers. Like RF2a, RF2b activates the RTBV promoter in transient assays and in transgenic tobacco plants. Both RF2a and RF2b are predominantly expressed in vascular tissues. However, RF2a and RF2b have different DNA-binding affinities to Box II, show distinctive expression patterns in different rice organs, and exhibit different patterns of subcellular localization. Furthermore, transgenic rice plants with reduced levels of RF2b exhibit a disease-like phenotype. We propose that the regulation of phloem-specific expression of the RTBV promoter and potentially the control of RTBV replication are mainly achieved via interactions of the Box II cis element with multiple host factors, including RF2a and RF2b. We also propose that quenching/titration of these and perhaps other transcription factors by RTBV is involved in the development of the symptoms of rice tungro disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of the C-terminal domains of rice (Oryza sativa L.) bZIP proteins RF2a and RF2b in regulating transcription.Biochem J. 2007 Jul 15;405(2):243-9. doi: 10.1042/BJ20061375. Biochem J. 2007. PMID: 17371296 Free PMC article.
-
Essential role of the Box II cis element and cognate host factors in regulating the promoter of Rice tungro bacilliform virus.J Gen Virol. 2006 Mar;87(Pt 3):715-722. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.81488-0. J Gen Virol. 2006. PMID: 16476995
-
RF2a, a bZIP transcriptional activator of the phloem-specific rice tungro bacilliform virus promoter, functions in vascular development.EMBO J. 1997 Sep 1;16(17):5247-59. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.17.5247. EMBO J. 1997. PMID: 9311985 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenic rice plants that overexpress transcription factors RF2a and RF2b are tolerant to rice tungro virus replication and disease.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Dec 30;105(52):21012-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0810303105. Epub 2008 Dec 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 19104064 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor RF2a alters expression of the rice tungro bacilliform virus promoter in transgenic tobacco plants.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Jun 19;98(13):7635-40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.121186398. Epub 2001 Jun 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11390974 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparative Seeds Storage Transcriptome Analysis of Astronium fraxinifolium Schott, a Threatened Tree Species from Brazil.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 10;23(22):13852. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213852. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430327 Free PMC article.
-
VIP1 is very important/interesting protein 1 regulating touch responses of Arabidopsis.Plant Signal Behav. 2016 Jun 2;11(6):e1187358. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2016.1187358. Plant Signal Behav. 2016. PMID: 27171129 Free PMC article.
-
Virus-induced gene silencing in rice using a vector derived from a DNA virus.Planta. 2010 Nov;232(6):1531-40. doi: 10.1007/s00425-010-1273-z. Epub 2010 Sep 25. Planta. 2010. PMID: 20872012
-
Profiling of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 and Their Roles in Gene Subfunctionalization in Allotetraploid Cotton.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Dec 15;12:761059. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.761059. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34975944 Free PMC article.
-
Dehydration-responsive nuclear proteome of rice (Oryza sativa L.) illustrates protein network, novel regulators of cellular adaptation, and evolutionary perspective.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2009 Jul;8(7):1579-98. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M800601-MCP200. Epub 2009 Mar 25. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2009. PMID: 19321431 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lemon, B. & Tjian, R. (2000) Genes Dev. 14, 2551–2569. - PubMed
-
- Levine, M. & Tjian, R. (2003) Nature 424, 147–151. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharyya-Pakrasi, M., Peng, J., Elmer, J. S., Laco, G., Shen, P., Kaniewska, M. B., Kononowicz, H., Wen, F., Hodges, T. K. & Beachy, R. N. (1993) Plant J. 4, 71–79. - PubMed
-
- Hehn, A. & Rohde, W. (1998) J. Gen. Virol. 79, 1495–1499. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

