Estradiol and selective estrogen receptor modulators differentially regulate target genes with estrogen receptors alpha and beta
- PMID: 14699072
- PMCID: PMC363122
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e03-06-0360
Estradiol and selective estrogen receptor modulators differentially regulate target genes with estrogen receptors alpha and beta
Abstract
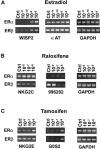
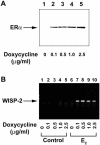
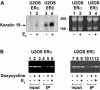
Estrogens and selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) interact with estrogen receptor (ER) alpha and beta to activate or repress gene transcription. To understand how estrogens and SERMs exert tissue-specific effects, we performed microarray analysis to determine whether ERalpha or ERbeta regulate different target genes in response to estrogens and SERMs. We prepared human U2OS osteosarcoma cells that are stably transfected with a tetracycline-inducible vector to express ERalpha or ERbeta. Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunoprecipitation studies confirmed that U2OS-ERalpha cells synthesized only ERalpha and that U2OS-ERbeta cells expressed exclusively ERbeta. U2OS-ERalpha and U2OS-ERbeta cells were treated either with 17beta-estradiol (E2), raloxifene, and tamoxifen for 18 h. Labeled cRNAs were hybridized with U95Av2 GeneChips (Affymetrix). A total of 228, 190, and 236 genes were significantly activated or repressed at least 1.74-fold in U2OS-ERalpha and U2OS-ERbeta cells by E2, raloxifene, and tamoxifen, respectively. Most genes regulated in ERalpha cells in response to E2, raloxifene, and tamoxifen were distinct from those regulated in ERbeta cells. Only 38 of the 228 (17%) genes were regulated by E2 in both U2OS-ERalpha and U2OS-ERbeta cells. Raloxifene and tamoxifen regulated only 27% of the same genes in both the ERalpha and ERbeta cells. A subset of genes involved in bone-related activities regulated by E2, raloxifene, and tamoxifen were also distinct. Our results demonstrate that most genes regulated by ERalpha are distinct from those regulated by ERbeta in response to E2 and SERMs. These results indicate that estrogens and SERMs exert tissue-specific effects by regulating unique sets of targets genes through ERalpha and ERbeta
Figures


Similar articles
-
Estrogen and the selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) protection against cell death in estrogen receptor alpha and beta expressing U2OS cells.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2008 Jul 16;289(1-2):38-48. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2008.03.005. Epub 2008 Mar 25. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18455292
-
Estrogen receptor alpha and beta heterodimers exert unique effects on estrogen- and tamoxifen-dependent gene expression in human U2OS osteosarcoma cells.Mol Endocrinol. 2005 Jun;19(6):1555-68. doi: 10.1210/me.2004-0381. Epub 2005 Mar 31. Mol Endocrinol. 2005. PMID: 15802376
-
Cell type- and estrogen receptor-subtype specific regulation of selective estrogen receptor modulator regulatory elements.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2009 Feb 27;299(2):204-11. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2008.10.050. Epub 2008 Nov 18. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19059307 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of estrogen action: selective ligands and receptor pharmacology.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2000 Nov 30;74(5):279-85. doi: 10.1016/s0960-0760(00)00104-7. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 11162936 Review.
-
Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs): mechanisms of anticarcinogenesis and drug resistance.Mutat Res. 2005 Dec 11;591(1-2):247-63. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2005.02.028. Epub 2005 Aug 3. Mutat Res. 2005. PMID: 16083919 Review.
Cited by
-
Adjunctive selective estrogen receptor modulator increases neural activity in the hippocampus and inferior frontal gyrus during emotional face recognition in schizophrenia.Transl Psychiatry. 2016 May 3;6(5):e795. doi: 10.1038/tp.2016.59. Transl Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27138794 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Estrogen receptor α antagonists mediate changes in CCL20 and CXCL1 secretions in the murine female reproductive tract.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2013 Feb;69(2):159-67. doi: 10.1111/aji.12021. Epub 2012 Oct 1. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23025258 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical update on the use of ospemifene in the treatment of severe symptomatic vulvar and vaginal atrophy.Int J Womens Health. 2016 Oct 26;8:617-626. doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S110035. eCollection 2016. Int J Womens Health. 2016. PMID: 27822125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide dynamics of chromatin binding of estrogen receptors alpha and beta: mutual restriction and competitive site selection.Mol Endocrinol. 2010 Jan;24(1):47-59. doi: 10.1210/me.2009-0252. Epub 2009 Nov 6. Mol Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 19897598 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorine-substituted cyclofenil derivatives as estrogen receptor ligands: synthesis and structure-affinity relationship study of potential positron emission tomography agents for imaging estrogen receptors in breast cancer.J Med Chem. 2006 Apr 20;49(8):2496-511. doi: 10.1021/jm0512037. J Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16610793 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdelrahim, M., Samudio, I., Smith, R., 3rd, Burghardt, R., and Safe, S. (2002). Small inhibitory RNA duplexes for Sp1 mRNA block basal and estrogen-induced gene expression and cell cycle progression in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 28815-28822. - PubMed
-
- An, J., Ribeiro, R.C., Webb, P., Gustafsson, J.A., Kushner, P.J., Baxter, J.D., and Leitman, D.C. (1999). Estradiol repression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha transcription requires estrogen receptor activation function-2 and is enhanced by coactivators. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 15161-15166. - PMC - PubMed
-
- An, J., Tzagarakis-Foster, C., Scharschmidt, T.C., Lomri, N., and Leitman, D.C. (2001). Estrogen receptor beta-selective transcriptional activity and recruitment of coregulators by phytoestrogens. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 17808-17814. - PubMed
-
- Anzick, S.L., Kononen, J., Walker, R.L., Azorsa, D.O., Tanner, M.M., Guan, X.Y., Sauter, G., Kallioniemi, O.P., Trent, J.M., and Meltzer, P.S. (1997). AIB1, a steroid receptor coactivator amplified in breast and ovarian cancer. Science 277, 965-968. - PubMed
-
- Baker, V., Draper, M., Paul, S., Allerheiligen, S., Glant, M., Shirfren, J., and Jaffe, R. (1998). Reproductive endocrine and endometrial effects of raloxifene hydrochloride, a selective estrogen receptor modulator, in women with regular menstrual cycles. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 83, 6-13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

