Tethering sigma70 to RNA polymerase reveals high in vivo activity of sigma factors and sigma70-dependent pausing at promoter-distal locations
- PMID: 14630944
- PMCID: PMC280631
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1142203
Tethering sigma70 to RNA polymerase reveals high in vivo activity of sigma factors and sigma70-dependent pausing at promoter-distal locations
Abstract
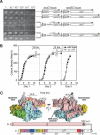
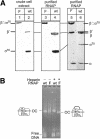
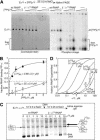
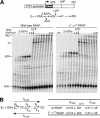
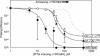
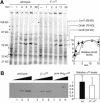
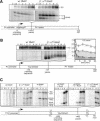
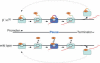
Bacterial sigma factors compete for binding to RNA polymerase (RNAP) to control promoter selection, and in some cases interact with RNAP to regulate at least the early stages of transcript elongation. However, the effective concentration of sigmas in vivo, and the extent to which sigma can regulate transcript elongation generally, are unknown. We report that tethering sigma70 to all RNAP molecules via genetic fusion of rpoD to rpoC (encoding sigma70 and RNAP's beta' subunit, respectively) yields viable Escherichia coli strains in which alternative sigma-factor function is not impaired. beta'::sigma70 RNAP transcribed DNA normally in vitro, but allowed sigma70-dependent pausing at extended -10-like sequences anywhere in a transcriptional unit. Based on measurement of the effective concentration of tethered sigma70, we conclude that the effective concentration of sigma70 in E. coli (i.e., its thermodynamic activity) is close to its bulk concentration. At this level, sigma70 would be a bona fide elongation factor able to direct transcriptional pausing even after its release from RNAP during promoter escape.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcriptional organization and in vivo role of the Escherichia coli rsd gene, encoding the regulator of RNA polymerase sigma D.J Bacteriol. 1999 Jun;181(12):3768-76. doi: 10.1128/JB.181.12.3768-3776.1999. J Bacteriol. 1999. PMID: 10368152 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction between sigmaS, the stationary phase sigma factor, and the core enzyme of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase.Genes Cells. 2002 Mar;7(3):233-47. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2443.2002.00517.x. Genes Cells. 2002. PMID: 11918668
-
Interaction of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase σ70 subunit with promoter elements in the context of free σ70, RNA polymerase holoenzyme, and the β'-σ70 complex.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jan 7;286(1):270-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.174102. Epub 2010 Oct 15. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 20952386 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular basis of selective promoter activation by the sigmaS subunit of RNA polymerase.Mol Microbiol. 2007 Mar;63(5):1296-306. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05601.x. Mol Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17302812 Review.
-
σ70 and PhoB activator: getting a better grip.Transcription. 2012 Jul-Aug;3(4):160-4. doi: 10.4161/trns.20444. Epub 2012 Jul 1. Transcription. 2012. PMID: 22771992 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Initial transcribed region sequences influence the composition and functional properties of the bacterial elongation complex.Genes Dev. 2011 Jan 1;25(1):77-88. doi: 10.1101/gad.1991811. Genes Dev. 2011. PMID: 21205867 Free PMC article.
-
A common feature from different subunits of a homomeric AAA+ protein contacts three spatially distinct transcription elements.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Oct;40(18):9139-52. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks661. Epub 2012 Jul 5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22772990 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of upstream DNA on open complex formation by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Jan 11;102(2):285-90. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0405779102. Epub 2004 Dec 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15626761 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid isolation and identification of bacteriophage T4-encoded modifications of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: a generic method to study bacteriophage/host interactions.J Proteome Res. 2008 Mar;7(3):1244-50. doi: 10.1021/pr070451j. Epub 2008 Feb 14. J Proteome Res. 2008. PMID: 18271525 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Transcriptional Pausing in Bacteria.J Mol Biol. 2019 Sep 20;431(20):4007-4029. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.07.017. Epub 2019 Jul 13. J Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31310765 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arndt K.M. and Chamberlin, M.J. 1988. Transcription termination in Escherichia coli. Measurement of the rate of enzyme release from Rho-independent terminators. J. Mol. Biol. 202: 271-285. - PubMed
-
- Artsimovitch I. and Landick, R. 2002. The transcriptional regulator RfaH stimulates RNA chain synthesis after recruitment to elongation complexes by the exposed nontemplate DNA strand. Cell 109: 193-203. - PubMed
-
- Bar-Nahum G. and Nudler, E. 2001. Isolation and characterization of σ70-retaining transcription elongation complexes from Escherichia coli. Cell 106: 443-451. - PubMed
-
- Bentley S.D., Chater, K.F., Cerdeno-Tarraga, A.M., Challis, G.L., Thomson, N.R., James, K.D., Harris, D.E., Quail, M.A., Kieser, H., Harper, D., et al. 2002. Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 417: 141-147. - PubMed
-
- Bremer H. and Dennis, P. 1996. Modulation of cell parameters by growth rate. In Escherichia coli and Salmonella: Cellular and molecular biology, 2nd ed. (eds. F. Neidhardt et al.), pp. 1553-1569. ASM press, Washington, DC.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
