Distinct domains in the SHP-2 phosphatase differentially regulate epidermal growth factor receptor/NF-kappaB activation through Gab1 in glioblastoma cells
- PMID: 14701753
- PMCID: PMC343802
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.2.823-836.2004
Distinct domains in the SHP-2 phosphatase differentially regulate epidermal growth factor receptor/NF-kappaB activation through Gab1 in glioblastoma cells
Abstract
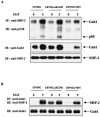
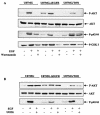
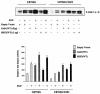
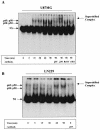
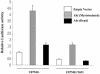
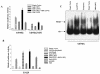
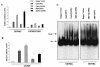
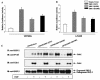
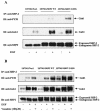
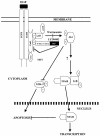
The transcription factor nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) plays an important role in inflammation and cancer, is activated by a variety of stimuli including tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-1, UV irradiation, and viruses, as well as receptor tyrosine kinases, such as epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Although previous studies suggest that EGFR can induce NF-kappaB, the mechanism of this activation remains unknown. In this study, we identify the components of the EGFR-induced signalosome in human glioblastoma cells required to regulate NF-kappaB activation. Immunoprecipitation analyses with ErbB-modulated cells indicate that association between SHP-2 and Grb2-associated binder 1 (Gab1) is the critical step in the formation of the signalosome linking EGFR to NF-kappaB activation. We also show that EGFR-induced NF-kappaB activation is mediated by the PI3-kinase/Akt activation loop. Overexpression of SHP-2, Gab1, and myristoylated Akt significantly upregulated NF-kappaB transcriptional activity and DNA binding activity in glioblastoma cells. Interestingly, overexpression of either one of the two SH2 domain mutants of SHP-2, R32E or R138E, slightly reduced NF-kappaB activity relative to that of wild-type SHP-2, indicating that the SH2 domains of SHP-2 are required for EGFR-induced NF-kappaB activation. On the other hand, ectopic overexpression of either a Gab1 mutant incapable of binding to SHP-2 (Y627F) or a phosphatase-inactive SHP-2 mutant (C459S) caused a significant increase in NF-kappaB activity. Moreover, SHP-2 C459S-expressing cells displayed higher Gab1 phosphotyrosine content, suggesting that SHP-2 regulates Gab1 phosphorylation through its phosphatase domain, which confers a negative regulatory effect on NF-kappaB activity. These results indicate that SHP-2/Gab1 association is critical for linking EGFR to NF-kappaB transcriptional activity via the PI3-kinase/Akt signaling axis in glioblastoma cells and that SHP-2 acts as a dual regulator of NF-kappaB activation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of the Grb2-associated binder 1/SHP-2 interaction in cell growth and transformation.Cancer Res. 2004 Mar 15;64(6):2007-15. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.can-03-2886. Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15026337
-
The tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 is required for mediating phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt activation by growth factors.Oncogene. 2001 Sep 20;20(42):6018-25. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204699. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11593409
-
Receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand stimulates recruitment of SHP-1 to the complex containing TNFR-associated factor 6 that regulates osteoclastogenesis.J Immunol. 2003 Oct 1;171(7):3620-6. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.7.3620. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14500659
-
Epithelial growth factor receptor-activated nuclear factor κB signaling and its role in epithelial growth factor receptor-associated tumors.Cancer J. 2013 Nov-Dec;19(6):461-7. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0000000000000001. Cancer J. 2013. PMID: 24270344 Review.
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2: a proto-oncogene product that promotes Ras activation.Cancer Sci. 2009 Oct;100(10):1786-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01257.x. Epub 2009 Jun 23. Cancer Sci. 2009. PMID: 19622105 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NF-κB inhibitor reverses temozolomide resistance in human glioma TR/U251 cells.Oncol Lett. 2015 Jun;9(6):2586-2590. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.3130. Epub 2015 Apr 21. Oncol Lett. 2015. PMID: 26137111 Free PMC article.
-
The role of NF-κB in the pathogenesis of glioma.Mol Cell Oncol. 2014 Dec 23;1(3):e963478. doi: 10.4161/23723548.2014.963478. eCollection 2014 Jul-Sep. Mol Cell Oncol. 2014. PMID: 27308348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alternate paths from epidermal growth factor receptor to Akt in malignant versus nontransformed lung epithelial cells: ErbB3 versus Gab1.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2005 Nov;33(5):490-9. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2005-0049OC. Epub 2005 Jul 29. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 16055672 Free PMC article.
-
The NFκB pathway: a therapeutic target in glioblastoma.Oncotarget. 2011 Aug;2(8):646-53. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.322. Oncotarget. 2011. PMID: 21896960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor RGFP109 Overcomes Temozolomide Resistance by Blocking NF-κB-Dependent Transcription in Glioblastoma Cell Lines.Neurochem Res. 2016 Dec;41(12):3192-3205. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-2043-5. Epub 2016 Sep 8. Neurochem Res. 2016. PMID: 27632183
References
-
- Arrandale, J. M., A. Gore-Willse, S. Rocks, J. M. Ren, J. Zhu, A. Davis, J. N. Livingston, and D. U. Rabin. 1996. Insulin signaling in mice expressing reduced levels of Syp. J. Biol. Chem. 271:21353-21358. - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle, P. A., and T. Henkel. 1994. Function and activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 12:141-179. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin, A. S., Jr. 1996. The NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 14:649-683. - PubMed
-
- Basile, J. R., A. Eichten, V. Zacny, and K. Munger. 2003. NF-kappaB-mediated induction of p21(Cip1/Waf1) by tumor necrosis factor alpha induces growth arrest and cytoprotection in normal human keratinocytes. Mol. Cancer Res. 1:262-270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
