Expressing functional siRNAs in mammalian cells using convergent transcription
- PMID: 14604435
- PMCID: PMC280659
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6750-3-21
Expressing functional siRNAs in mammalian cells using convergent transcription
Abstract
Background: The use of small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) as genetic inhibitors of gene expression has been shown to be an effective way of studying gene function in mammalian cells. Recently, different DNA vectors for expression of small hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) or co-expression of sense and antisense RNAs have been developed that direct siRNA-mediated gene silencing. One expression cassette design that has been used to express long sense and antisense RNAs in non-mammalian cell types is symmetric transcription using convergent promoters. However, convergent transcription as a way to generate functional siRNAs in mammalian cells has not been reported. This vector design permits the generation of expression constructs containing no repeat sequences, but capable of inducing RNA interference (RNAi)-mediated gene silencing.
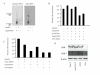
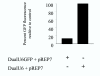
Results: With the aim of simplifying the construction of RNAi expression vectors, we report on the production and application of a novel convergent promoter cassette capable of expressing sense and antisense RNAs, that form double-stranded RNA, and mediate gene silencing in mammalian cells. We use this cassette to inhibit the expression of both the EGFP transgene and the endogenous TP53 gene. The gene silencing effect is Dicer-dependent and the level of gene inactivation achieved is comparable to that produced with synthetic siRNA. Furthermore, this expression system can be used for both short and long-term control of specific gene expression in mammalian cells.
Conclusion: The experiments performed in this study demonstrate that convergent transcription can be used in mammalian cells to invoke gene-specific silencing via RNAi. This method provides an alternative to expression of shRNAs and co-expression of sense and antisense RNAs from independent cassettes or a divergent promoter. The main advantage of the present vector design is the potential to produce a functional siRNA expression cassette with no repeat sequences. Furthermore, the cassette design reported is ideal for both routine use in controlling specific gene expression and construction of randomised RNAi expression libraries for use in unbiased forward genetic selections.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Construction of simple and efficient DNA vector-based short hairpin RNA expression systems for specific gene silencing in mammalian cells.Methods Mol Biol. 2007;408:223-41. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-547-3_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 18314586
-
High-throughput screening of effective siRNAs from RNAi libraries delivered via bacterial invasion.Nat Methods. 2005 Dec;2(12):967-73. doi: 10.1038/nmeth812. Epub 2005 Nov 18. Nat Methods. 2005. PMID: 16299483
-
[Specific inhibition of hTERT gene expression by short interfering RNAs in gastric cancer SGC7901 cell].Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2004 Nov 22;42(22):1372-6. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2004. PMID: 15634407 Chinese.
-
Short hairpin RNA-mediated gene silencing.Methods Mol Biol. 2013;942:205-32. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-119-6_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23027054 Review.
-
Vectors for RNA interference.Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2004 Aug;6(4):367-72. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2004. PMID: 15468595 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA interference: its use as antiviral therapy.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2006;173(173):117-50. doi: 10.1007/3-540-27262-3_7. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16594614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A plasmid-based system for expressing small interfering RNA libraries in mammalian cells.BMC Cell Biol. 2004 Apr 30;5:16. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-5-16. BMC Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15119963 Free PMC article.
-
Convergent transcription induces transcriptional gene silencing in fission yeast and mammalian cells.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Nov;19(11):1193-201. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2392. Epub 2012 Sep 30. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 23022730 Free PMC article.
-
New construct approaches for efficient gene silencing in plants.Plant Physiol. 2006 Aug;141(4):1508-18. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.082271. Epub 2006 Jun 9. Plant Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16766670 Free PMC article.
-
RNA modulators of complex phenotypes in mammalian cells.PLoS One. 2009;4(3):e4758. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004758. Epub 2009 Mar 9. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19270743 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

