In vivo requirements for rDNA chromosome condensation reveal two cell-cycle-regulated pathways for mitotic chromosome folding
- PMID: 14701879
- PMCID: PMC314280
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1150404
In vivo requirements for rDNA chromosome condensation reveal two cell-cycle-regulated pathways for mitotic chromosome folding
Erratum in
- Genes Dev. 2004 Feb 1;18(3):355
Abstract
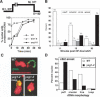
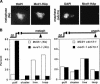
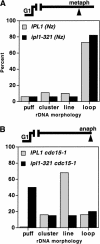
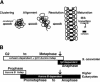
Chromosome condensation plays an essential role in the maintenance of genetic integrity. Using genetic, cell biological, and biochemical approaches, we distinguish two cell-cycle-regulated pathways for chromosome condensation in budding yeast. From G(2) to metaphase, we show that the condensation of the approximately 1-Mb rDNA array is a multistep process, and describe condensin-dependent clustering, alignment, and resolution steps in chromosome folding. We functionally define a further postmetaphase chromosome assembly maturation step that is required for the maintenance of chromosome structural integrity during segregation. This late step in condensation requires the conserved mitotic kinase Ipl1/aurora in addition to condensin, but is independent of cohesin. Consistent with this, the late condensation pathway is initiated during the metaphase-to-anaphase transition, supports de novo condensation in cohesin mutants, and correlates with the Ipl1/aurora-dependent phosphorylation of condensin. These data provide insight into the molecular mechanisms of higher-order chromosome folding and suggest that two distinct condensation pathways, one involving cohesins and the other Ipl1/aurora, are required to modulate chromosome structure during mitosis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
In vivo analysis of chromosome condensation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Feb;18(2):557-68. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e06-05-0454. Epub 2006 Dec 6. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17151360 Free PMC article.
-
Cdc14 phosphatase induces rDNA condensation and resolves cohesin-independent cohesion during budding yeast anaphase.Cell. 2004 May 14;117(4):471-82. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00415-5. Cell. 2004. PMID: 15137940
-
Polo kinase regulates mitotic chromosome condensation by hyperactivation of condensin DNA supercoiling activity.Mol Cell. 2009 May 14;34(4):416-26. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.04.013. Mol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19481522
-
Three-step model for condensin activation during mitotic chromosome condensation.Cell Cycle. 2010 Aug 15;9(16):3243-55. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.16.12620. Epub 2010 Aug 7. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 20703077 Review.
-
Protein kinases in mitotic phosphorylation of budding yeast CENP-A.Curr Genet. 2019 Dec;65(6):1325-1332. doi: 10.1007/s00294-019-00997-5. Epub 2019 May 22. Curr Genet. 2019. PMID: 31119371 Review.
Cited by
-
Levels of Ycg1 Limit Condensin Function during the Cell Cycle.PLoS Genet. 2016 Jul 27;12(7):e1006216. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006216. eCollection 2016 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27463097 Free PMC article.
-
Cdc14p/FEAR pathway controls segregation of nucleolus in S. cerevisiae by facilitating condensin targeting to rDNA chromatin in anaphase.Cell Cycle. 2004 Jul;3(7):960-7. doi: 10.4161/cc.3.7.1003. Epub 2004 Jul 4. Cell Cycle. 2004. PMID: 15190202 Free PMC article.
-
G1-Cyclin2 (Cln2) promotes chromosome hypercondensation in eco1/ctf7 rad61 null cells during hyperthermic stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.G3 (Bethesda). 2022 Jul 29;12(8):jkac157. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac157. G3 (Bethesda). 2022. PMID: 35736360 Free PMC article.
-
Putting the brake on FEAR: Tof2 promotes the biphasic release of Cdc14 phosphatase during mitotic exit.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Jan;20(1):245-55. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-08-0879. Epub 2008 Oct 15. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 18923139 Free PMC article.
-
Cdc14 inhibits transcription by RNA polymerase I during anaphase.Nature. 2009 Mar 12;458(7235):219-22. doi: 10.1038/nature07652. Epub 2009 Jan 21. Nature. 2009. PMID: 19158678 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amon A., Irniger, S., and Nasmyth, K. 1994. Closing the cell cycle circle in yeast: G2 cyclin proteolysis initiated at mitosis persists until the activation of G1 cyclins in the next cycle. Cell 77: 1037–1050. - PubMed
-
- Bazett-Jones D.P., Kimura, K., and Hirano, T. 2002. Efficient supercoiling of DNA by a single condensin complex as revealed by electron spectroscopic imaging. Mol. Cell 9: 1183–1190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
