Characterization of recombinant nonecotropic murine leukemia viruses from the wild mouse species Mus spretus
- PMID: 14610199
- PMCID: PMC262560
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.23.12773-12781.2003
Characterization of recombinant nonecotropic murine leukemia viruses from the wild mouse species Mus spretus
Abstract
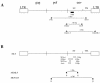
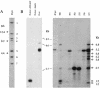
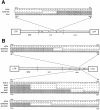
The wild mouse species most closely related to the common laboratory strains contain proviral env genes of the xenotropic/polytropic subgroup of mouse leukemia viruses (MLVs). To determine if the polytropic proviruses of Mus spretus contain functional genes, we inoculated neonates with Moloney MLV (MoMLV) or amphotropic MLV (A-MLV) and screened for viral recombinants with altered host ranges. Thymus and spleen cells from MoMLV-inoculated mice were plated on Mus dunni cells and mink cells, since these cells do not support the replication of MoMLV, and cells from A-MLV-inoculated mice were plated on ferret cells. All MoMLV-inoculated mice produced ecotropic viruses that resembled their MoMLV progenitor, although some isolates, unlike MoMLV, grew to high titers in M. dunni cells. All of the MoMLV-inoculated mice also produced nonecotropic virus that was infectious for mink cells. Sequencing of three MoMLV- and two A-MLV-derived nonecotropic recombinants confirmed that these viruses contained substantial substitutions that included the regions of env encoding the surface (SU) protein and the 5' end of the transmembrane (TM) protein. The 5' recombination breakpoint for one of the A-MLV recombinants was identified in RNase H. The M. spretus-derived env substitutions were nearly identical to the corresponding regions in prototypical laboratory mouse polytropic proviruses, but the wild mouse infectious viruses had a more restricted host range. The M. spretus proviruses contributing to these recombinants were also sequenced. The seven sequenced proviruses were 99% identical to one another and to the recombinants; only two of the seven had obvious fatal defects. We conclude that the M. spretus proviruses are likely to be recent germ line acquisitions and that they contain functional genes that can contribute to the production of replication-competent virus.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The mouse "xenotropic" gammaretroviruses and their XPR1 receptor.Retrovirology. 2010 Nov 30;7:101. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-7-101. Retrovirology. 2010. PMID: 21118532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generation of novel syncytium-inducing and host range variants of ecotropic moloney murine leukemia virus in Mus spicilegus.J Virol. 2003 May;77(9):5065-72. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.9.5065-5072.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12692209 Free PMC article.
-
Structures of endogenous nonecotropic murine leukemia virus (MLV) long terminal repeats in wild mice: implication for evolution of MLVs.J Virol. 1999 May;73(5):4327-40. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.5.4327-4340.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10196331 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant Origins of Pathogenic and Nonpathogenic Mouse Gammaretroviruses with Polytropic Host Range.J Virol. 2017 Oct 13;91(21):e00855-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00855-17. Print 2017 Nov 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28794032 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics of endogenous murine leukemia viruses.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;567:39-49. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb16457.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989. PMID: 2552892 Review.
Cited by
-
Endogenous gammaretrovirus acquisition in Mus musculus subspecies carrying functional variants of the XPR1 virus receptor.J Virol. 2013 Sep;87(17):9845-55. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01264-13. Epub 2013 Jul 3. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23824809 Free PMC article.
-
Precise identification of endogenous proviruses of NFS/N mice participating in recombination with moloney ecotropic murine leukemia virus (MuLV) to generate polytropic MuLVs.J Virol. 2005 Apr;79(8):4664-71. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.8.4664-4671.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15795252 Free PMC article.
-
Six host range variants of the xenotropic/polytropic gammaretroviruses define determinants for entry in the XPR1 cell surface receptor.Retrovirology. 2009 Oct 7;6:87. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-6-87. Retrovirology. 2009. PMID: 19811656 Free PMC article.
-
Selective sweeps versus introgression - population genetic dynamics of the murine leukemia virus receptor Xpr1 in wild populations of the house mouse (Mus musculus).BMC Evol Biol. 2015 Nov 10;15:248. doi: 10.1186/s12862-015-0528-5. BMC Evol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26555287 Free PMC article.
-
The mouse "xenotropic" gammaretroviruses and their XPR1 receptor.Retrovirology. 2010 Nov 30;7:101. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-7-101. Retrovirology. 2010. PMID: 21118532 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bonhomme, F., S. Martin, and L. Thaler. 1978. Hybridation en laboratoire de Mus musculus et Mus spretus Lataste. Sep. Exper. 34:1140. - PubMed
-
- Boursot, P., J.-C. Auffray, J. Britton-Davidian, and F. Bonhomme. 1993. The evolution of house mice. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 24:119-152.
-
- Ch'ang, L.-Y., W. K. Yang, F. E. Myer, C. K. Koh, and L. R. Boone. 1989. Specific sequence deletions in two classes of murine leukemia virus-related proviruses in the mouse genome. Virology 168:245-255. - PubMed
-
- Cloyd, M. W., M. M. Thompson, and J. W. Hartley. 1985. Host range of mink cell focus-inducing viruses. Virology 140:239-248. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

