The Granzyme B ELISPOT assay: an alternative to the 51Cr-release assay for monitoring cell-mediated cytotoxicity
- PMID: 14697097
- PMCID: PMC317386
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-1-14
The Granzyme B ELISPOT assay: an alternative to the 51Cr-release assay for monitoring cell-mediated cytotoxicity
Abstract
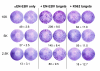
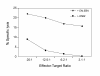
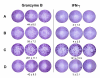
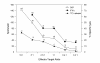
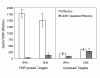
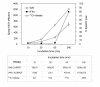
BACKGROUND: The interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) ELISPOT assay is one of the most useful techniques for immunological monitoring of cancer vaccine trials and has gained increased application as a measure of specific T cell activation. However, it does not assess cell-mediated cytotoxicity directly as IFN-gamma secretion is not limited to only cytolytic cells. Granzyme B (GrB) is a key mediator of target cell death via the granule-mediated pathway. Therefore, the release of GrB by cytolytic lymphocytes upon effector-target interaction may be a more specific indicator of CTL and NK cytotoxic ability than IFN-gamma secretion. METHODS: We assessed whether the GrB ELISPOT assay is a viable alternative to the 51Cr-release and IFN-gamma ELISPOT assays for measuring antigen-specific CTL cytotoxicity. Direct comparisons between the three assays were made using human CTL cell lines (alphaEN-EBV and alphaJY) and an in vitro stimulated anti-Flu matrix peptide (FMP)-specific CTL. RESULTS: When the GrB ELISPOT was directly compared to the IFN-gamma ELISPOT and 51Cr-release assays, excellent cross-correlation between all three assays was shown. However, measurable IFN-gamma secretion in the ELISPOT assay was observed only after 1 hour of incubation and cytotoxicity assessed via the 51Cr-release assay after 4 hours, whereas GrB secretion was detectable within 10 min of effector-target contact with significant secretion observed after 1 h. Titration studies demonstrated a strong correlation between the number of effector cells and GrB spots per well. Irrelevant targets or antigens did not induce significant GrB secretion. Additionally, GrB secretion was abrogated when CTL cultures were depleted of CD8+ cells. CONCLUSION: Our findings demonstrate that the GrB ELISPOT assay is a superior alternative to the 51Cr-release assay since it is significantly more sensitive and provides an estimation of cytotoxic effector cell frequency. Additionally, unlike the IFN-gamma ELISPOT assay, the GrB ELISPOT directly measures the release of a cytotolytic protein. Detection of low frequency tumor-specific CTL and their specific effector functions can provide valuable insight with regards to immunological responses.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluating the cytotoxicity of innate immune effector cells using the GrB ELISPOT assay.J Transl Med. 2004 Sep 20;2(1):31. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-2-31. J Transl Med. 2004. PMID: 15380049 Free PMC article.
-
New approaches for monitoring CTL activity in clinical trials.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;601:273-84. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-72005-0_29. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17713015 Review.
-
Application of the granzyme B ELISPOT assay for monitoring cancer vaccine trials.J Immunother. 2006 May-Jun;29(3):328-35. doi: 10.1097/01.cji.0000203079.35612.c8. J Immunother. 2006. PMID: 16699376
-
A novel cytotoxicity assay to evaluate antigen-specific CTL responses using a colorimetric substrate for Granzyme B.J Immunol Methods. 2003 May 1;276(1-2):89-101. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(03)00073-5. J Immunol Methods. 2003. PMID: 12738362
-
New flow cytometric assays for monitoring cell-mediated cytotoxicity.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2010 Jun;9(6):601-16. doi: 10.1586/erv.10.49. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2010. PMID: 20518716 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor impairs CD8(+) T cell functionality by interfering with central activation elements.Clin Exp Immunol. 2016 Jul;185(1):107-18. doi: 10.1111/cei.12794. Epub 2016 May 13. Clin Exp Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26990855 Free PMC article.
-
Pushing the frontiers of T-cell vaccines: accurate measurement of human T-cell responses.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2012 Dec;11(12):1459-70. doi: 10.1586/erv.12.125. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2012. PMID: 23252389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monitoring of pathogen-specific T-cell immune reconstitution after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.Front Immunol. 2013 Sep 17;4:276. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00276. Front Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24062744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rad52 deficiency decreases development of lung squamous cell carcinomas by enhancing immuno-surveillance.Oncotarget. 2017 May 23;8(21):34032-34044. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16371. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28415565 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of assays to measure CAR T-cell-mediated cytotoxicity.Nat Protoc. 2021 Mar;16(3):1331-1342. doi: 10.1038/s41596-020-00467-0. Epub 2021 Feb 15. Nat Protoc. 2021. PMID: 33589826 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Keilholz U, Weber J, Finke JH, Gabrilovich DI, Kast WM, Disis ML, Kirkwood JM, Scheibenbogen C, Schlom J, Maino VC, Lyerly HK, Lee PP, Storkus W, Marincola F, Worobec A, Atkins MB. Immunologic monitoring of cancer vaccine therapy: results of a workshop sponsored by the Society for Biological Therapy. J Immunother. 2002;25:97–138. doi: 10.1097/00002371-200203000-00001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lim DG, Bourcier K Bieganowska, Freeman GJ, Hafler DA. Examination of CD8+ T cell function in humans using MHC class I tetramers: similar cytotoxicity but variable proliferation and cytokine production among different clonal CD8+ T cells specific to a single viral epitope. J Immunol. 2000; 165:6214–6220. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

